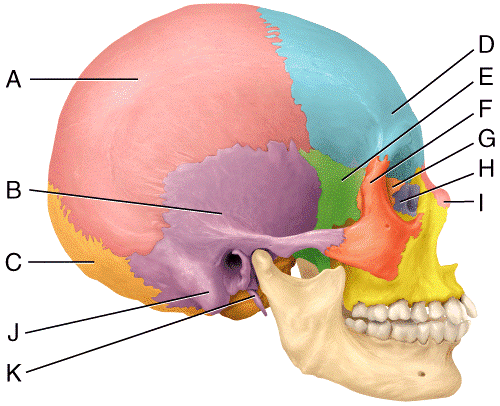
42 in the diagram, where is the styloid process?
In the diagram, where is the styloid process? K. Which of the following statements is NOT true with regard to bones of the skull? The bones of the skull contain foramina but no fissures. In the diagram, where is the cribriform plate? F. Which of the following is NOT true of surface markings on bone?
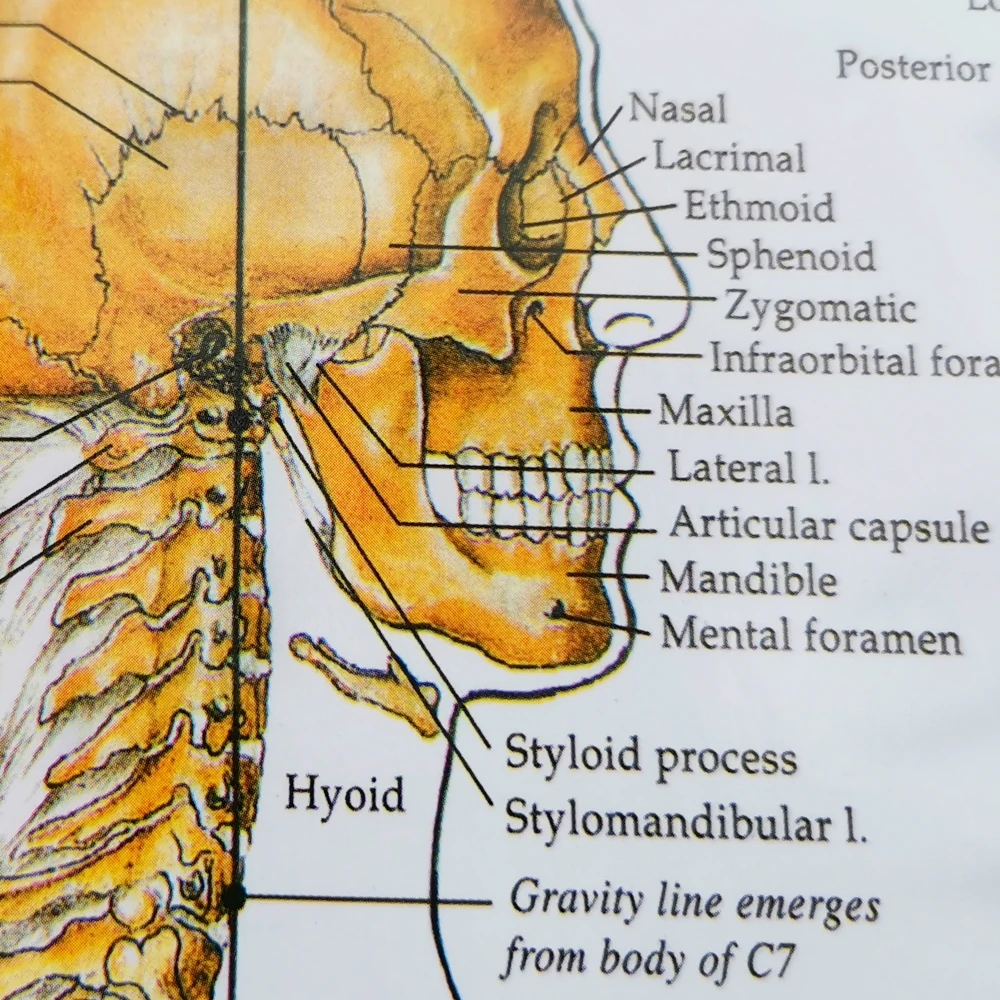
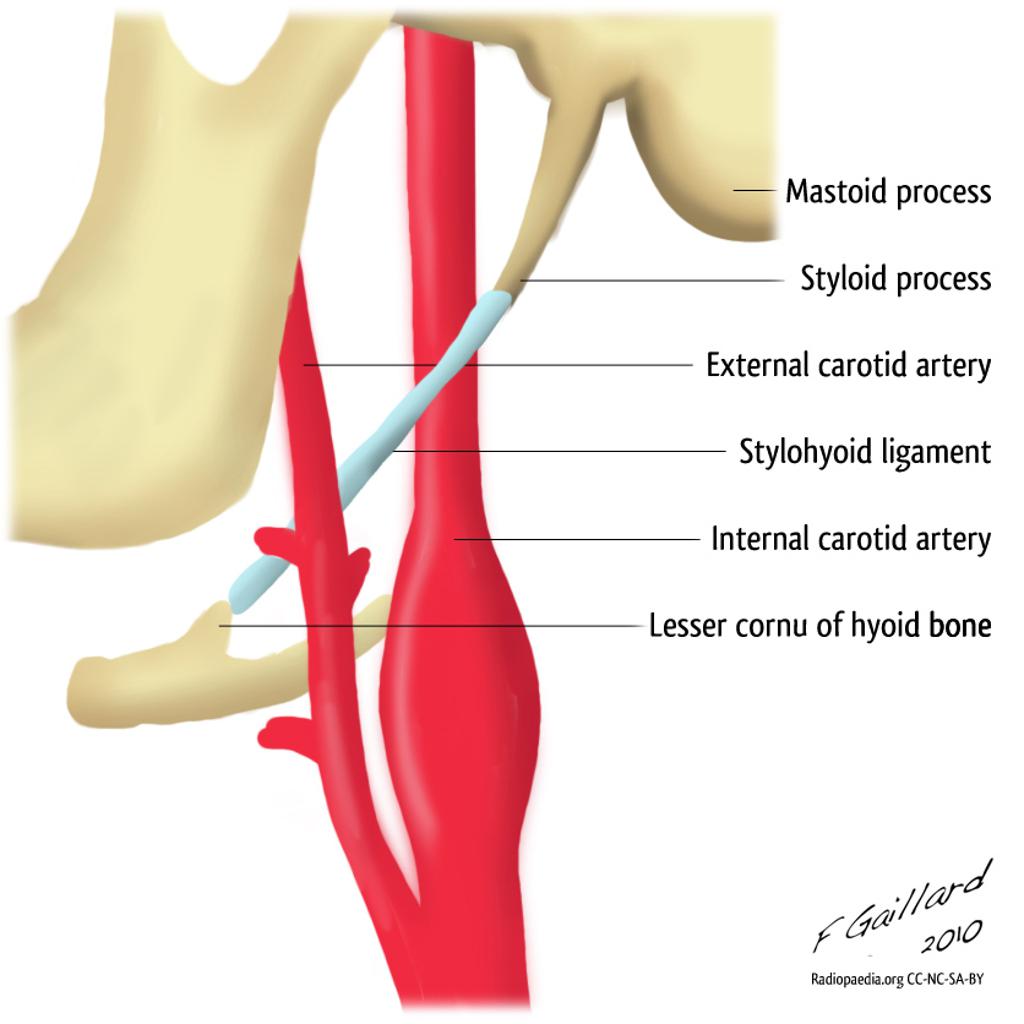
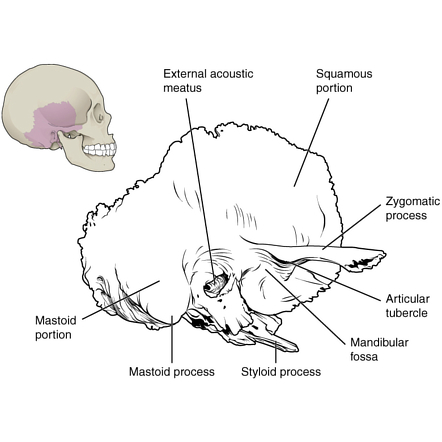
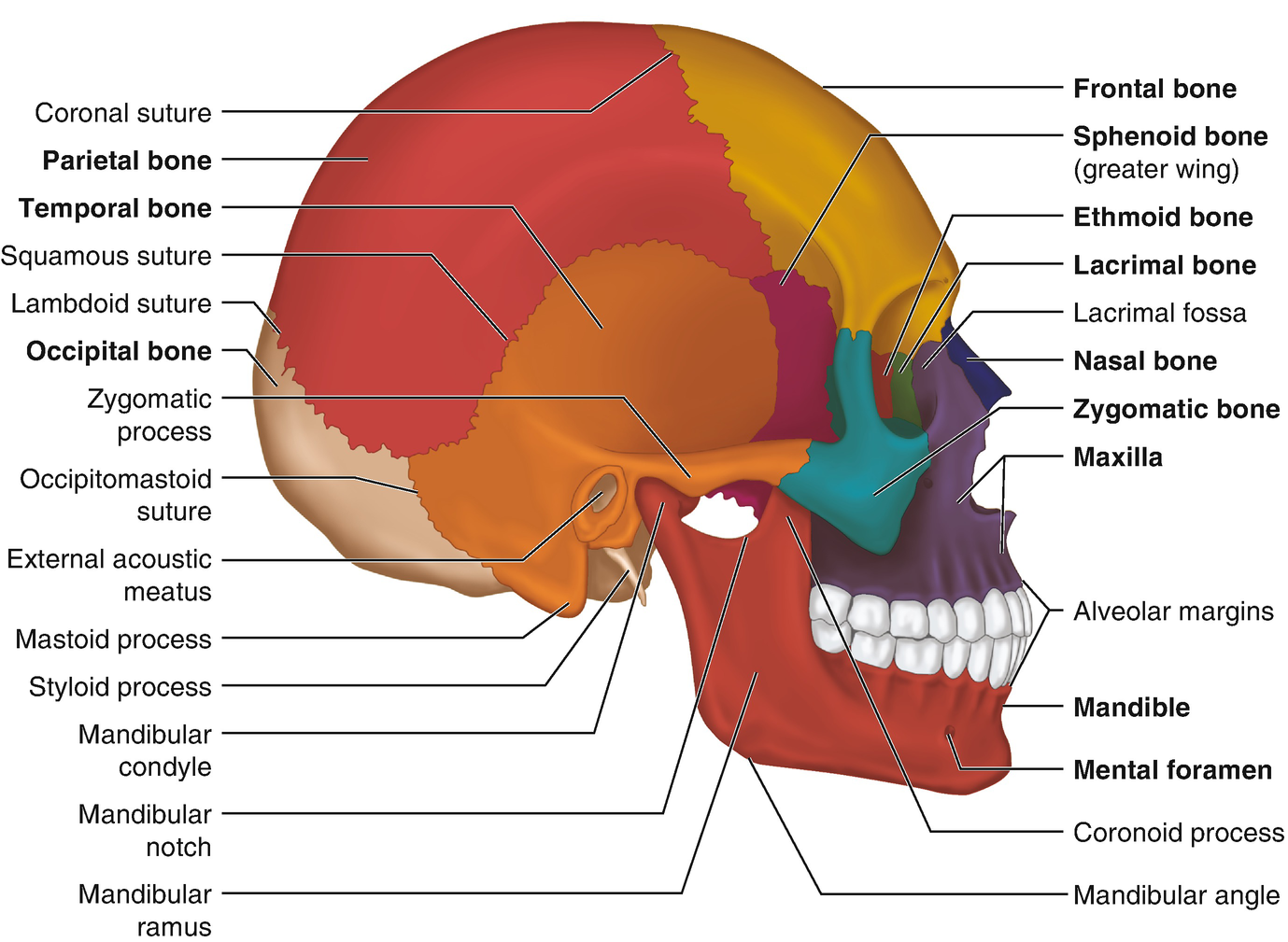
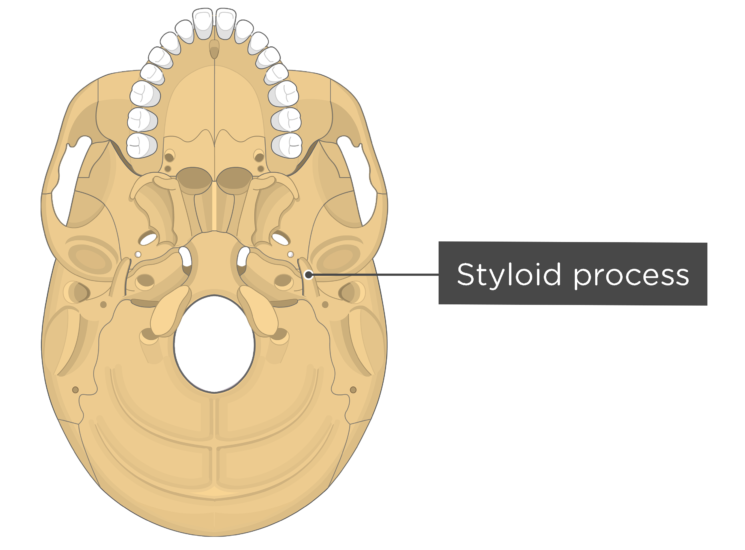
The styloid process lies anterior and medial to the mastoid process, and in between them is the stylomastoid foramen. This foramen allows the muscular branch of the facial nerve to leave the skull and go onto innervate the muscles of facial expression. The mastoid bone is normally pneumatised or air filled by the mastoid air cells.
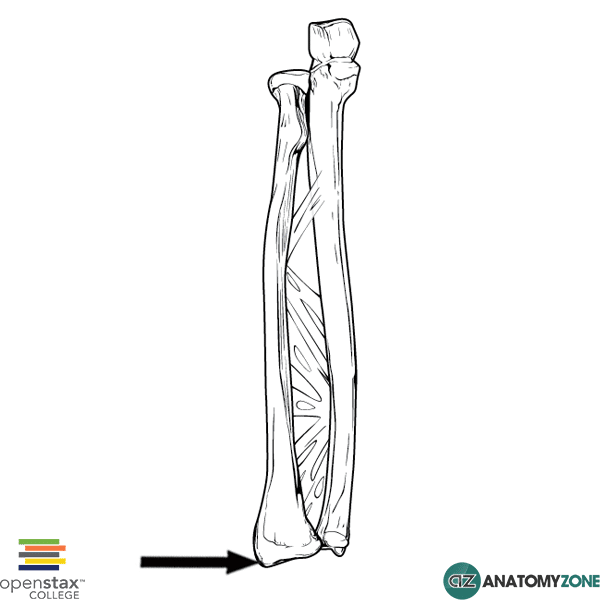
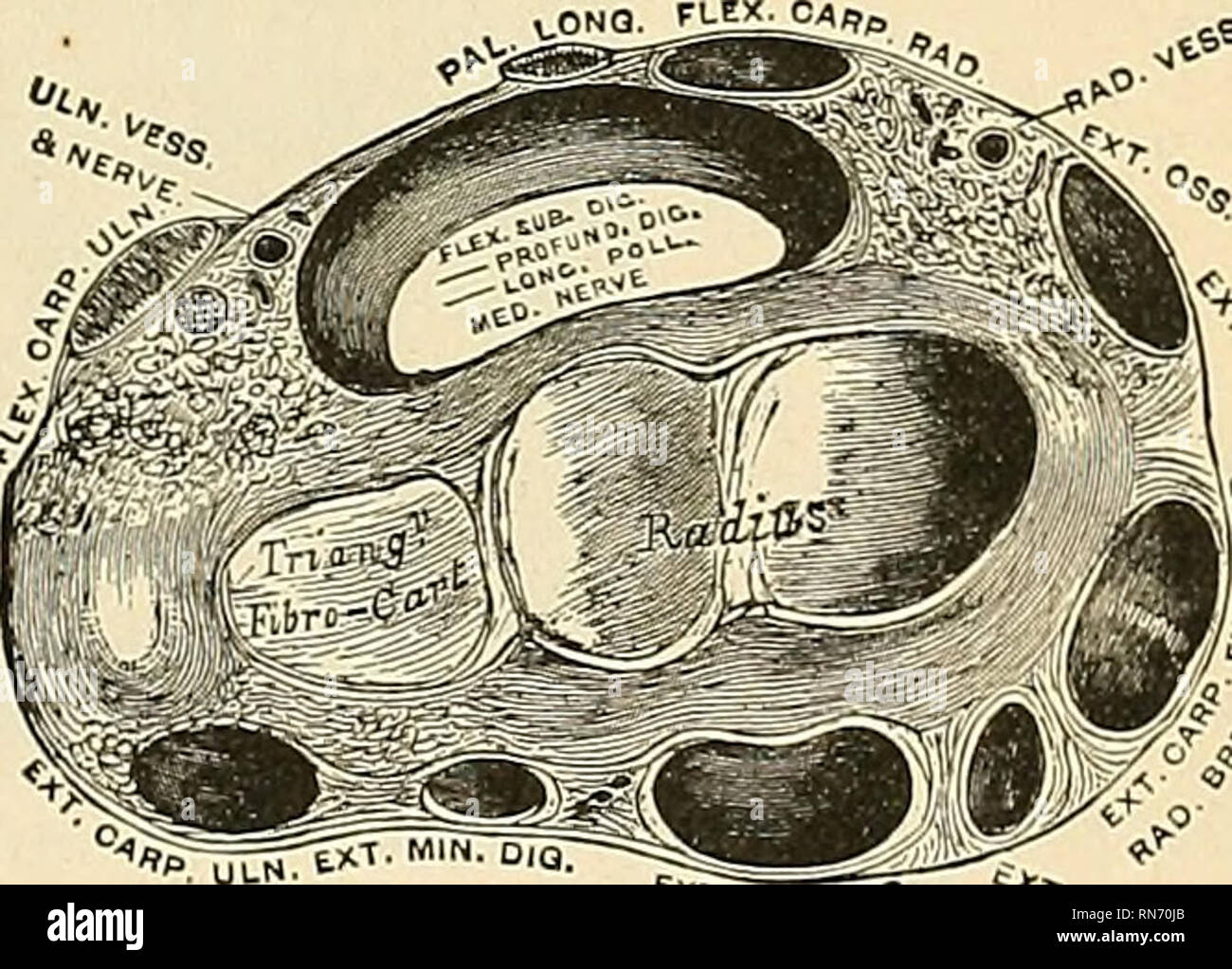
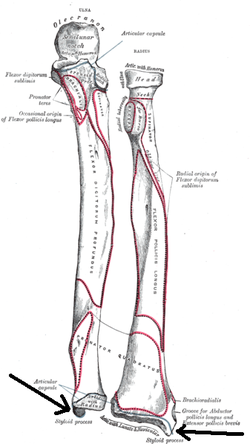
Styloid Process of Ulna - There is a small pointy projection that comes off the head of the ulna, called the styloid process of the ulna. This projection provides an attachment point for the ulnar collateral ligament of the wrist. Radius Bone Anatomy (also called Radial Bone)

In the diagram, where is the styloid process?
Slightly inferior to it on the opposite side sits the insertion of the brachioradialis muscle, which is just above the styloid process - an extrusion of the suprastyloid crest. This is a projection of the lateral aspect of the distal end of the radial bone that margins the carpal articular surface superiorly.
The styloid process located immediately underneath the opening to the auditory meatus. It acts as an attachment point for muscles and ligaments, such as the stylomandibular ligament of the TMJ. Petromastoid. This portion of the temporal bone is located posteriorly. It can be split into a mastoid and petrous parts.
Styloid process. The lateral part of the radius has a sharp projection in its distal part. This is termed the Styloid process or Radial Styloid. Suprastyloid Crest. The Suprastyloid crest is an oblique crest running from the styloid process. Brachioradialis muscle is attached here. Lister's tubercle
In the diagram, where is the styloid process?.
Where is the coronoid process in the diagram? A. This fontanel usually closes within 18 to 24 months after birth. B. This fontanel usually closes about 2 months after birth. D. These are the smallest fontanels in size at birth. C.
Ulnar styloid impaction syndrome. This ulnar-sided wrist pain is caused by impaction between an excessively long ulnar styloid process and the triquetral bone.66 The ulnar styloid process is a continuation of the prominent subcutaneous ridge of the shaft of the ulna, which projects distally towards the triquetral bone for a variable distance (2 ...
It is the terminal end of the facial canal, transmitting the facial nerve and the stylomastoid artery. The styloid process is a narrow, pointed projection that extends downwards and anteriorly from the inferior surface of the temporal bone. Its length is variable, but is usually on average 2.5cm in length.
1.A styloid process projecting distally on the lateral side. 2. A prominent dorsal tubercle (or Lister's tubercle) on the dorsal surface [3] 3. The ulnar notch on the medial side [1] Surfaces and Articulations: 1. The concave surface of the ulnar notch articulating with the ulnar head (distal radio-ulnar joint) [2] 2.
The styloid process arises from the medial and posterior aspect of the distal ulna, is non-articular in nature, and is the point of origin of the ulnar collateral ligament. The styloid process is separated from the head by a shallow depression where the triangular fibrocartilage attaches.
Figure 15 Diagram (coronal view) illustrates the USPI, which is calculated by subtracting the degree of ulnar variance (B) from the length of the ulnar styloid process (C) and dividing the difference by the transverse diameter of the ulnar head (A). The USPI has a normal range of 0.21 ± 0.07.
In the diagram, where is the styloid process? E. Which of the labeled structures in the diagram is the spine of the scapula? A. In the diagrams of the pelvis, where is the iliac crest. H. In the diagram, which letter is a floating rib? f.
This is a spool-shaped process on distal end of the humerus that is found medial to the capitulum and articulates with the ulna. Trochela The medial and lateral epicondyles are found on the distal end of the humerus and are used for
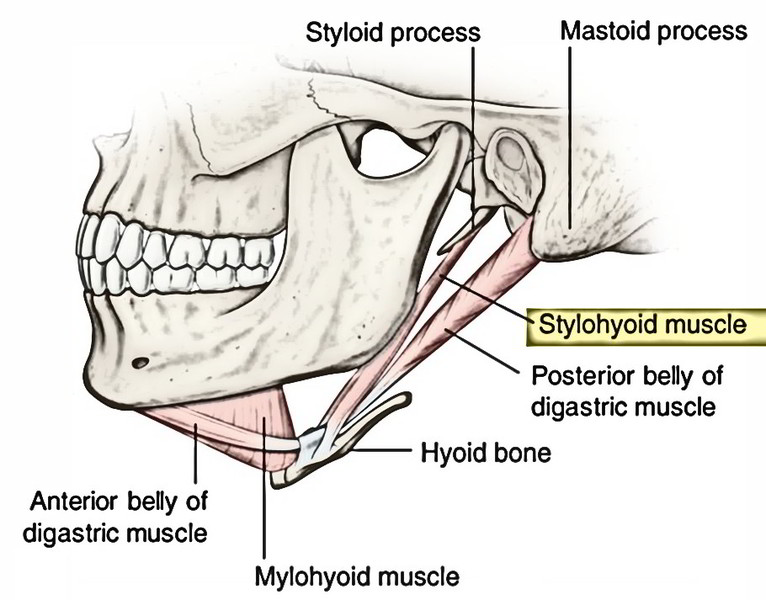
The styloid process of the temporal bone is a slender osseous projection that points anteroinferiorly from the inferior surface of the petrous part of the temporal bone. It serves as an anchor point for several muscles associated with the tongue and larynx: styloglossus muscle stylohyoid muscle stylopharyngeus muscle stylohyoid ligament
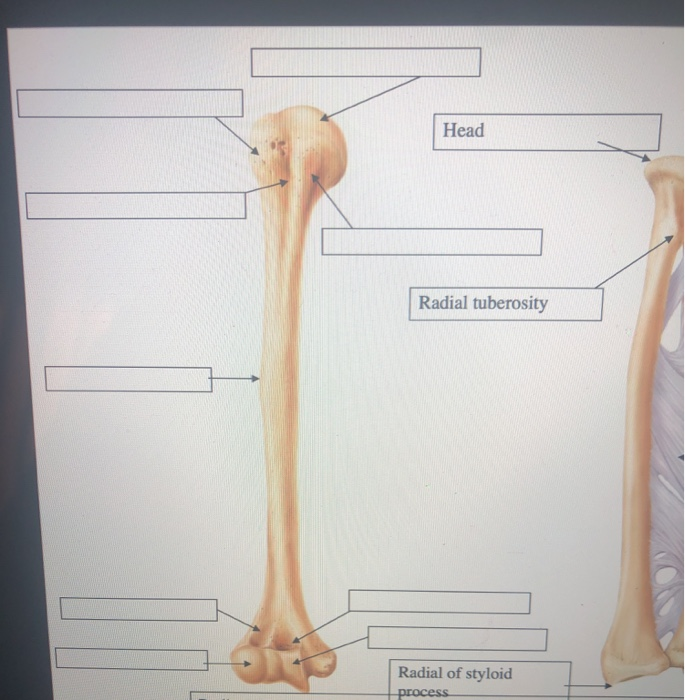
Styloid process R. S Trochlea Co nold fossa Deltoid tuberosity G enoid cavity rus carpals Olecranon fossa Otecranon process Phalanges Radial tuberosity O. Radius B. c. E. Acromion Capitulum Carpals Clavicle Coracoid process T. Ulna Raised area on lateral surface of humerus to which deltoid muscle attaches Bones composing the shoulder girdle 6.
The styloid process of the temporal bone is a small bony growth protruding in the downward direction from the temporal bone. This thorn-shaped bone acts as a point of attachment for the muscles associated with the tongue and the larynx. This anchoring of muscles plays a crucial role in the proper movement of delicate organs such as the tongue.
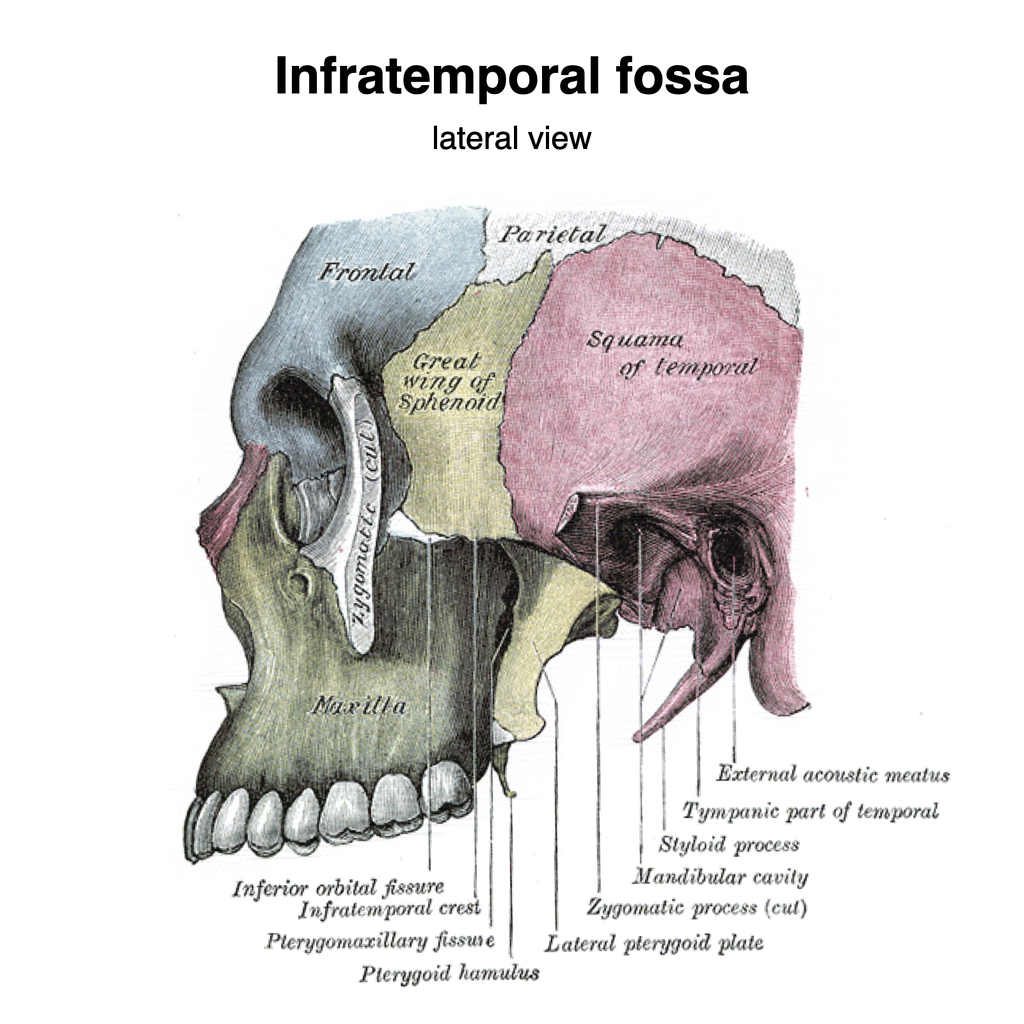
• styloid process (a muscle attachment site). • mastoid process (the lump behind the ears where neck muscles are anchored). • stylomastoid foramen (between the styloid and mastoid processes, where the facial nerves leave the skull) • posterior part of the middle cranial fossa (where the temporal lobes of the brain sit).
Each temporal bone is composed of five osseous parts: the squamous, mastoid, petrous, tympanic, and styloid portions. Several intrinsic channels, intrinsic fissures, and extrinsic sutures are often apparent on CT images and can mimic fractures (pseudofractures) ( 1 ).
And you've also got this little styloid process medially. Just like you've got the styloid process on the radius, you've got the styloid process of the ulna. Just looking here at an image I stole from Wikipedia, you've got the coronoid process. You've got the radial notch on the ulna articulating with the radial head.
Styloid Process: This is a narrow projection of bone coming out of the temporal bone. Variable in length, it is angled downward and forward, accessing on the inner side the tympanic part that encloses it, and on the outer side to ligaments that connect to the stylohyoid and other muscles involved with chewing motions.
The styloid process is a small bony protrusion extending from the posterior medial side of the head [7]. This is where the ulnar collateral ligament (UCL) of the wrist attaches [8]. Muscle and Ligament Attachments. The borders and surfaces of the ulnar shaft are the primary site for muscular attachments to this bone [3]:
Hand radial inverted imaging is the whole-body figure, which is located on the dorsal side of the radial side of the hand. It is distributed around the first and second phalanges, the metacarpal bone, the scaphoid bone, the trapezium bone, and the radial styloid process. a. Head.
styloid process - sharp process near the mastoid process to which ligaments and tendons attach. stylomastoid foramen - opening between the base of the styloid and mastoid processes through which the facial nerve passes.
It fits into the cartilage of your wrist joint and plays an important role in the strength and flexibility of your wrist and forearm. Any sort of break in this area is called an ulnar styloid...
Styloid process, radius; Joint. Identified between distal humeral epicondyle and lateral tuberosity of the radius. The collateral ligament runs between these two landmarks. Soft tissue. Extensor carpi radialis; Common digital extensor; Extensor carpi ulnaris and flexor carpi ulnaris, the groove between these two muscles can be felt caudally
The scaphoid originates from the fusion of two chondrification zones, known as the centralia. 3 This process is not completed until the seventh week, when the embryo reaches 50 mm in crown-to-rump length. 4 If these two elements do not fuse, then a supernumerary bone, interposed between the distal part of the scaphoid and the neck of the ...
A persistent ulnar styloid ossicle is an anatomical variant where the ulna styloid ossification center fails to unite with the ulna.. Radiographic features. Seen as a well-corticated ossification just adjacent to the ulnar styloid. Differential diagnosis. os triangulare: a small accessory ossicle located between the ulnar styloid, lunate and triquetrum ...
The muscle starts at the styloid process, a pointed part of the skull's temporal bone, which lies just below the ear and functions as an anchor point for a number of muscles. The stylohyoid is ...
"sistem kerangka" pvc tahan air grafik hd medis poster manusia skeleton anatomi atlas kelas rumah sakit dekorasi










![Solved] In the Diagram of the Ulna and Radius,where Is the Styloid ...](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6090/11ea7fbb_48ea_f17b_8673_5760e1c573f9_TB6090_00_TB6090_00.jpg)





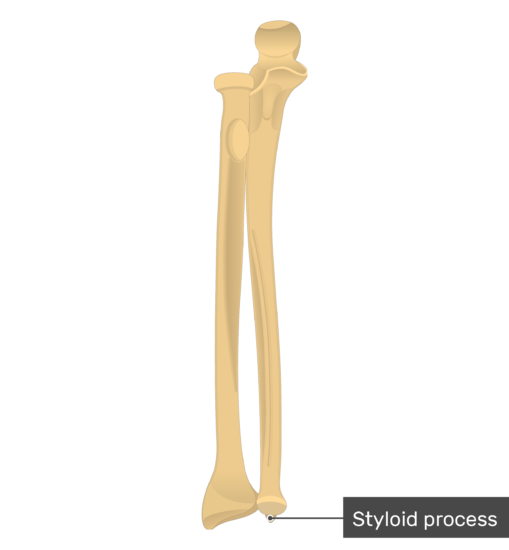








0 Response to "42 in the diagram, where is the styloid process?"
Post a Comment