37 convex mirror ray diagram
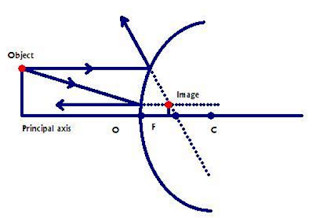
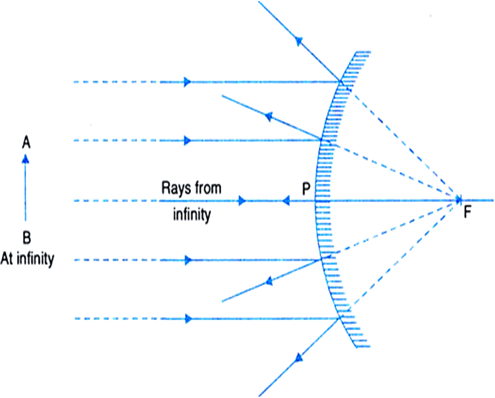
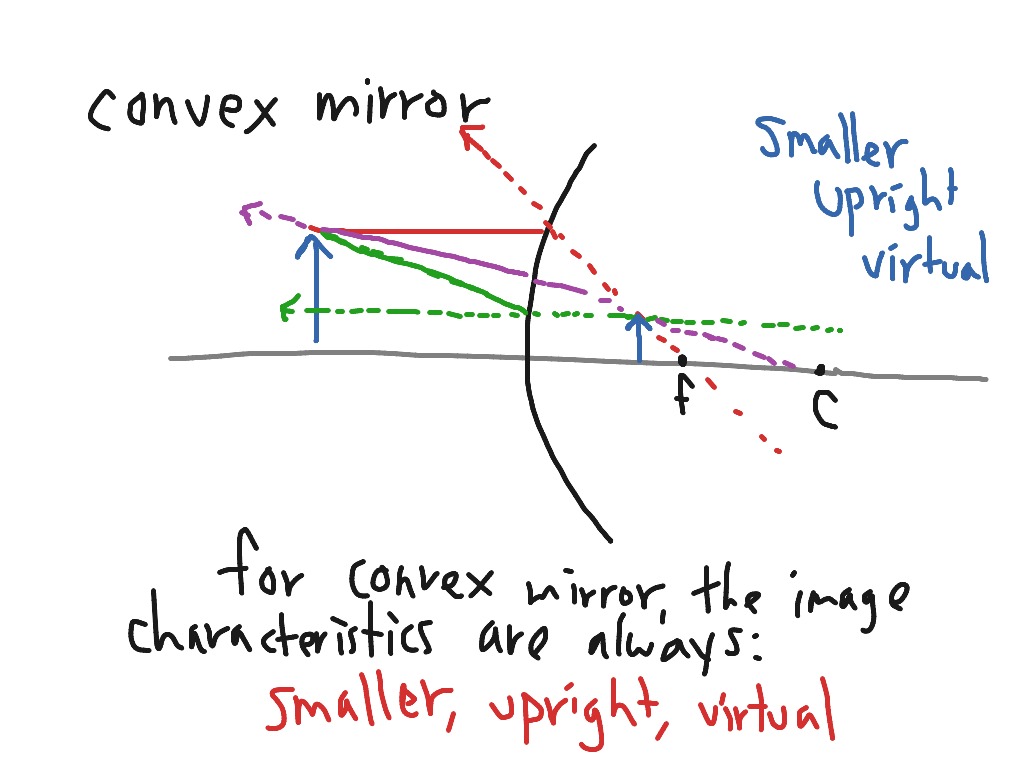
A convex mirror or diverging mirror is a curved mirror in which the reflective surface bulges towards the light source. Convex mirrors reflect light outwards, therefore they are not used to focus light. Such mirrors always form a virtual image, since the focal point (F) and the centre of curvature (2F) are both imaginary points "inside" the mirror, that cannot be reached. The ray diagram above illustrates that the image of an object in front of a convex mirror will be located at a position behind the convex mirror. Furthermore, the image will be upright, reduced in size (smaller than the object), and virtual. This is the type of information that we wish to obtain from a ray diagram.
Convex & concave mirror ray diagrams. Transcript. Let's explore the ray tracing technique to figure out the properties of images when things are kept in front of a concave or a convex mirror. Created by Mahesh Shenoy.

Convex mirror ray diagram
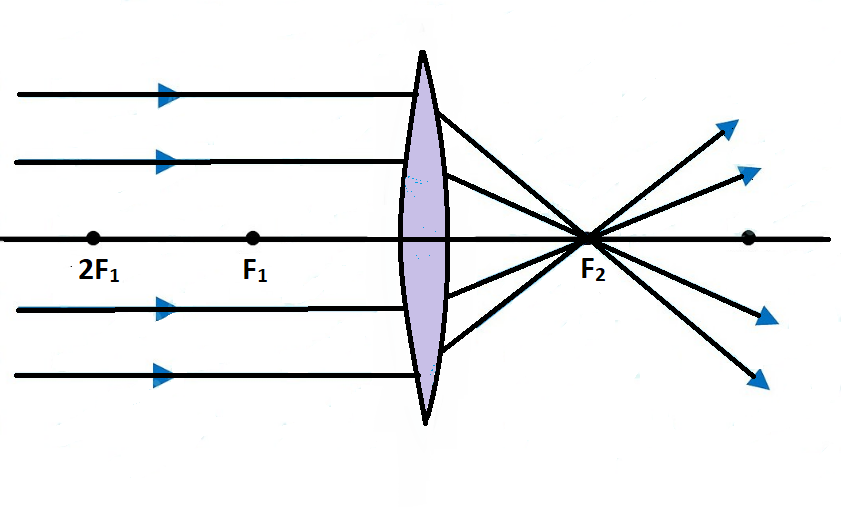
A convex mirror forms a virtual image.The cartesian sign conventionis used here. Using a ray parallel to the principal axis and one incident upon the center of the mirror, the position of the image can be constructed by back-projecting the rays which reflect from the mirror. Ray diagrams are necessary for understanding the formation of an image by a convex mirror. For constructing ray diagrams and to learn the image formation, we should consider at least two incident rays coming from the object. The intersection of these two reflected rays gives the position of an image of the object. Convex Mirror - Ray diagram Last updated at April 23, 2020 by Teachoo For a Convex Mirror, The focus and center of curvature is on the right side of the mirror So, there will only be 2 cases. They are Object is Placed at Infinity Object is Placed between Principal axis and Infinity Case 1 - Object is Placed at infinity
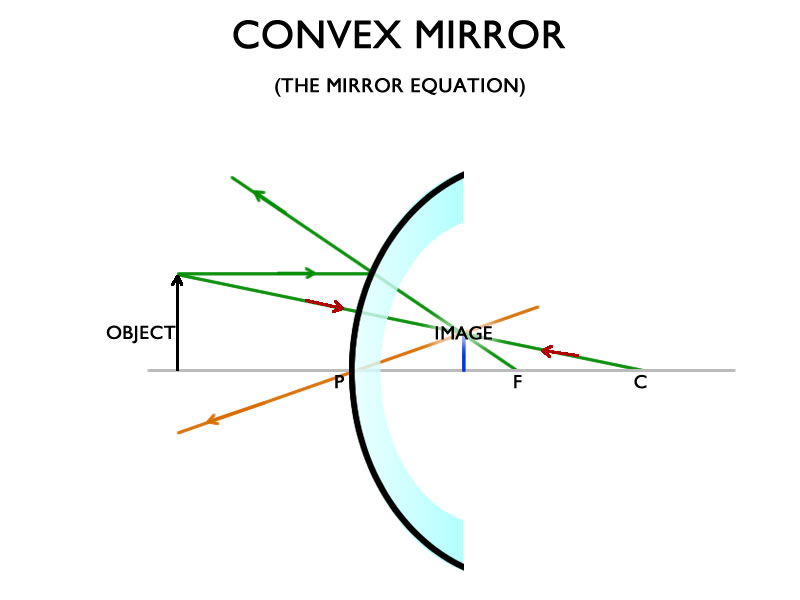
Convex mirror ray diagram. There are, again, two alternative methods of locating the image formed by a convex mirror. The first is graphical, and the second analytical. According to the graphical method, the image produced by a convex mirror can always be located by drawing a ray diagram according to four simple rules: . An incident ray which is parallel to the principal axis is reflected as if it came from the virtual ... Convex Mirror • Image is virtual, upright, reduced ... and magnification. Ray diagram. 11 1 pq f + = 111 qf p = − fp q pf = − (10)(30) 15cm 30 10 == − q15 M0.5 p30 =− =− =− Real image Inverted Reduced. 10 Example • F 30 cm 10 cm An object is placed 30 cm in front of a diverging lens with a focal length of -10 cm. Find the image distance and magnification 11 1 pq f += 111 qf p ... 10.05.2016 · GRAPHICAL METHOD/RAY DIAGRAMMING Case 4: Object at F NO IMAGE FORMED!!! For the case of the object located at the focal point (F), the light rays neither converge nor diverge after reflecting off the mirror. As shown in the diagram above, the reflected rays are traveling parallel to each other. Subsequently, the light rays will not converge on the object's … Our top 5% students will be awarded a special scholarship to Lido. Q40) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of image of an object placed on the principal axis of a convex mirror. State the position, size and nature of the image. What happens to the image as the object is moved away from the mirror?
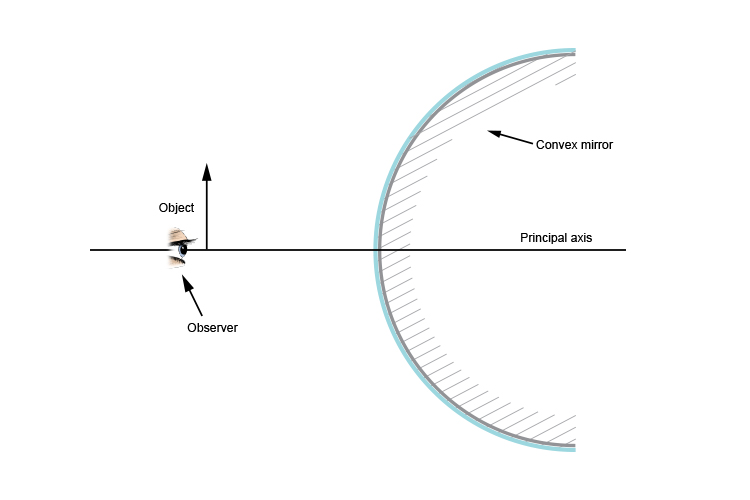
Below are the ray diagram rules for convex mirrors, which allow you to predict where the light rays from an object will travel and then focus in the eye of an observer. Rule 1. Take a line from an object parallel to the principal axis and where it touches the convex mirror take another line to the principal focal point. Rule 2. Concave Mirror Ray Diagram Concave Mirror Ray Diagram lets us understand that, when an object is placed at infinity, a real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller compared to that of the object. When an object is placed behind the center of curvature, a real image is formed between the center of curvature and focus. Ray diagram 1 : The ray 1 or the light beam 1 that come to the convex mirror are drawn parallel to the principal axis and touch the upper end of the object, then reflected by the convex mirror where the beam of light reflects as if from the focal point (f). and (b) convex spherical mirror. ± Ray Optics and Optical Instruments 313 virtual if the rays do not actually meet but appear to diverge from the point when produced backwards. An image is thus a point-to-point correspondence with the object established through reflection and/or refraction. In principle, we can take any two rays emanating from a point on an object, trace …
How to Draw a Ray Diagram for a Convex Mirror. Step 1: Identify the distance of the object from the mirror (d), the center of curvature (c) of the mirror, and the focal length (f) which is equal ... Image Formation By Concave Mirror And Their Ray Diagrams When the object is kept at infinity: As the parallel rays coming from the object converge at the principal focus, F of a concave mirror; after reflection through it. Therefore, when the object is at infinity the image will form at F. Object at Infinity 18.11.2021 · Convex Lens - Ray diagram. Last updated at Nov. 18, 2021 by . For a Convex Lens, object can be kept at different positions Hence, we take different cases Case 1 - Object is Placed at infinity In this Case, Object is kept far away from lens (almost at infinite distance) So, we draw rays parallel to principal axis Since ray parallel to principal axis passes through the Focus … Ray diagrams and curved mirrors Our mission is to provide a free, world-class education to anyone, anywhere. Khan Academy is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization.
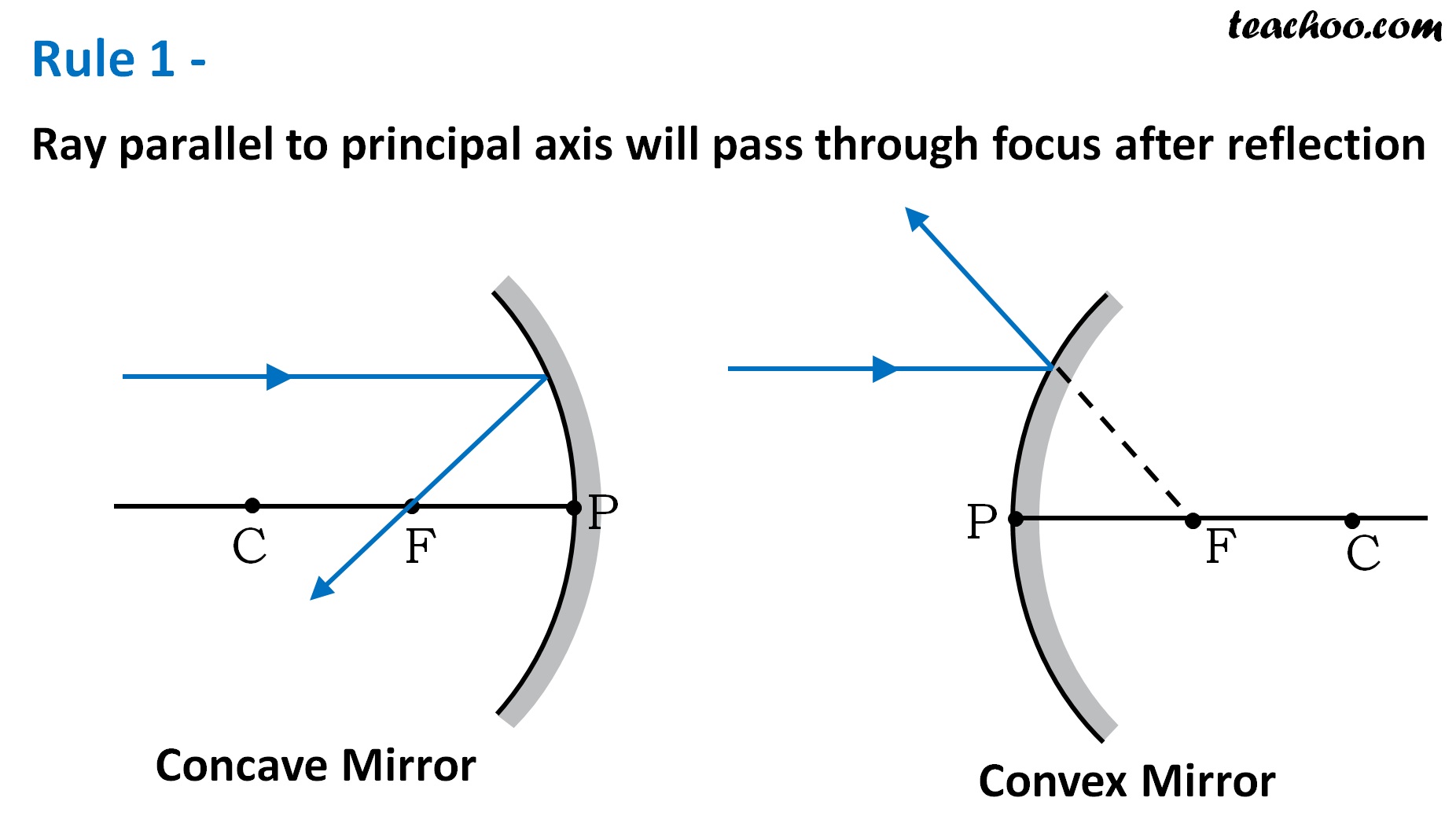
Rules For Making Ray Diagrams By Spherical Mirror (i) A ray passing to the principal axis, after reflection, will pass through the principal focus in case of a concave mirror or appear to diverge from the principal focus in case of a convex mirror
Concave spherical mirrors and ray diagrams A spherical mirror is a reflective segment of a sphere with a radius of curvature R. It can be convex (outside surface of a sphere) or concave (inside surface). First we will consider a concave spherical mirror. The mirror has a radius R, and the distance from the mirror to the object is p.
How to predict where the image of an object is, in a convex mirror.The image is close to the mirror, upright, small and virtual.
Summary of method for drawing ray diagrams - Convex mirror Below is a simplified version of the last section that you will see in most text books. To draw a ray diagram and find the location of the virtual image (not real) you only need to draw two ray lines. This is sometimes referred to as "the two rules of reflection for a convex mirror".
This Demonstration lets you visualize the ray diagrams for concave and convex spherical mirrors. By manipulating the object and mirror locations, you can create real or virtual images. The ray parallel to the principal axis and the ray that hits the center of the mirror are drawn.
oPhysics: Interactive Physics Simulations. Concave and Convex Mirrors. Concave and Convex Mirrors - GeoGebra Materials. Description. Simulation of image formation in concave and convex mirrors. Move the tip of the Object arrow or the point labeled focus. Move the arrow to the right side of the mirror to get a convex mirror.
Simple ray diagram showing typical chief and marginal rays. A meridional ray or tangential ray is a ray that is confined to the plane containing the system's optical axis and the object point from which the ray originated. A skew ray is a ray that does not propagate in a plane that contains both the object point and the optical axis. Such rays do not cross the optical axis anywhere, …

Image from page 481 of "The silver sunbeam : a practical and theoretical text-book on sun drawing and photographic printing" (1873)
15.05.2020 · Convex Mirror - Ray diagram Uses of Concave and Convex Mirrors Sign convention for Spherical Mirrors Mirror Formula Refraction of Light Refraction through a Rectangular Glass Slab Laws of Refraction Refractive Index Concave and Convex Lens ...
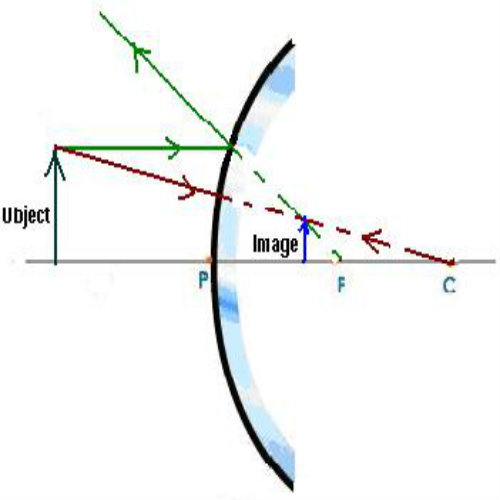
A ray diagram shows the path of light from an object to mirror to an eye. Incident rays - at least two - are drawn along with their corresponding reflected rays. Each ray intersects at the image location and then diverges to the eye of an observer. Every observer would observe the same image location and every light ray would follow the law of reflection.
Description of how to draw ray diagrams for convex mirrors for grade 10 science
Convex mirrors diverge light, and they produce virtual upright images on the opposite side of the mirror. As with the previous mirror problem, we only need to draw two rays here. First, we draw a dotted line from the tip of the object to the focal point on the opposite side of the mirror.

Image from page 223 of "A high-school astronomy: in which the descriptive, physical, and practical are combined .." (1859)
A ray diagram that shows the position and the magnification of the image formed by a convex mirror. The animation illustrates the ideas of magnification, of real and virtual images. Click and drag the candle along the optic axis. Click and drag its flame to change its size.
o All convex mirrors have negative focal lengths. Convex mirrors always form reduced, virtual images. To determine image heights and distances from a ray diagram, draw the principal rays and look for their intersections: 1. Draw a line from the top of the object to the mirror, parallel to the axis. Reflect the ray through the focal point. 2.
While making ray diagrams, these two rules are important for students. The purpose of drawing ray diagrams is to find the location, size, direction, and type of image formed by a convex mirror. The steps involved in drawing ray diagrams are quite simple and easy to understand.
Ray Diagram for Convex and Concave Mirror. Is this page helpful? A mirror is a part of a smooth and highly polished reflecting surface.What are convex and concave mirrors?: If the i...Position: Depends on the position of the objectImage: Concave mirrors can form inverted and ...Size: Size can be smaller, larger or of the same ...Q 1: How is the image formed by a concave and convex mirror?Q 2: Which type of image is formed by a convex mirror?
L3-02. Optical Board - Ray Diagram - Convex Mirror Purpose. To determine the image position for an object in front of a convex mirror using the three principal rays. Equipment. Optical board with convex lens, half-silvered and rotating full-silvered mirrors, convex mirror. Images. Description
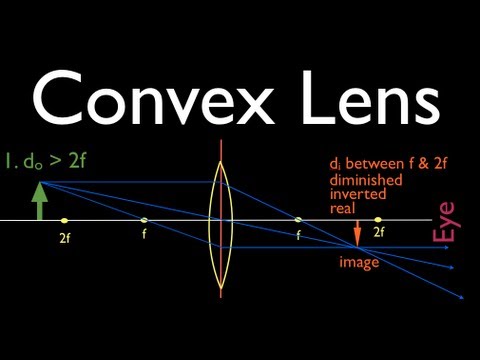
This means that the magnification is positive but less than 1. The ray diagram in Figure 13 shows that the image is on the same side of the lens as the object and, hence, cannot be projected—it is a virtual image. Note that the image is closer to the lens than the object. This is a case 3 image, formed for any object by a negative focal length or diverging lens. Figure 13. Ray tracing ...
Convex Mirror - Ray diagram Last updated at April 23, 2020 by Teachoo For a Convex Mirror, The focus and center of curvature is on the right side of the mirror So, there will only be 2 cases. They are Object is Placed at Infinity Object is Placed between Principal axis and Infinity Case 1 - Object is Placed at infinity
Ray diagrams are necessary for understanding the formation of an image by a convex mirror. For constructing ray diagrams and to learn the image formation, we should consider at least two incident rays coming from the object. The intersection of these two reflected rays gives the position of an image of the object.
A convex mirror forms a virtual image.The cartesian sign conventionis used here. Using a ray parallel to the principal axis and one incident upon the center of the mirror, the position of the image can be constructed by back-projecting the rays which reflect from the mirror.






















0 Response to "37 convex mirror ray diagram"
Post a Comment