40 space time diagram tutorial
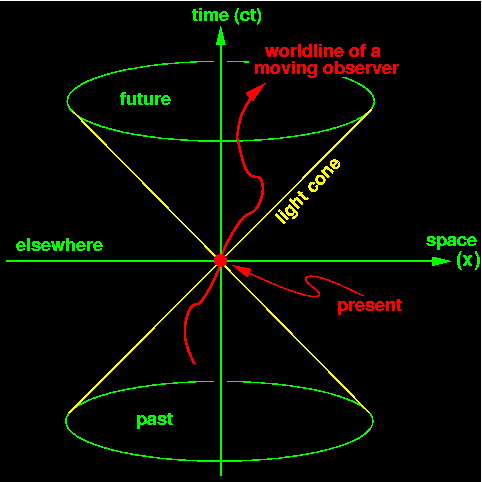
Space-Time Diagrams: Visualizing Special Relativity A space-time diagram shows the history of objects moving through space (usually in just one dimension). A speci c point on a space-time diagram is called an \event." To make a space-time diagram, take many snapshots of the objects over time and set them on top of each other. Lines in the diagram are like \contrails" through time. Introduction To Spacetime Diagrams - Department of Physics ... In the jargon of spacetime diagrams, the green point on Tom’s and Sarah’s plots is an event and the red or blue trajectories are worldlines. An event is anything that can be characterized by a single point on a spacetime diagram (or on a position vs time graph). An event must have both a time and a place, and
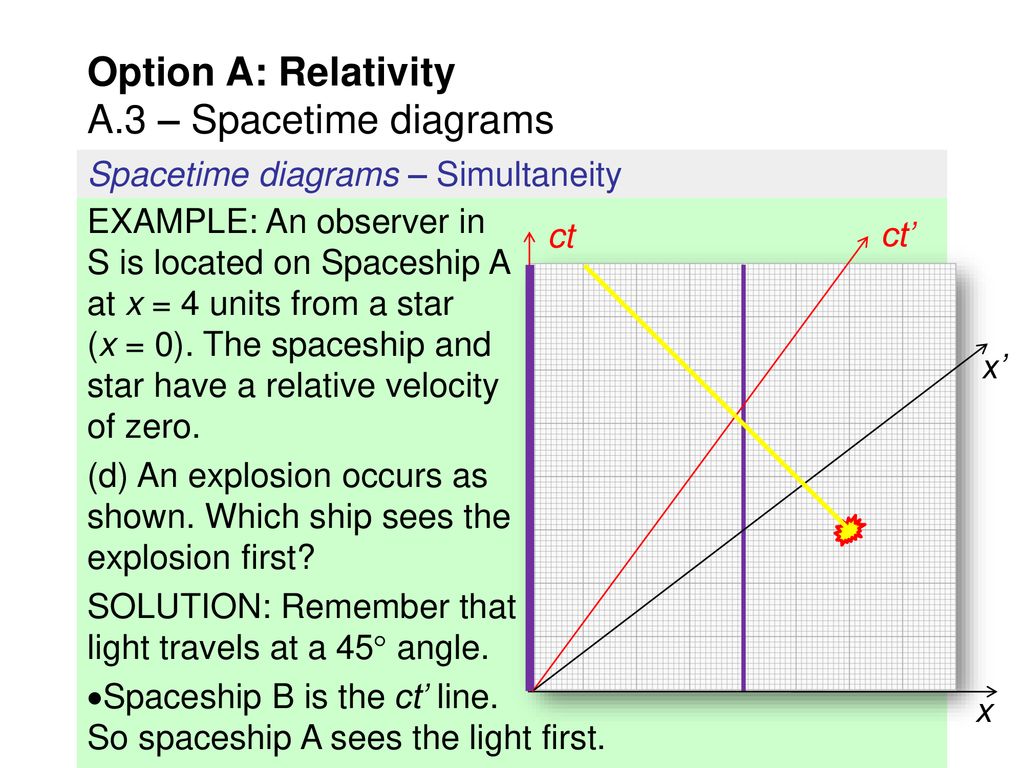
Topic 14 | Spacetime Diagrams Use our spacetime diagram to show that Mavis, who moves in the positive x-direction relative to Stanley, measures event 2 to occur before event 1. SOLUTION Events that are simultaneous in S have the same time t, so in Fig. T14.2 we draw a dashed line parallel to the x-axis (constant t). We

Space time diagram tutorial
Interactive Minkowski diagram / spacetime diagram The two events may also be shown in "real time" by pressing the buttons " Play worldline t" or " Play worldline t'". The two events will then appear in space and time (given time unit = 1 second). Below the animation is a more detailed tutorial and some examples and excercises. Space-Time Diagrams A space-time diagram is nothing more than a graph showing the position of objects as a function of time. The usual convention is that time runs up the diagram, so the bottom is the past, or early times, and the top is the future, or late times. A point on this graph describes both a position (the horizontal or x coordinate) and a time (the ... PDF Spacetime Diagrams and Einstein's Theory For Dummies 1. In this diagram, which events (out of A, B, C and D) occur at the same time? Which events occur at the same place? 2. One division of the space axis corresponds to 1 meter. Construct a world line of the particle that is resting at 2 m from the reference event. time space A D B C O. time space
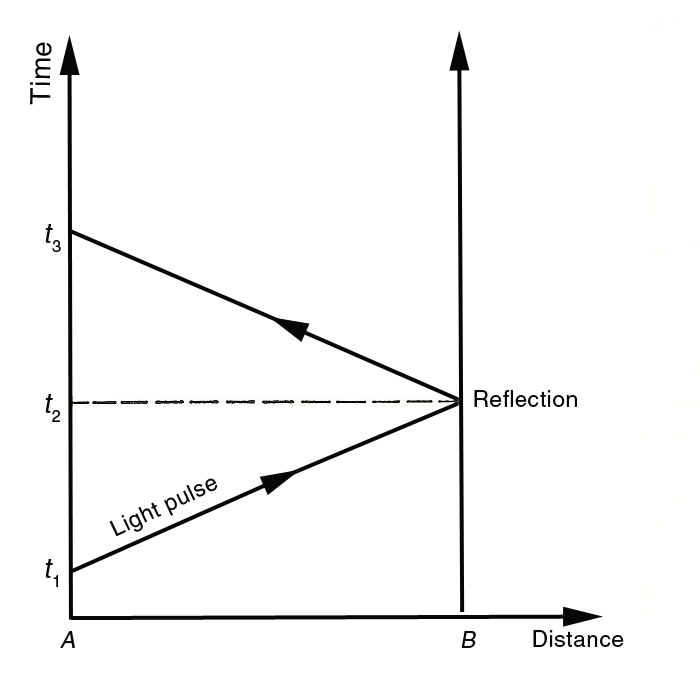
Space time diagram tutorial. Minkowski spacetime - Simple English Wikipedia, the free ... In special relativity, the Minkowski spacetime is a four-dimensional manifold, created by Hermann Minkowski. It has four dimensions: three dimensions of space (x, y, z) and one dimension of time. Minkowski spacetime has a metric signature of (-+++), and describes a flat surface when no mass is present. Learn About Spacetime Diagrams of Light Clocks | Physics ... We demonstrate a method for constructing spacetime diagrams for special relativity on graph paper that has been rotated by 45 degrees. Many quantitative results can be read off a spacetime diagram simply by counting boxes, with very little algebra—I like to describe this as a method for doing "visual calculations" in relativity. Cosmology Tutorial - Part 3 The conformal space-time diagram is a good tool use for describing the meaning of CMB anisotropy observations. The Universe was opaque before protons and electrons combined to form hydrogen atoms when the temperature fell to about 3,000 K at a redshift of 1+z = 1090. After this time the photons of the CMB have traveled freely through the PDF Drawing a spacetime diagram - Cockcroft { A point on the spacetime diagram is called an event. This is a point in space at a speci c moment in time. { The vertical value of this event is the time as measured by observer 1. { The horizontal value event is the position of the event as measured by observer 1. { Take a line from the event, parallel to the space axis of observer 2.
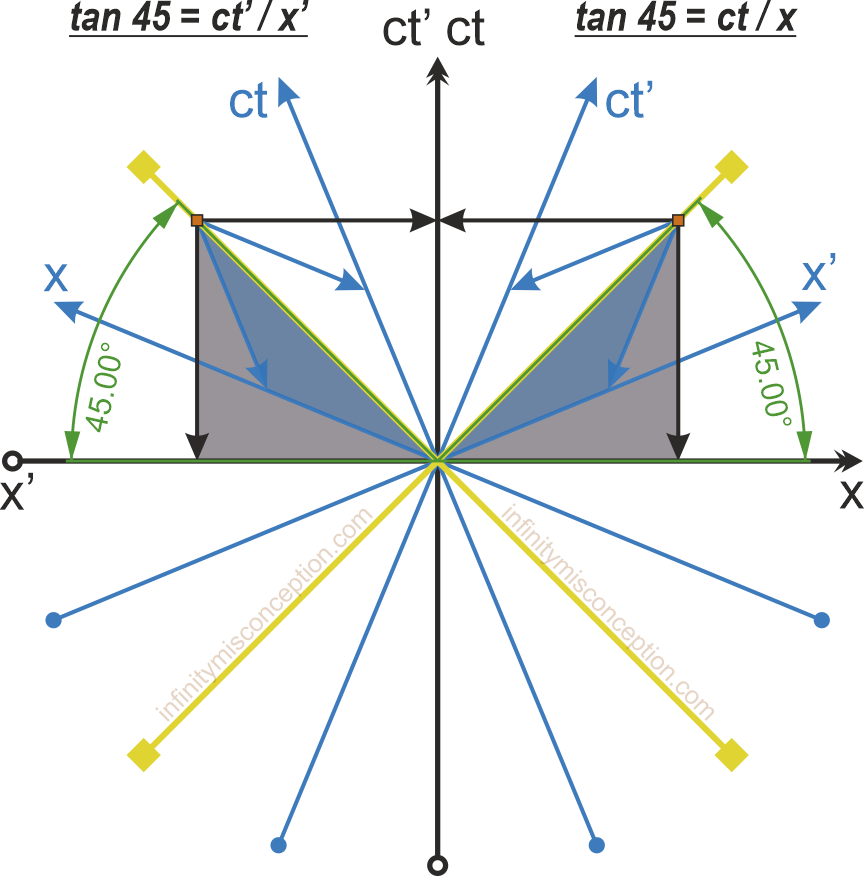
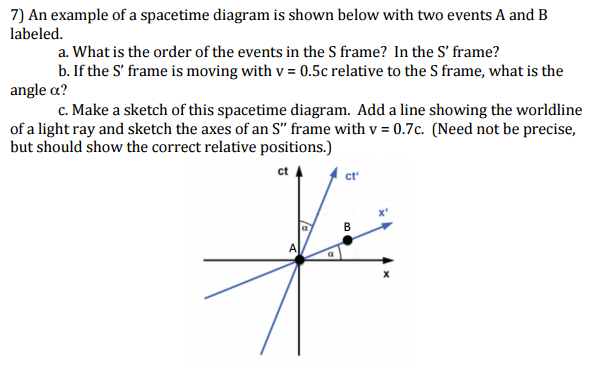
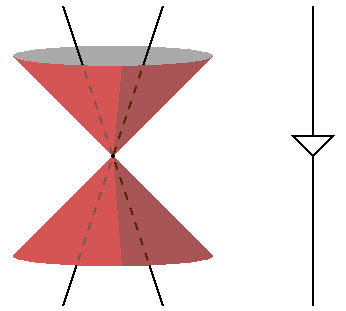
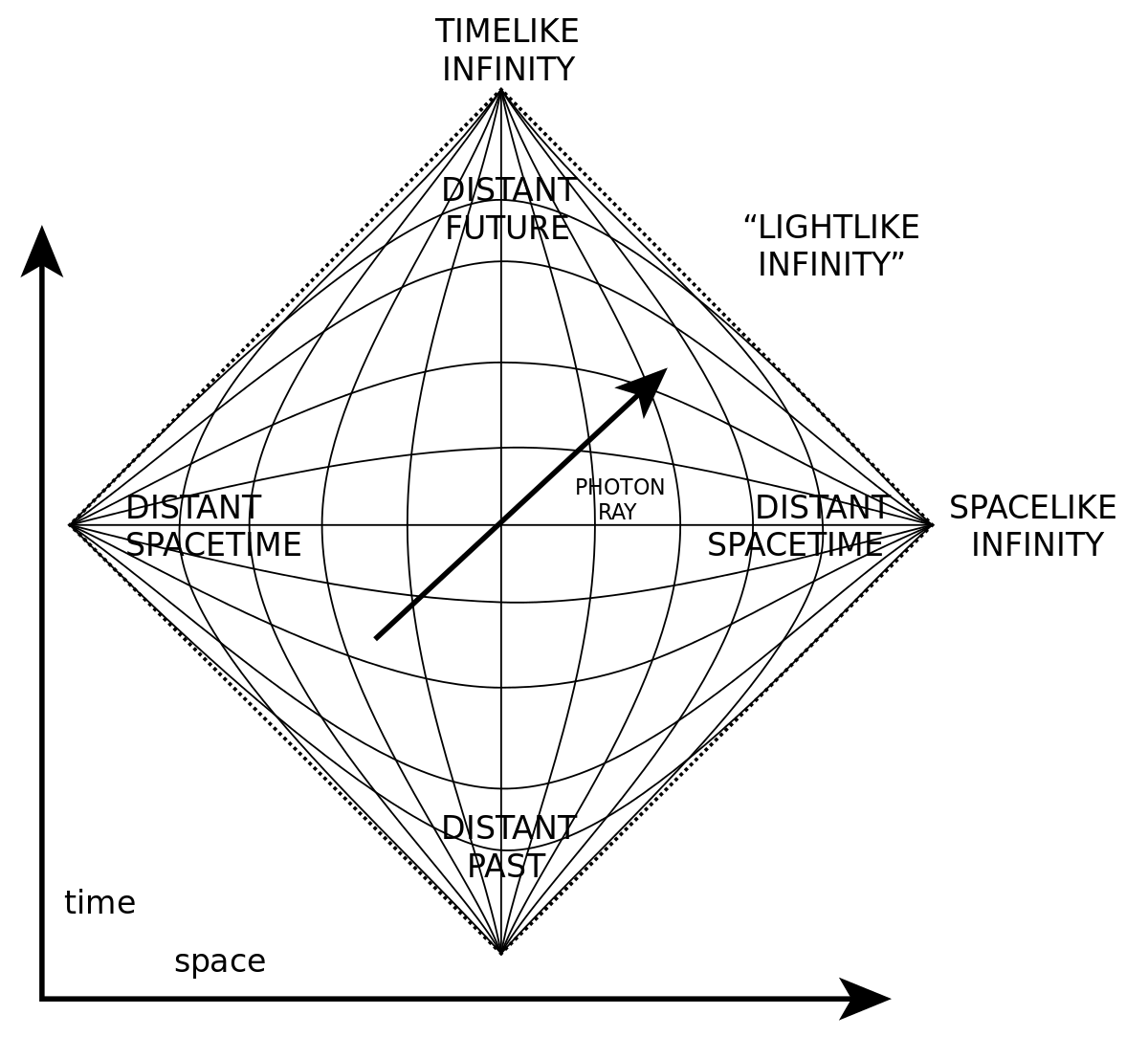
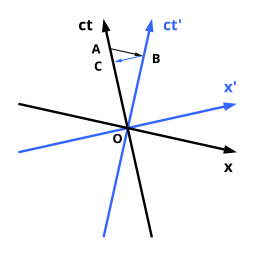
Spacetime Diagram - Wolfram Demonstrations Project Mar 07, 2011 · A spacetime diagram (or Minkowski diagram) is a combination of two coordinate systems: one in which an observer is at rest relative to certain events, and another for an observer in relative motion to the first. In such a diagram, light rays always follow paths with a 45° slope. The time of an event is indicated by its intersection with the appropriate time axis. Relativity Tutorial - University of California, Los Angeles Because the speed of light is special, space-time diagrams are often drawn in units of seconds and light-seconds, or years and light-years, so a unit slope [45 degree angle] corresponds to the speed of light. The set of all light speed world lines going through an event defines the light conesof that event: the past light cone Special Relativity Practice Problem 13 - Virginia Tech on the space-time diagram. Assume that the planet is not moving relative to the star. The Enterprise will fly by at a constant velocity past the planet and beam up the students without stopping. The star goes supernova at space-time point S. supernova spreads out in both directions along the trajectories shown. Answer the following questions: PDF Minkowski Diagrams and Lorentz Transformations Figure 7: Diagram for showing time dilation for events located at a fixed point in frame S. Now we want to show that the measurement of time intervals in the S frame are not the same as those in the S0frame using Minkowski diagrams. In Figure 7 we mark two events, A and B, located at the same point in space but different points in time, in the ...
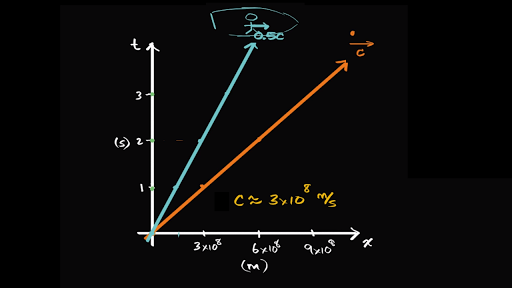
Introduction to special relativity and Minkowski spacetime ... So after one second, she would be here, after two seconds, she would be there, and we set up our scales so that on our time axis, one second is the same length as on our space axis, or on our path axis, three times ten to the eighth meters. Special Relativity: 2 - Spacetime Diagrams - YouTube An introduction to spacetime diagrams which are a valuable tool used to understand special relativity. The second in a series on special and general relativ... 2.1: Spacetime Diagrams - Physics LibreTexts Dec 24, 2020 — What is more, these diagrams give both axes the same units by scaling the vertical axis by the speed of light, c. The resulting representation ... Spacetime diagram - Wikipedia Minkowski diagrams are two-dimensional graphs that depict events as happening in a universe consisting of one space dimension and one time dimension. Unlike a ...
Minkowski Diagrams One frequently used method of visualizing spacetime is the Minkowski Diagram. Such diagrams are a subset of the general spacetime diagrams presented earlier. The defining feature of a Minkowski diagram is that light rays are drawn at a 45 degree angle to the line or plane respresenting space. This means that if the time axis
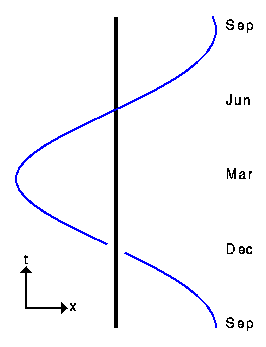
Minkowski's Four-Dimensional Space-Time In this spacetime, we can observe that the events siuated at distance +1 of the the origin lie all either on the upper hyperbola (t positive) or either all on the lower hyperbola ( t negative), which marks a real progress compared to our galilean circle. Language Breadcrumbs You are here: Home Special Relativity
How Create Space Time Cube works—ArcGIS Pro - Esri There are three tools that create a space-time cube for analysis: Create Space Time Cube By Aggregating Points, Create Space time Cube From Defined Locations, and Create Space Time Cube From Multidimensional Raster Layer.
PDF dSPACE and Real-Time Interface in Simulink This document provides a tutorial introduction to the dSPACE software (ControlDesk Next Generation version 4.2.1), the dSPACE DS1104 R&D controller board, and their use in development and implementation of maximum power point tracking (MPPT) for a single photovoltaic (PV) module using extremum seeking (ES) in Simulink software.
PDF Spacetime Diagrams and Einstein's Theory For Dummies 1. In this diagram, which events (out of A, B, C and D) occur at the same time? Which events occur at the same place? 2. One division of the space axis corresponds to 1 meter. Construct a world line of the particle that is resting at 2 m from the reference event. time space A D B C O. time space
Space-Time Diagrams A space-time diagram is nothing more than a graph showing the position of objects as a function of time. The usual convention is that time runs up the diagram, so the bottom is the past, or early times, and the top is the future, or late times. A point on this graph describes both a position (the horizontal or x coordinate) and a time (the ...
Interactive Minkowski diagram / spacetime diagram The two events may also be shown in "real time" by pressing the buttons " Play worldline t" or " Play worldline t'". The two events will then appear in space and time (given time unit = 1 second). Below the animation is a more detailed tutorial and some examples and excercises.


















0 Response to "40 space time diagram tutorial"
Post a Comment