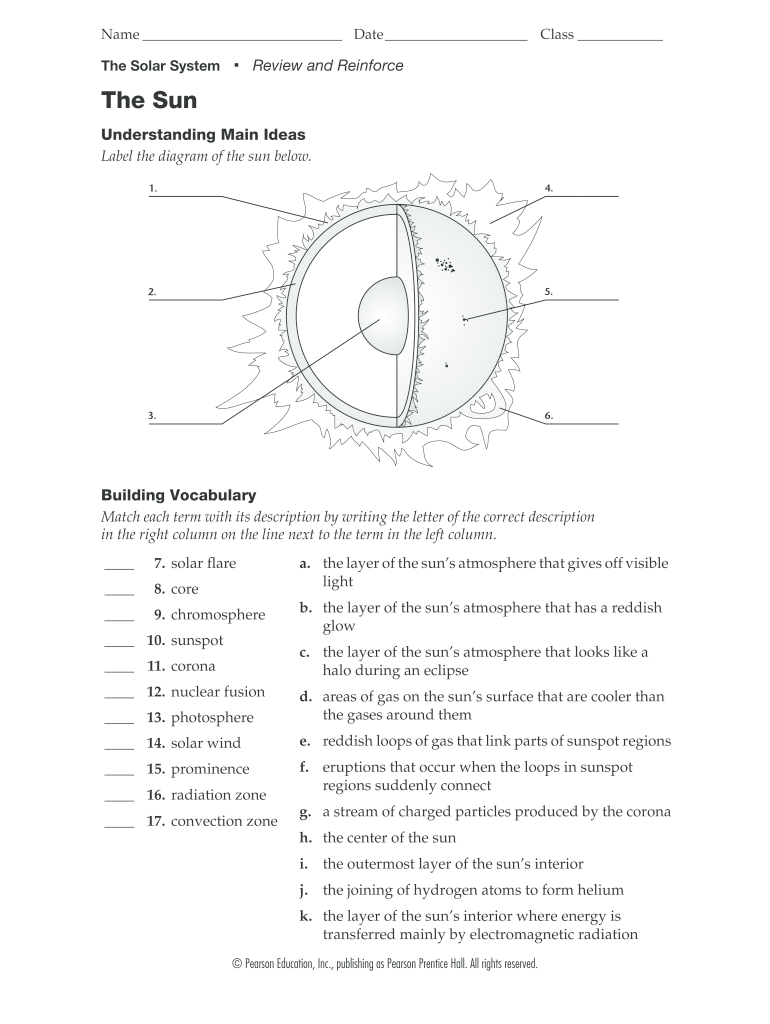
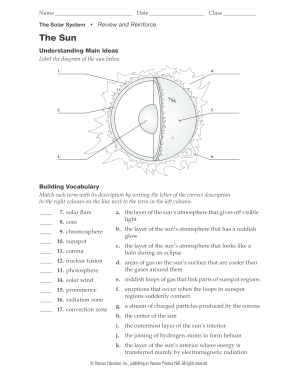
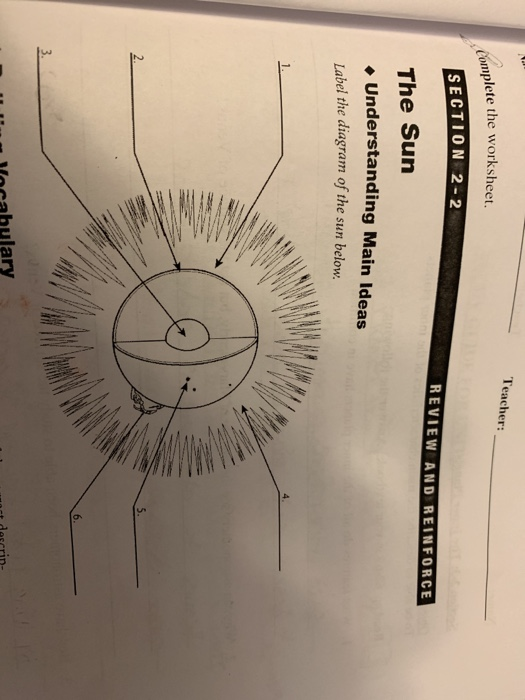
42 label the diagram of the sun below
7. solar flare a. the layer of the sun's atmosphere that gives off visible light 8. core 9. Question: The Solar System The Sun Understanding Main Ideas Label the diagram of the sun below. Building Vocabulary Match each term with its description by writing the letter of the correct description in the right column on the line next to the term in ... Label the neap and spring tides drawn below. spring neap Earth Sun Moon Why does the lineup of the Earth, sun, and moon impact the tides? The gravitation pull is increased when they are lined up together. Ho w can you tell/ remember the difference between a neap and a spring tide from a diagram? Neap Tides are perpendicular
Diagram of lunar eclipse. Relative scale is correct! 2017 eclipse path visualization. Note that eclipses don't happen every month because the moon's orbit is tilted 5 degrees out of the earth-sun plane. So we really only get eclipse seasons twice a year (when the sun is on the "line of nodes" in the diagram below). Constellations
Label the diagram of the sun below
Understanding Main Ideas Label the diagram of the sun below.1.how to label the diagram of the sun 5.26.3.MO The parts of the inner layer are: 1. Core. It is the innermost layer of the sun, which is extremely dense where nuclear fusion generates energy in terms of photons by converting hydrogen into helium. The core is approximately 20% of the size of the solar interior and is found to be the hottest part of the sun. 2. The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram the various stages of stellar evolution. By far the most prominent feature is the main sequence (grey), which runs from the upper left (hot, luminous stars) to the bottom right (cool, faint stars) of the diagram. The giant branch and supergiant stars lie above the main sequence, and white dwarfs are found below it.
Label the diagram of the sun below. The sun is the real boss of the water cycle, and it doesn't even live here on Earth. The sun is what makes the water cycle work. The sun provides what almost everything on Earth needs to go—energy, or heat. The sun's heat allows liquid water to evaporate into water vapor, which in the main way water gets from the land surface back into the sky. There are two labelling activities and one sorting task to support work towards the end of the unit. There three sections are as follows: 1) Labelling a life cycle diagram of a flowering plant. 2) Sorting plants by method of seed dispersal. 3) Labelling the reproductive organs of a flower. Life Cycles 5b lesson outline See the diagram of the full moon below. Depending on earth's, moon's and sun's positions we see a different area of the moon being illuminated by the sun. The changing positions appear to us as different moon phases. When the earth, the moon and the sun are almost aligned, most of the surface of the moon (as seen from the earth) is illuminated ... A practical demonstration, using visual aids, to show how the Sun shines on the Earth and how the Earth rotates to create day and night. The demonstrator talks about the Sun rising in the east and ...
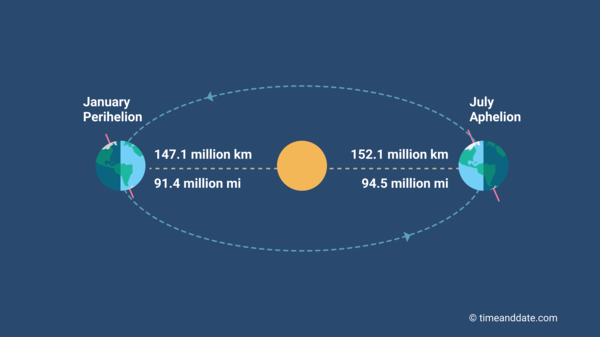
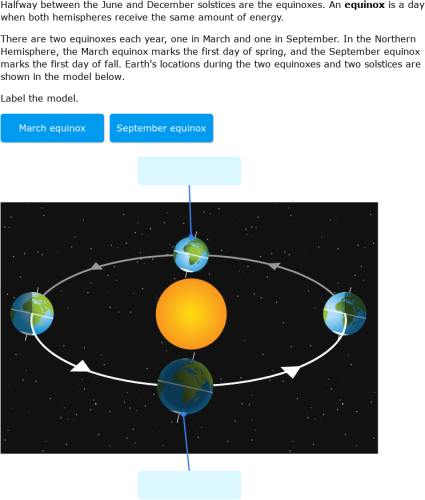
Question: Part 3: Earth-Sun Relations. Using the diagram below, draw in and label by name directly on the diagram each of the following as they would appear on the June solstice. Be sure to tilt the earth's axis the appropriate amount and direction. (I encourage you to use a straight edge and protractor to make your diagram more accurate.) In the diagram to the left, provide the labels for the structures involved in the reflex act when a person steps on a tack and jerks their leg away. Brain Anatomy Provide the labels for the diagram on the left below and provide descriptions of the functions of each structure on the blank lines. The sun’s atmosphere consists of the photosphere, the chromosphere, and the corona. The inner layer of the sun’s atmosphere is called the photosphere. Photo means “light,” so the photosphere is the sphere that gives off visible light. ... Label the diagram of the sun below. an area on the Sun where magnetic fields are concentrated; sunspots, prominences, flares, and CMEs all tend to occur in active regions. apparent brightness. a measure of the amount of light received by Earth from a star or other object—that is, how bright an object appears in the sky, as contrasted with its luminosity.
Main Sequence Stars - The main sequence is the point in a star's evolution during which it maintains a stable nuclear reaction. It is this stage during which a star will spend most of its life. Our Sun is a main sequence star. A main sequence star will experience only small fluctuations in … Luminosity of stars if often expressed in units of the Sun's luminosity (L = 3.9 x 10 26 Joules/s). The HR diagram spans a rather large range in luminosity, from 10-4 L on the low end to as much as 10 6 L on the high end. This interactive applet might help you visualize some of … Part 2: Making an H-R diagram The table below lists the color index and luminosity of 50 stars, whose distances were determined via parallax measurements using the Hipparcos satellite. Luminosities are all expressed in units of the Sun’s luminosity, i.e., an entry of 0.01 means that the star is (1/100) of the solar luminosity (100 times less ... the sun. Together, the stratosphere and the mesosphere are often called the “middle atmosphere.” The thermosphere lies above the mesosphere, starting at about 50 miles above sea level. This layer is often called the “upper atmosphere.” Any person trav-eling at an altitude of more than 50 miles above sea level is considered an astronaut.
Hi everyone i'm neetu jacob I'm a tutor. in lido and welcome you all to lido learning so you can see a very good diagram over right here and what is this diagram this is the diagram of a neuro so the The question is given below is a diagram of a neuron name the paths numbered from one to five and you can see certain numbers that are written here diagram is not labeled Your question, the ...
The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram the various stages of stellar evolution. By far the most prominent feature is the main sequence (grey), which runs from the upper left (hot, luminous stars) to the bottom right (cool, faint stars) of the diagram. The giant branch and supergiant stars lie above the main sequence, and white dwarfs are found below it.
The parts of the inner layer are: 1. Core. It is the innermost layer of the sun, which is extremely dense where nuclear fusion generates energy in terms of photons by converting hydrogen into helium. The core is approximately 20% of the size of the solar interior and is found to be the hottest part of the sun. 2.
Understanding Main Ideas Label the diagram of the sun below.1.how to label the diagram of the sun 5.26.3.MO

Exercise2 2a Seasons Key Pdf Class Exercise 2 2a The Sun S Path Through The Year Key Part 1 Terrestrial Coordinates The Diagram Below Shows The Earth Course Hero

The Lancet Global Health Commission On Global Eye Health Vision Beyond 2020 The Lancet Global Health




















0 Response to "42 label the diagram of the sun below"
Post a Comment