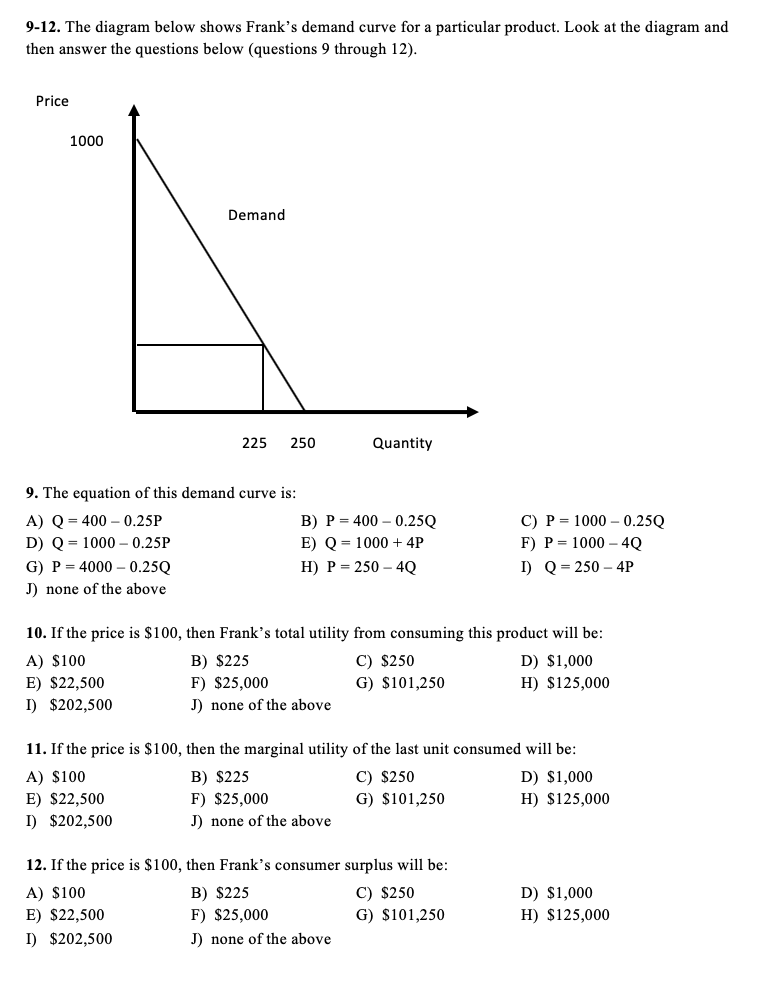
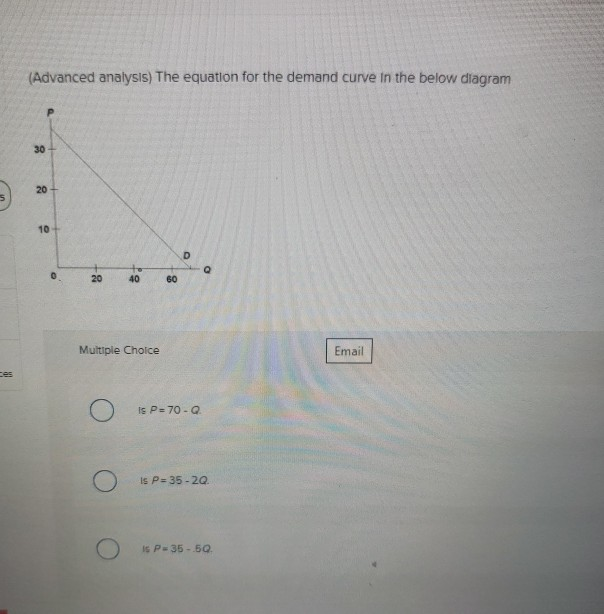
42 the equation for the demand curve in the below diagram
A linear demand curve can be plotted using the following equation. Qd = a – b(P) Q = quantity demand; a = all factors affecting price other than price (e.g. income, fashion) b = slope of the demand curve; P = Price of the good. Inverse demand equation. The inverse demand equation can also be written as. P = a -b(Q) a = intercept where price is 0 (Advanced analysis) The equation for the demand curve in the diagram shown. is P = 35 − .5Q. One reason that the quantity demanded of a good increases when its price falls is that the
Economics questions and answers. (Advanced analysis) The equation for the demand curve in the below diagram 30 20 5 10 D о 0 to 40 20 60 Multiple Choice Email is P= 70 - Is P=35-20 Is P-35-50.
The equation for the demand curve in the below diagram
A. a straight line with a negative slope of twice the demand curve slope. The demand equation for a single price monopolist is P = 50 - Q. The marginal revenue equation for this monopolist is. A. 25 - Q. B. 50 - 2Q. C. 50 - Q. D. 100 - Q. B. 50 - 2Q. The demand equation for a single price monopolist is P = 120 - 3Q. (Advanced analysis) The equation for the demand curve in the below diagram: is P = 35 - .5Q. Refer to the diagram. A decrease in demand is depicted by a. In the diagram below, draw a demand curve. a. In the diagram below, draw a demand curve. Instructions: Use the tool provided 'Demand' to graphically show demand. This line should only contain the two endpol Demand Schedule Demand Product price Quantity demanded b. Use the midpoint formula for Eg to determine price elasticity of demand for each ...
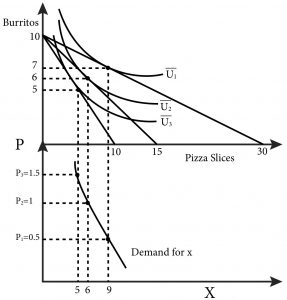
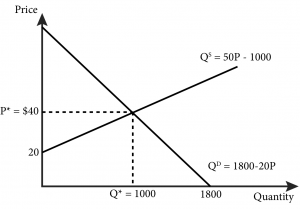
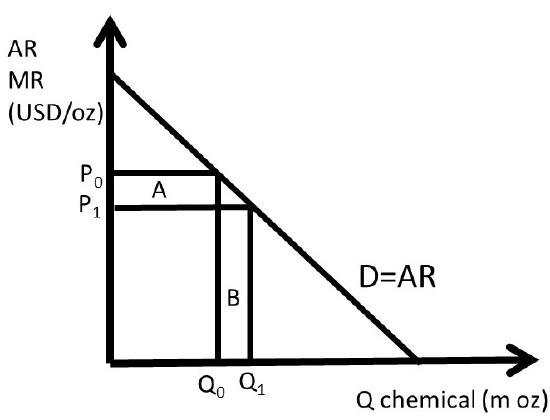
The equation for the demand curve in the below diagram. Some of the important types of demand curves are listed below: Type # 1. Negatively Sloped Straight Lines Demand Curves: It is evident that the value of e at any (p, q) point on a curvilinear demand curve and the value of e at the same (p, q) point on a straight line demand curve—which is a tangent to the former demand curve at the said point—are identical. Use the demand diagram below to answer this question. Note that P × Q equals $900 at every point on this demand curve. Which of the following statements correctly describes own-price elasticity of demand, for this particular demand curve? I. Demand is unit elastic at a price of $30, and elastic at all prices greater than $30. II. Slope of a curve = _____ horizontal difference (change) Then, the slope of the above demand curve is = ∆P/ ∆Qd In order to calculate the slope of the curve we need to consider two points on the demand curve . Now refer the below diagram. You can see four points are marked on the demand curve- A, B C, and D . Consider the following weekly supply and demand tables for product X: Draw the supply and demand curves on the same diagram. Determine the equilibrium price and ...1 answer · 0 votes: #Please rate positively...thank you 1) Answer-B , P= 4+.30. at price 10 to Q=20 Quanity is 20 P = 4 +0.39 P = 4+ 3x20 P- 4+ 6.0 P= 10 e=h 2) Answer. ...
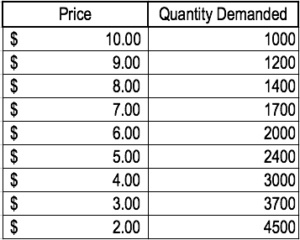
Drawing a Demand Curve. The demand curve is based on the demand schedule. The demand schedule shows exactly how many units of a good or service will be purchased at various price points. For example, below is the demand schedule for high-quality organic bread: It is important to note that as the price decreases, the quantity demanded increases. Use a specific example to illustrate the Cournot model. The equation of the market inverse demand curve is p= 100−Q=100−(q 1 +q 2), (1) where q 1 is the output of firm 1 and q 2 is the output of firm 2. Firms have identical cost functions, with constant average and marginal cost, 10 per unit of output: C(q 1)=10q 1 C(q 2)=10q 2. (2) If the demand curve for product B shifts to the right as the price of product A declines, then: a)both A and B are inferior goods. b)A is a superior good ... In the diagram below, draw a demand curve. a. In the diagram below, draw a demand curve. Instructions: Use the tool provided 'Demand' to graphically show demand. This line should only contain the two endpol Demand Schedule Demand Product price Quantity demanded b. Use the midpoint formula for Eg to determine price elasticity of demand for each ...
(Advanced analysis) The equation for the demand curve in the below diagram: is P = 35 - .5Q. Refer to the diagram. A decrease in demand is depicted by a. A. a straight line with a negative slope of twice the demand curve slope. The demand equation for a single price monopolist is P = 50 - Q. The marginal revenue equation for this monopolist is. A. 25 - Q. B. 50 - 2Q. C. 50 - Q. D. 100 - Q. B. 50 - 2Q. The demand equation for a single price monopolist is P = 120 - 3Q.

In The Following Diagram Ae Is The Linear Demand Curve Of A Commodity On The Basis Of The Given Diagram State Whether The Following Statement Is True Or False Economics






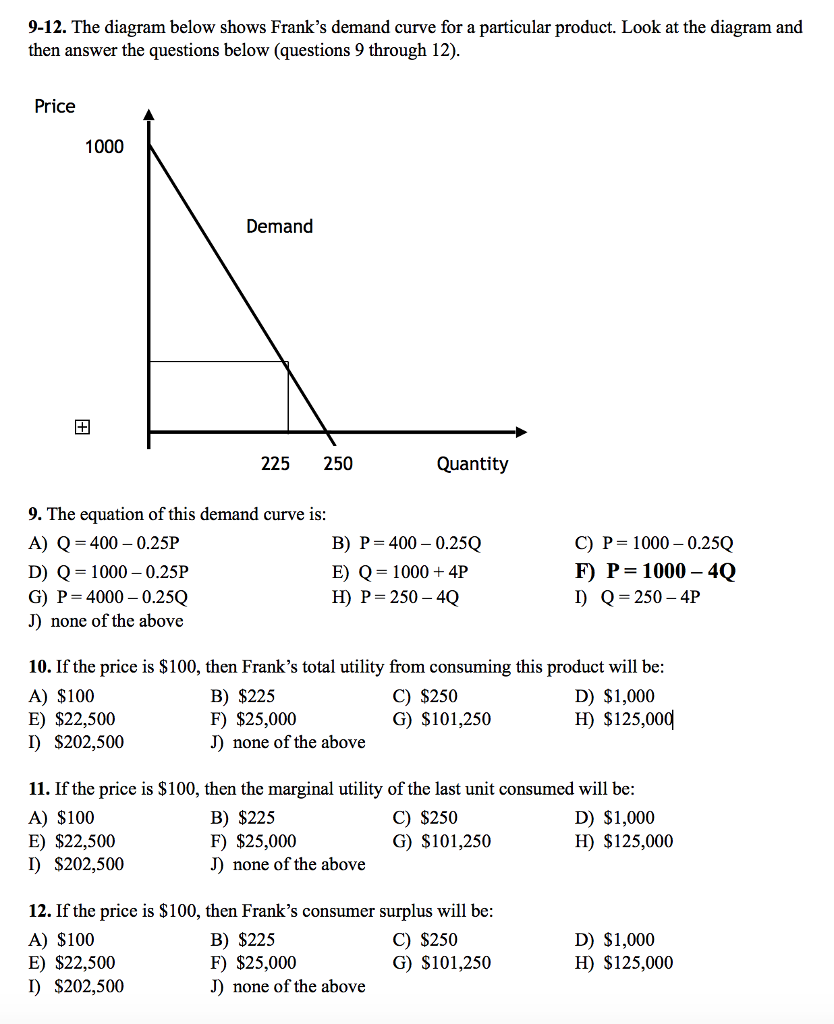












0 Response to "42 the equation for the demand curve in the below diagram"
Post a Comment