39 actin and myosin diagram
polymer known as F actin and is composed of individual monomeric protein subunits known as G actin. The F actin polymers twist together, and being composed of G actin subunits, gives the appearance of two strings of beads twisted together. Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils.It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of over 100 μM; its mass is roughly 42 kDa, with a diameter of 4 to 7 nm.. An actin protein is the monomeric subunit of two types of filaments in cells ...
2). Period of Contraction The actin is sliding over the myosin and the muscle fibers shorten.The contraction phase ends roughly 15 milliseconds (msec) after stimulation. 3). Period of Relaxation During this period the Ca++ reenters the sarcoplasmic reticulum through active transport, active sites are being covered by tropomyosin, and the number ...
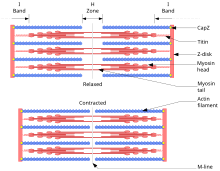
Actin and myosin diagram
The binding of the myosin heads to the muscle actin is a highly regulated process. When a muscle is resting, actin and myosin are separated. To keep actin from binding to the active site on myosin, regulatory proteins block the molecular binding sites. These regulatory proteins are tropomyosin and troponin. H zone becomes smaller by increasing actin overlap and myosin filaments, due to this muscles shorten. Sarcomere Diagram. Sarcomere Anatomy: Anatomical is said to be the term of microanatomy. The sarcomere is the basic unit function with muscle fiber cells. This is a distinguishing unit in some types of muscle tissue. Actin and myosin proteins form filaments arranged in the myofibrils in a longitudinal manner. The main difference between actin and myosin is that actin forms a thin filament whereas myosin forms a thick filament. The sliding over of the two filaments over one another in a series of repetitive events leads to the contraction of the muscles.
Actin and myosin diagram. A: With respect to muscular contraction, a cross-bridge refers to the attachment of myosin with actin within the muscle cell. All types of muscles - whether discussing skeletal, cardiac or smooth - contract by cross-bridge cycling - that is, repeated attachment of actin and myosin within the cell. 1. Blocking of myosin head: Actin and myosin overlaps each other forming cross bridge. The cross bridge is active only when myosin head attached like hook to the actin filament. When muscle is at rest, the overlapping of actin filament to the myosin head is blocked by tropomyosin. The actin myofilament is said to be in OFF position. 2. Structure and Function of Actin & Myosin Outline: Actin Structure and Regulation Myosin Structure and Regulation Functions of Actin and Myosin in Cells Paper: Control of microtubule dynamics by the antagonistic activities of XMAP215 and XKCM1 in Xenopus egg extracts. Stationary cell - stress fibers. Actin: Myosin: Definition: Actin is a group of globular proteins that are the most abundant proteins in most eukaryotic cells and help in providing shape, structure, and mobility to the body. Myosin is a family of motor proteins that, together with actin proteins, form the basis for the contraction of muscle fibers. Found in
Actin, protein that is an important contributor to the contractile property of muscle and other cells. In muscle, two long strands of actin molecules are twisted together to form a thin filament, bundles of which alternate with bundles of myosin. The temporary fusion of actin and myosin results in muscle contraction. Dodge Durango Wiring Diagram. Start studying UNIT 5: Label the parts of the Sarcomere. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Draw and label a diagram to show the structure of a sarcomere, including Z lines, actin filaments, myosin filaments with heads, and the resultant light and dark bands. Actin and myosin are two protein molecules present in muscles and are mainly involved in the contraction of the muscle in both humans and animals. Both actin and myosin function by controlling the voluntary muscular movements within the body, along with the regulatory proteins known as troponin, tropomyosin and meromyosin. The outer edges of the A bands are darkest as they contain both actin and myosin filaments overlapping. The inner edges of the A bands are not quite so dark, as they only contain myosin filaments. This region is called the H zone. The middle of the H zone is called the M line, or sometimes the M band, which can be remembered as M stands for middle.
Muscle contraction has to do with the bonding of two proteins called actin and myosin. Explore myosin molecules and thick filaments, actin molecules and thin filaments, the organization of myosin ... Actin Myosin Interaction. Create healthcare diagrams like this example called Actin Myosin Interaction in minutes with SmartDraw. SmartDraw includes 1000s of professional healthcare and anatomy chart templates that you can modify and make your own. Draw a neat labelled diagram of (a) An actin filament (b) Myosin. Welcome to Sarthaks eConnect: A unique platform where students can interact with teachers/experts/students to get solutions to their queries. V. Myosin - Actin Interaction. The interaction of a myosin II S1 subfragment with an actin filament has been modeled. As can be observed, actin binding is mediated by residues in the upper and lower subdomain cleft. Residues 335-372 in an actin monomer of the filament show the most extensive contact with these loops.
To visualize the movement of myosin molecules, small polystyrene beads (diameter - 1μm: visible under an ordinary light microscope) are coated with myosin and applied to the actin cables in the presence of ATP. When a bead comes in close contact with the actin cables, the myosin on its surface interacts with actin and pulls the bead.
Allowing myosin to bind (to actin) / crossbridge formation; 1. Accept presence of calcium ions leads to movement instead of binds Accept references to troponin Head (of myosin) binds to actin and moves / pulls / slides actin past; Q (Myosin) detaches from actin and re-sets / moves further along (actin) 1. Accept myosin power stroke (to move ...
Actin and myosin work together to produce muscle contractions and, therefore, movement. First, a motor neuron delivers an electrical signal to the muscle cell from the brain.This triggers the release of a chemical called acetylcholine. Acetylcholine causes calcium ions to be released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
filaments lack myosin heads. Myosin heads are present only in areas of myosin-actin overlap. Longitudinal section of filaments within one sarcomere of a myofibril Portion of a thick filament Portion of a thin filament Myosin molecule Actin subunits
The thin actin filaments also have binding sites for the myosin heads—a cross-bridge forms when a myosin head binds with an actin filament. The process of cross-bridge cycling is shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{6}\). A cross-bridge cycle begins when the myosin head binds to an actin filament. ADP and P i are also bound to the myosin head at this ...
Actin filaments, usually in association with myosin, are responsible for many types of cell movements. Myosin is the prototype of a molecular motor—a protein that converts chemical energy in the form of ATP to mechanical energy, thus generating force and movement. The most striking variety of such movement is muscle contraction, which has provided the model for understanding actin-myosin ...
Schematic diagram depicting separation of nascent spindle poles (centrosomes; grey spheres) during mitotic spindle assembly powered by myosin-2 and F-actin-based cortical flow. The microtubules (red) are attached to the cortical network of F-actin and myosin-2 (green) by an as-yet unidentified anchor (yellow) and to the condensing DNA (blue).
The diagram above shows a fully contracted muscle with lots of overlap between the actin and myosin. Because the thin actin filaments have overlapped there is a reduced potential for cross bridges to form again. Therefore, there will be low force production from the muscle.
The myosin and actin work together to move the skeletal muscle. These movements are also responsible for cleaving a cell in two during cell division. Structure of Myosin
c. myosin head cocked/assumes high energy configuration; d. myosin head binds to actin / forms a cross-bridge; e. actin filament slides towards center of sarcomere / dark band; f. combined sliding of actin filaments shortens muscle fiber / muscle; g. ATP binds to myosin head and breaks cross-bridge; Accept answers with properly annotated diagrams.
Nov 2021 GMT38.4 Muscle Contraction and Locomotion20272027 AnonymousAnonymous2falsefalse article topic Muscle Contraction troponin tropomyosin sarcomere authorname openstax actin acetylcholinesterase cardiac muscle motor end plate myofibril...
Actin and myosin proteins form filaments arranged in the myofibrils in a longitudinal manner. The main difference between actin and myosin is that actin forms a thin filament whereas myosin forms a thick filament. The sliding over of the two filaments over one another in a series of repetitive events leads to the contraction of the muscles.
H zone becomes smaller by increasing actin overlap and myosin filaments, due to this muscles shorten. Sarcomere Diagram. Sarcomere Anatomy: Anatomical is said to be the term of microanatomy. The sarcomere is the basic unit function with muscle fiber cells. This is a distinguishing unit in some types of muscle tissue.
The binding of the myosin heads to the muscle actin is a highly regulated process. When a muscle is resting, actin and myosin are separated. To keep actin from binding to the active site on myosin, regulatory proteins block the molecular binding sites. These regulatory proteins are tropomyosin and troponin.


0 Response to "39 actin and myosin diagram"
Post a Comment