37 law of reflection diagram
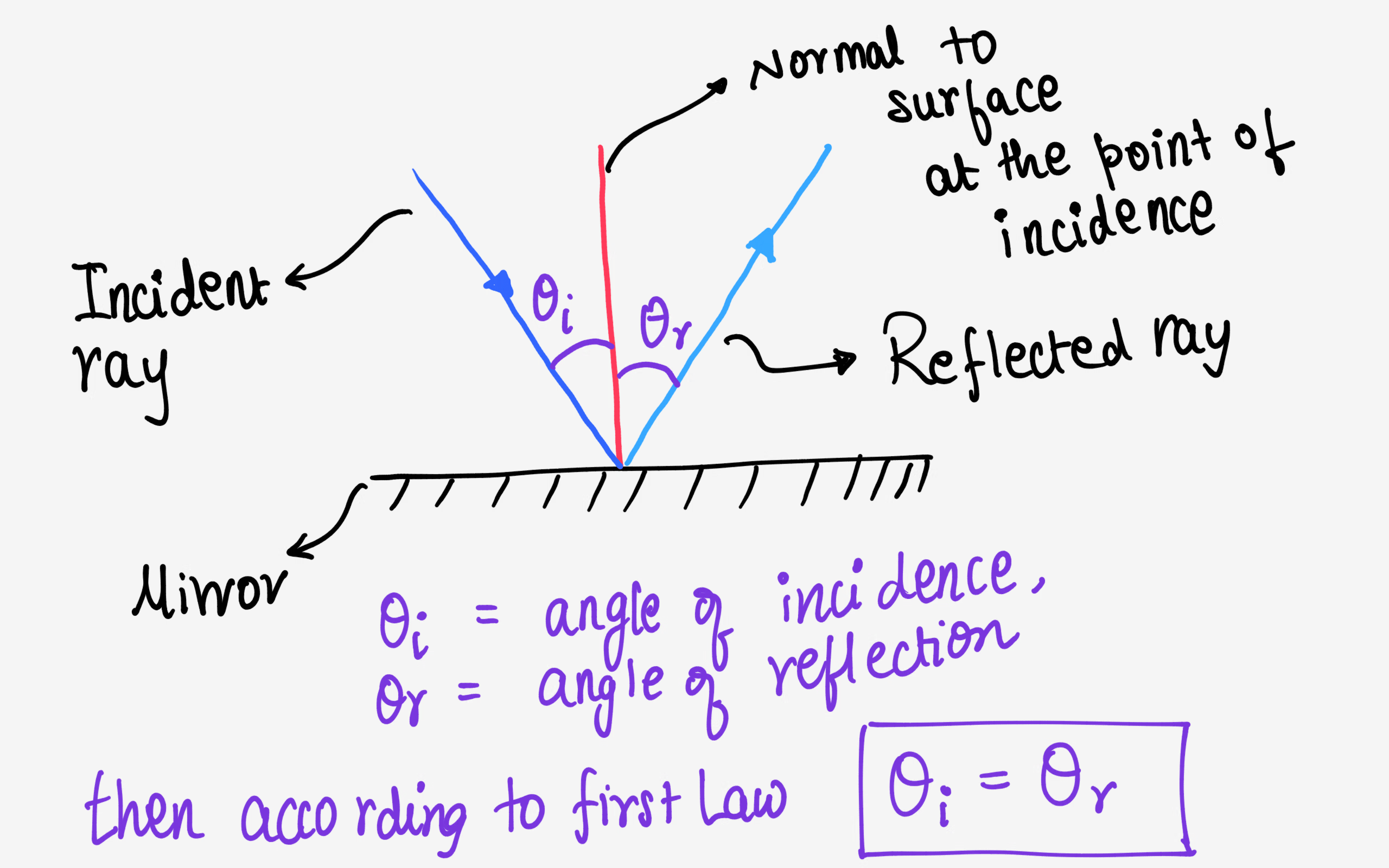
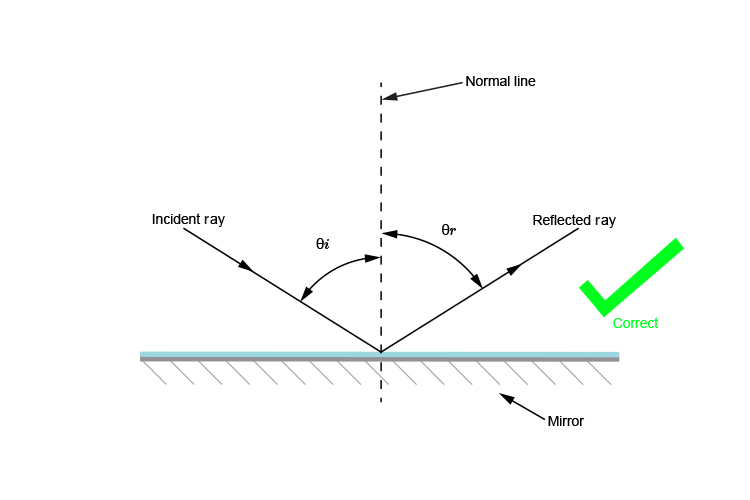
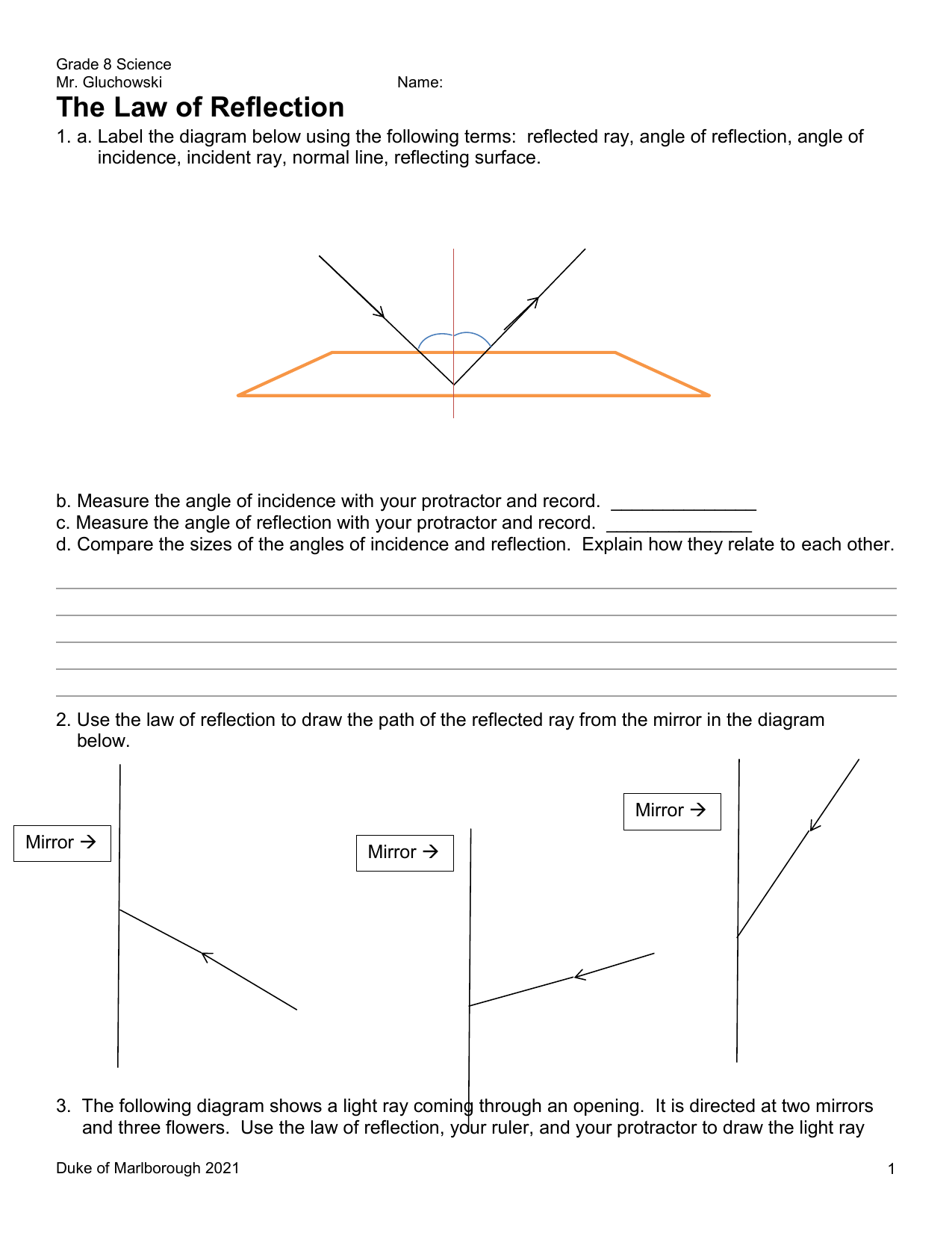
The Law of Reflection 23.1 The law of reflection works perfectly with light and the smooth surface of a mirror. However, you can apply this law to other situations. It can help you win a game of pool or pass a basketball to a friend on the court. In this practice activity, use a protractor to make your angles correct in your diagrams. The Law of Reflection says “the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection.” These angles are always measured from the normal line so that we have a common reference. In Illustration 1 we see that the angle is 42° coming in and 42° reflecting off. This is an example of regular (specular) reflection.
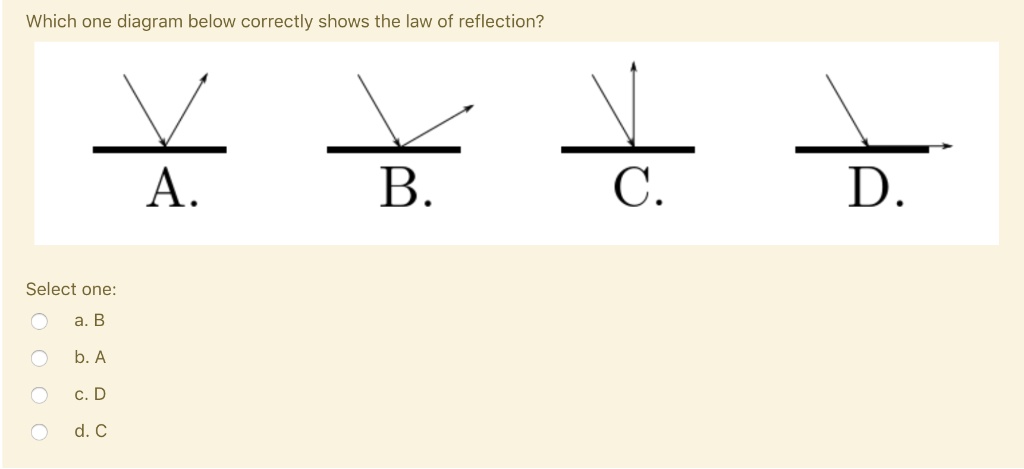
Q. In the given figure, which of the following holds TRUE? answer choices. The angle of incidence is 10°. The angle of incidence is 80°. The angle of reflection is 10°. The angle of reflection is 90°.
The angle of incidence is 10°.
. alternatives.
Law of reflection diagram
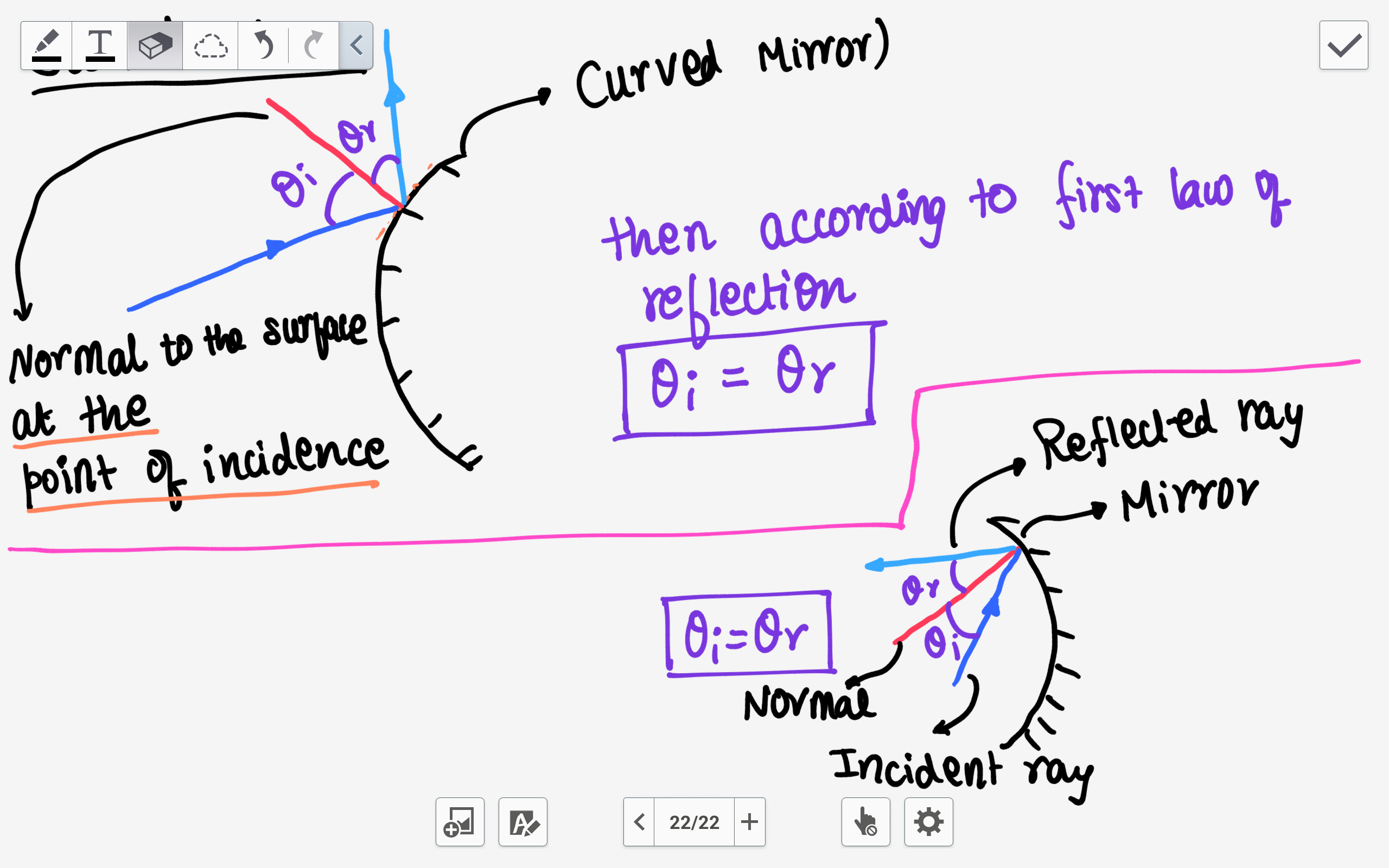
1) Students should be able to state the law of reflection and draw a ray diagram to illustrate it. 2) Students should be able to apply the law of reflection to predict the position of images formed by objects in front of a planar mirror. Material required: 1) Full length mirror hung horizontally Figure 1. The law of reflection states that the angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence—θr = θi. The angles are measured relative to the perpendicular ... In our diagram, we now label the reflected angle, along with triangles ABD and ACD, that we will use to prove the law of reflection. Using this diagram, we can form two triangles labelled ABD and ACD.
Law of reflection diagram. To figure out where the image of this object is located, a ray diagram can be used. In a ray diagram, rays of light are drawn from the object to the mirror, along with the rays that reflect off the mirror. The image will be found where the reflected rays intersect. Note that the reflected rays obey the law of reflection. reflection is the angle between this normal and the reflected ray. According to the law of reflection, the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. To view an image of an object in a mirror, you must sight along a line at the image location. As you sight at the image, light travels to your eye along the path shown in the diagram. The Diagram of specular reflection. Using the diagram, a vertical mirror O is struck by a light ray PO, producing reflected light OQ. The reflection of light can happen when light travels from a medium whose refractive index is one of the means of propagation into another medium whose refractive index is different, for reflection examples. Start studying Law of Reflection diagram. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
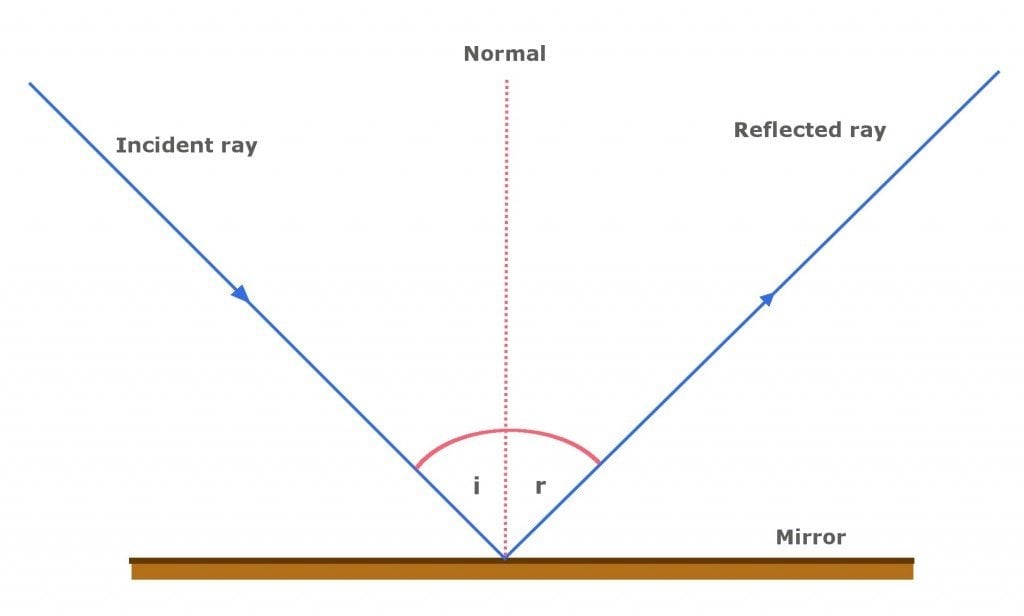
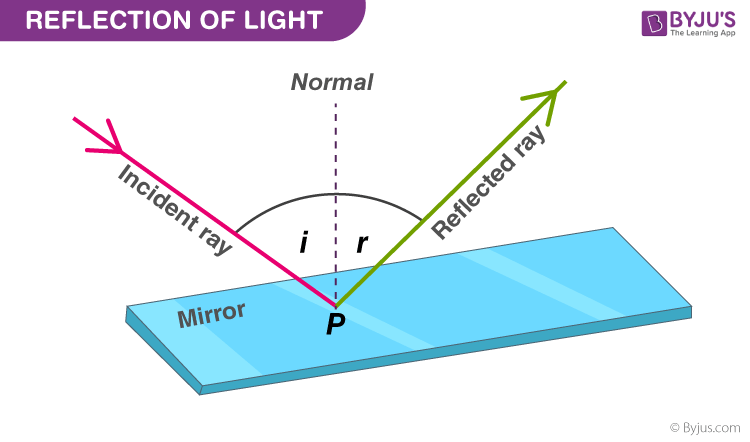
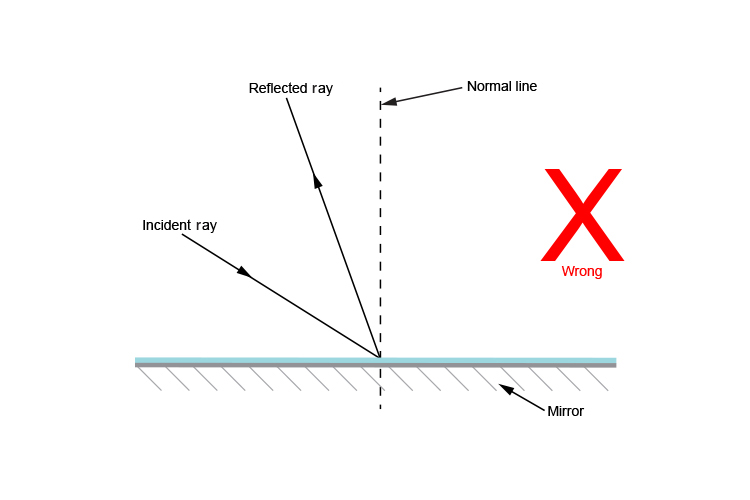
Description Simulation of image formation in concave and convex mirrors. Move the tip of the Object arrow or the point labeled focus. Move the arrow to … The diagram below illustrates the law of reflection. In the diagram, the ray of light approaching the mirror is known as the incident ray (labeled I in the diagram). The law of reflection states that when a ray of light reflects off a surface, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Light is known to behave in a very predictable manner. If a ray of light could be observed approaching and reflecting off of a flat mirror, then the behavior of the light as it reflects would follow a predictable law known as the law of reflection. The diagram below illustrates the law of reflection. In the diagram, the ray of light approaching the mirror is known as the incident ray (labeled I in the diagram). The first law of reflection states that the incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal to the surface of the mirror, all lie in the same plane. The second law of reflection states that t he angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence. Both angles are measured with respect to the normal to the mirror. See the diagram below for ...
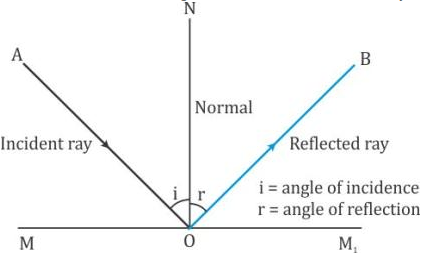
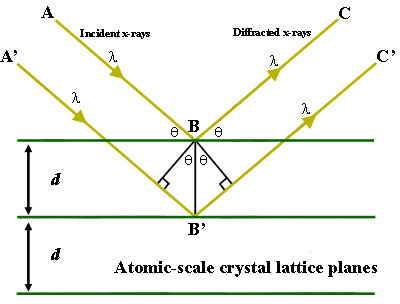
reflection and refraction. 19. Law of refraction (Snell's Law) Define the refraction index (n) and write its formula: _____ _____. Draw a diagram and explain the law of refraction by identifying the incident and refraction rays, incident and refraction angles, the refraction indices, and speeds of light. Shallow Water the normal (in this particular diagram, i = 45°). The incident ray is reflected by the mirror into another ray: the reflected ray of light with an angle of reflection r, again, measured from the normal. The angle of incidence and the angle of reflection are equal, or i = r. This is the law of specular reflection, from the Latin word ... Purpose To develop an understanding of the Law of Reflection, to apply the Law of Reflection to finding images formed by plane and spherical mirrors, and to learn to draw ray diagrams to assist in predicting the locations of images formed by spherical concave mirrors. Hypothesis According to the Law of Reflection, the angle of […] Here’s a diagram to help you visualize the law of reflection a bit better: Angle of incidence and angle of reflection In the diagram above, the light ray approaching the mirror is known as the incident ray, while the one that bounces off the mirror is called the reflected ray.
Sample Problems for The Law of Reflection Important Information When light is reflected from a surface, the angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection, where both angles are measured from the path of the light to the normal to the surface at the point at which light strikes the surface. This equality is known as the law of reflection.
Question 3. SURVEY. 30 seconds. Q. The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. answer choices. law of light. law of reflection. law of refraction.
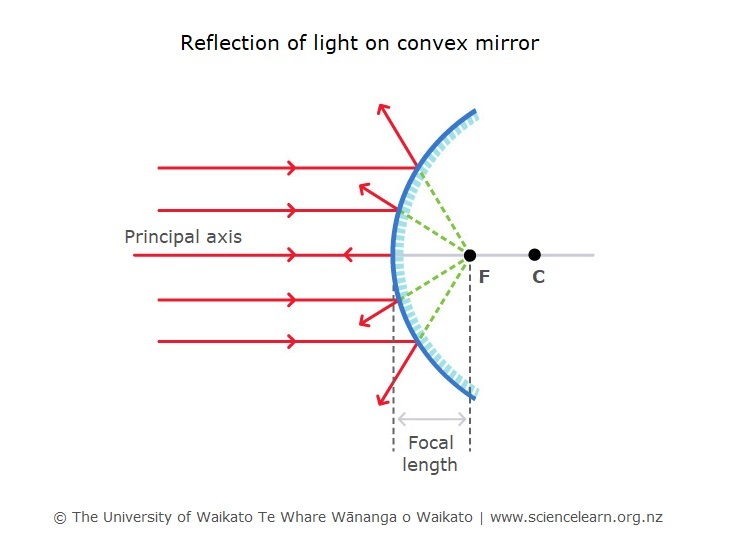
Using the law of reflection – Ray diagram rules. When we observe an object in a convex mirror there are three ways to try to work out how the light rays from an object focus into the eye of an observer. Use the ray diagram flat/plane mirror rules. Use the laws of reflection. Use new ray diagram rules and create a virtual image.
Unbalanced forces cause objects to accelerate. But not all objects accelerate at the same rate when exposed to the same amount of unbalanced force. Inertia describes the relative amount of resistance to change that an object possesses. The greater the mass the object possesses, the more inertia that it has, and the greater its tendency to not accelerate as much.
This collection of interactive simulations allow learners of Physics to explore core physics concepts by altering variables and observing the results. This section contains more than 70 simulations and the numbers continue to grow.
To figure out where the image of this object is located, a ray diagram can be used. In a ray diagram, rays of light are drawn from the object to the mirror, along with the rays that reflect off the mirror. The image will be found where the reflected rays intersect. Note that the reflected rays obey the law of reflection.
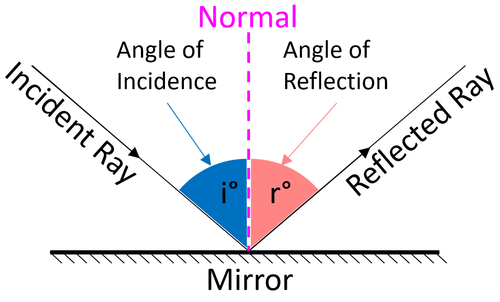
The angle measured between the incident ray and the normal. Angle of Reflection. The angle measured between the reflected ray and the normal. Mirror. Smooth, shiny surfaces make the best mirrors. The flat side on the diagram is the shiny side. Law of Reflection (plane mirror) Angle of incidence = Angle of Reflection.
(See diagram, above) With simple geometry this condition can be expressed as + =, where θ 1 is the angle of reflection (or incidence) and θ 2 is the angle of refraction. Using Snell's law, = ,
Solution. First, we consider reflection, as shown in the diagram below for a light wave striking a surface. We identify the incoming ray as the incident ray and the outgoing ray as the reflected ray. Concomitantly, the angleθ i. that the incoming ray makes with a line (dashed in the diagram) normal to the surface is called the angle of incidence.
The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection, i = r. It works for any angle. For example: the angle of reflection is 30° if the angle of incidence is 30 ...
The law of reflection tells us that ? 2 = ? 3; on the basis of this and our conclusion about the relationship of ? 1 and ? 3, we can express ? 2 in terms of ? 1 as follows. Practice Problem: Complete the diagram to show (approximately) the path of the ray upon reflection by the mirror shown below.
The three laws of reflection. Any mirror obeys the three laws of reflection, flat, curved, convex or concave. 1. The angle between the incident ray and the normal is equal to the angle between the reflected ray and the normal. 2. The incident ray, the normal and the reflected ray are all in the same plane. 3.
Law of reflection A ray diagram for reflection at a mirror. the hatched vertical line on the left represents the plane mirror; the dashed line is called the normal, drawn at 90° to the surface of ...
Oct 01, 2019 · 18. Redraw the diagram given below in your answer book and show the direction of the light ray after reflection from the mirror. [Delhi (C)] Answer. 19. Redraw the diagram given below in your answer book and show the direction of the light ray after reflection from the mirror. [Delhi (C)] Answer. 20.
In the diagram, the ray of light approaching the mirror is known as the incident ray. At the point of incidence where the ray strikes the mirror, a line can be drawn perpendicular to the surface of the mirror. This line is known as a normal line. ... The law of reflection holds true for rough surfaces as well. The law of reflection also states ...
The law of reflection defines that upon reflection from a smooth surface, the angle of the reflected ray is equal to the angle of the incident ray, with respect to the normal to the surface that is to a line perpendicular to the surface at the point of contact. The reflected ray is always in the plane defined by the incident ray and the normal ...
If the angle of reflection is 47.5o, the angle of incidence will also be 47.5o in accordance with the second law of reflection. Question 28: With the help of a labelled ray-diagram, describe how a plane mirror forms an image of a point source of light placed in front of it. State the characteristics of the image formed in a plane mirror. Solution :
Coloumb’s law is an experimental law that quantifies the amount of force between two stationary electrically charged particles. The electric force between stationary charged body is conventionally known as the electrostatic force or Coloumb’s force. Coulomb’s law describes the amount of electrostatic force between stationary charges.
Law 1. The first law of reflection states that the reflection angle is always equivalent to the angle of incidence. If the incident ray falls on the plane mirror along the normal, i.e. 90°, the reflected ray will travel along the same path. Law 2. The incident ray, reflected ray, angle of incidence and reflection, and point of incidence lie on ...
Convex Mirror Ray Diagram: A convex mirror with three rays drawn to locate the image. Each incident ray is reflected according to the Law of Reflection. The reflected rays diverge. If the reflected rays are extended behind the mirror, then their intersection gives the location of the image behind the mirror.
Nov 23, 2017 · 5. Reflection. Metals can reflect light. The electrons in a metal can absorb particular wavelength of light to jump to the higher energy level. When it comes back to original state, it emits the same wavelength of light. As the wavelength of incident light is same as emitted light, we see as reflection of light. 4.43/5 (28)
The Law of Reflection states that when waves are reflected from an interface, the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. The purpose of this lab is to experimentally verify this outcome. Given below are a sample screen capture and an accompanying image showing an example of the corresponding ray and angle constructions.
Aim : To verify the law of reflection. Procedure: 1) Take a drawing board and fix a white paper on it with the help of clamps. 2) Draw a straight line AB at the centre of the paper and also a normal (ON) to AB at point 'O'. 3) Draw a straight line PQ making certain angle (Angle i) with ON. 4) Fix two pins at the points P and Q on the paper ...
In our diagram, we now label the reflected angle, along with triangles ABD and ACD, that we will use to prove the law of reflection. Using this diagram, we can form two triangles labelled ABD and ACD.
Figure 1. The law of reflection states that the angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence—θr = θi. The angles are measured relative to the perpendicular ...
1) Students should be able to state the law of reflection and draw a ray diagram to illustrate it. 2) Students should be able to apply the law of reflection to predict the position of images formed by objects in front of a planar mirror. Material required: 1) Full length mirror hung horizontally
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ReflectionLaw-5946c6dd5f9b58d58a2f2efc.png)




















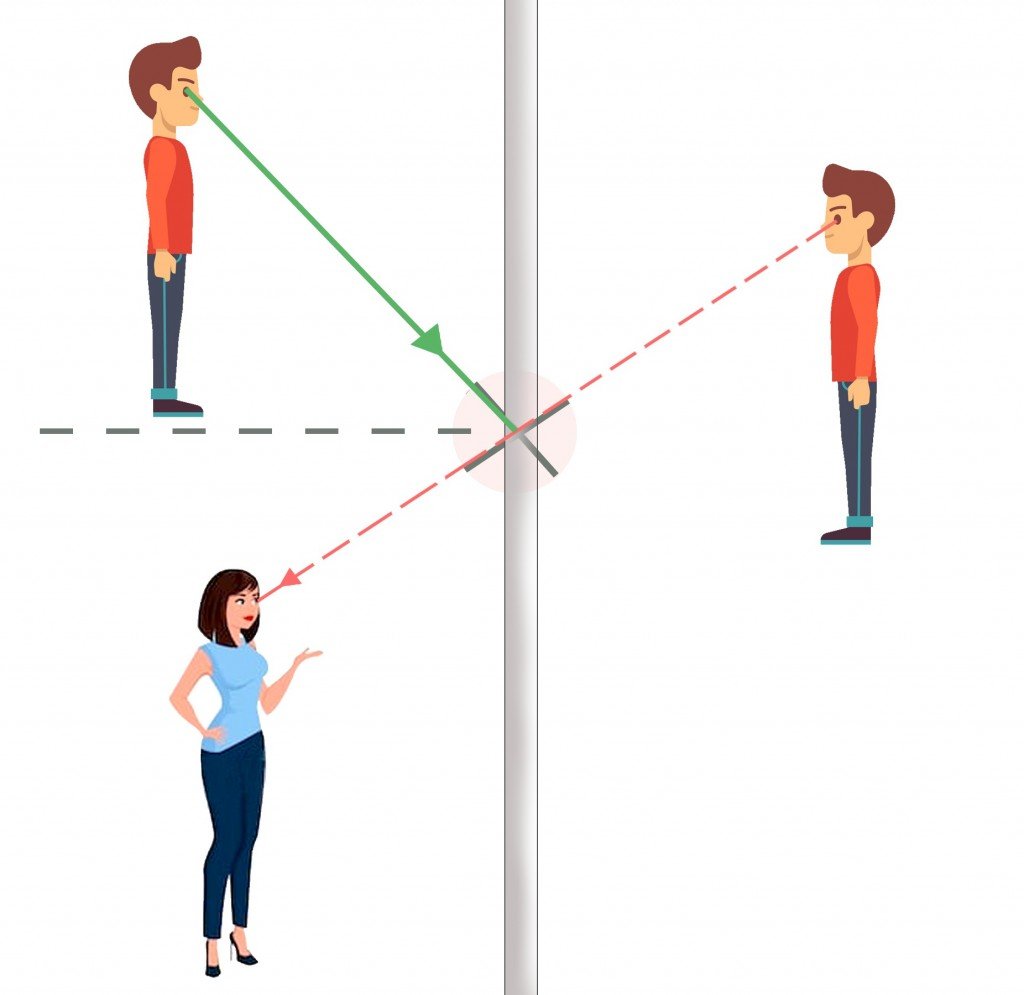
0 Response to "37 law of reflection diagram"
Post a Comment