41 cardiac cycle diagram labeled
EKG or ECG waveform parts are explained clearly to make EKG interpretation easy. Learn the meaning of each component of an EKG wave with this step-by-step labeled diagram of the conduction system of the heart. Provides information on atrial depolarization and the P wave, ventricular depolarization a Cardiac Cycle Phases. Following are the different phases that occur in a cardiac cycle: Atrial Diastole: In this stage, chambers of the heart are calmed. That is when the aortic valve and pulmonary artery closes and atrioventricular valves open, thus causing chambers of the heart to relax. Atrial Systole: At this phase, blood cells flow from ...
Function and anatomy of the heart made easy using labeled diagrams of cardiac structures and blood flow through the atria, ventricles, valves, aorta, pulmonary arteries veins, superior inferior vena cava, and chambers. Includes an exercise, review worksheet, quiz, and model drawing of an anterior vi
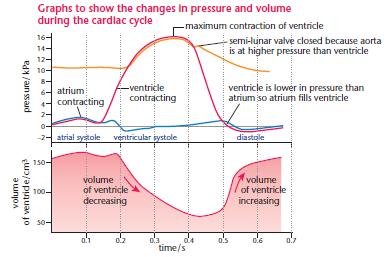
Cardiac cycle diagram labeled
THE CARDIAC CYCLE Objectives: Identifying Factors which affect heart rate Describe Cardiac Functional Anatomy (including a review of blood flow and valves) Understand the Wiggers Diagram of Cardiac Cycle Differentiate between Wiggers Diagram and the Pressure Volume Curve Review the electrical basis of excitable cardiac tissue The period of timethat begins with contraction of the atria and ends with ventricular relaxation is known as the cardiac cycle (Figure 19.3.1). The period of contraction that the heart undergoes while it pumps blood into circulation is called systole. The period of relaxation that occurs as the chambers fill with blood is called diastole. Both the atria and ventricles undergo systole and diastole, and it is essential that these components be carefully regulated and coordinated to ensure ... 1. Draw the Electrical Cardiac Cycle Events (ECG): Always start with the ECG. In ECG, R-R interval is the duration of cardiac cycle and 1 R-R interval represents 1 cardiac cycle. Peak of R wave: Corresponds to beginning of ventricular systole. Middle of T wave: Corresponds to beginning of ventricular diastole.
Cardiac cycle diagram labeled. Cardiac cycle explained: cardiac cycle phases, ECG, graph. Heart is a pumping machine which collects impure blood from our body, pumps it to lungs for purification. The pureblood is again collected in the heart which once again is pumped to different parts, muscle, cells and tissues of our body. All these series of events happens smoothly in a ... The cardiac cycle is defined as a sequence of alternating contraction and relaxation of the atria and ventricles in order to pump blood throughout the body. It starts at the beginning of one heartbeat and ends at the beginning of another. The process begins as early as the 4th gestational week when the heart first begins contracting.. Each cardiac cycle has a diastolic phase (also called ... • Outline the 5 phases of the cardiac cycle. • Describe cardiac conduction. • Describe the 5 phases of cardiac depolarization-repolarization. • Draw and label the normal EKG waveform, P to U and explain each part of the wave. • Discuss how different leads represent the heart. cardiac cycle duration increases with a decrease in the heart rate and on the other hand it shortens with increasing heart rate. At a normal heart rate of 75 beats per minute, one cardiac cycle lasts 0.8 second. Under resting conditions, systole occupies ⅓ and diastole ⅔ of the cardiac cycle duration. At an increasing heart rate
Oct 01, 2020 · The cardiac cycle has 2 phases, systole and diastole, defined by depolarization and contraction vs repolarization and relaxation. This step-by-step diagram provides easy notes and explanations of the cardiac cycle, blood flow through the heart in order, and the atrial and ventricular anatomy of the 1. Draw the Electrical Cardiac Cycle Events (ECG): Always start with the ECG. In ECG, R-R interval is the duration of cardiac cycle and 1 R-R interval represents 1 cardiac cycle. Peak of R wave: Corresponds to beginning of ventricular systole. Middle of T wave: Corresponds to beginning of ventricular diastole. The period of timethat begins with contraction of the atria and ends with ventricular relaxation is known as the cardiac cycle (Figure 19.3.1). The period of contraction that the heart undergoes while it pumps blood into circulation is called systole. The period of relaxation that occurs as the chambers fill with blood is called diastole. Both the atria and ventricles undergo systole and diastole, and it is essential that these components be carefully regulated and coordinated to ensure ... THE CARDIAC CYCLE Objectives: Identifying Factors which affect heart rate Describe Cardiac Functional Anatomy (including a review of blood flow and valves) Understand the Wiggers Diagram of Cardiac Cycle Differentiate between Wiggers Diagram and the Pressure Volume Curve Review the electrical basis of excitable cardiac tissue



0 Response to "41 cardiac cycle diagram labeled"
Post a Comment