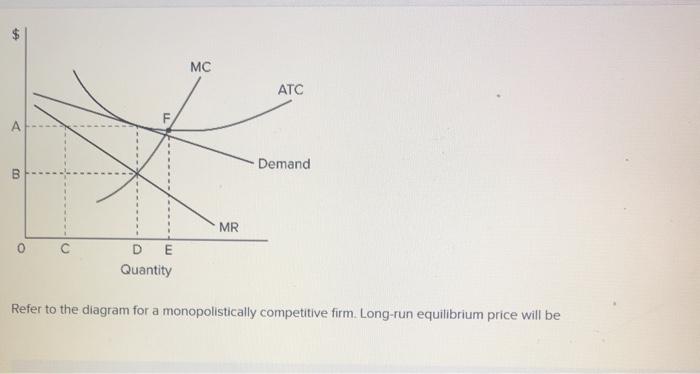
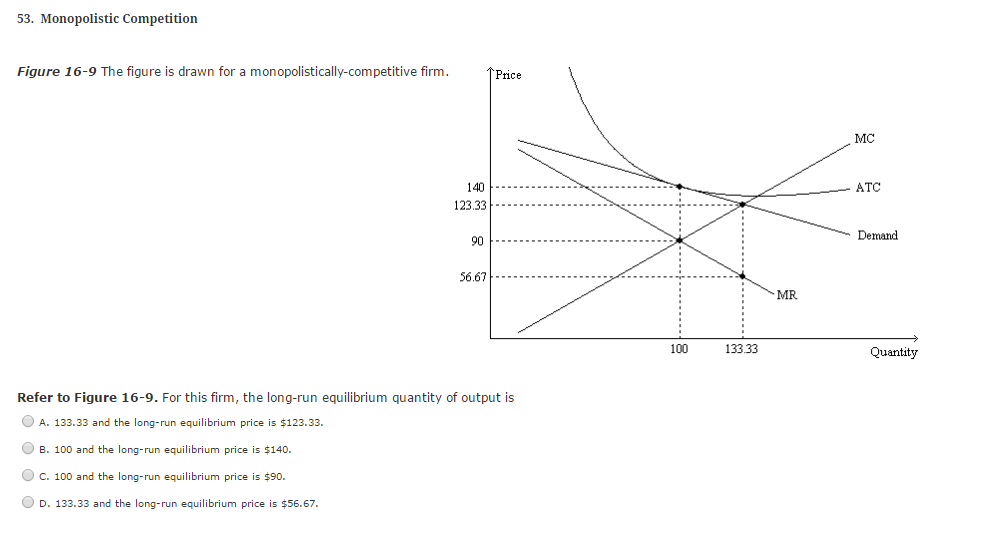
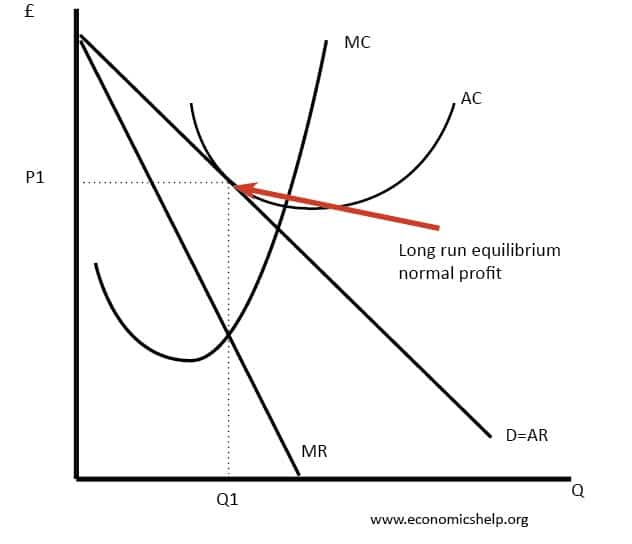
41 refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. long-run equilibrium price will be
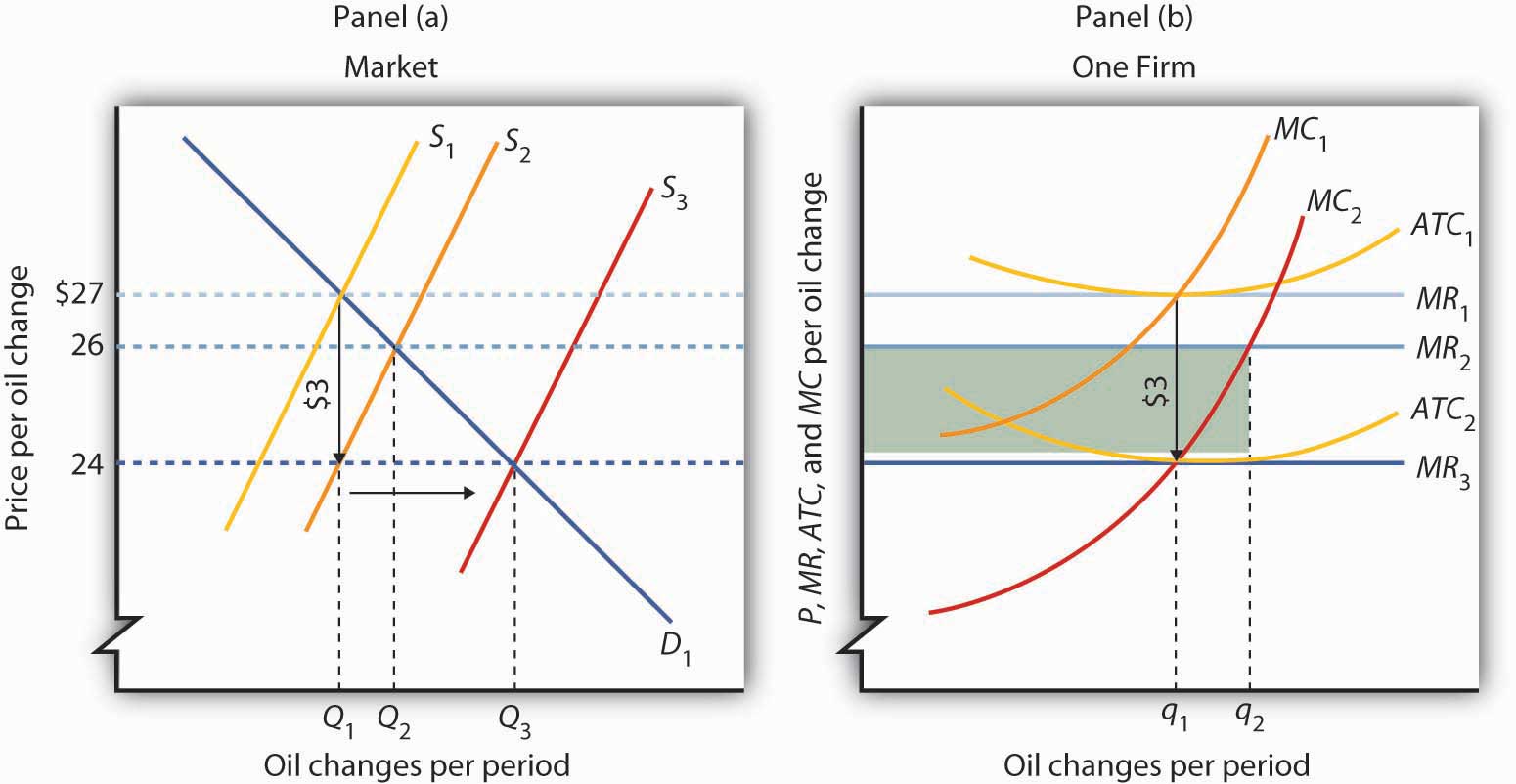
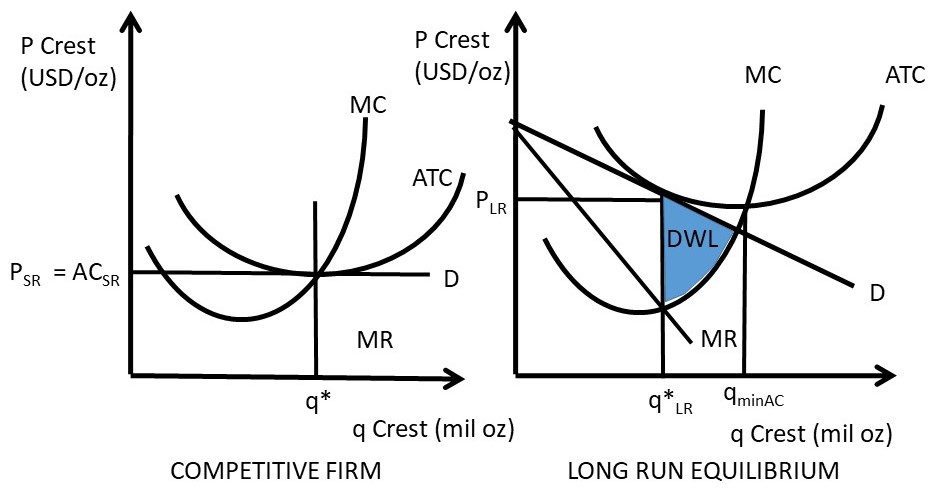
40 refer to the diagram. by producing at output level q ... PDF AP Unit 6 60. Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At output Q production will be unprofitable. True False 61. Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. The profit-maximizing price for this firm is J. True False 62. Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. Short-run and long-run equilibrium (Monopolistic ... Long-run equilibrium. Since producers are profit maximizers, they will produce the quantity where MC=MR (same procedure as for the short-run equilibrium). In a monopolistically competitive market there are low barriers to entry so it is easy for other firms to come in and steal economic profit from the firms currently in the market.
Answered: Draw a diagram of the long-run ... - bartleby Q: Monopolies can maintain economic profits in the short and long run because of barriers to entry whic... A: 1. Monopolistic competition is a market structure where large number of sellers exists to produce di...
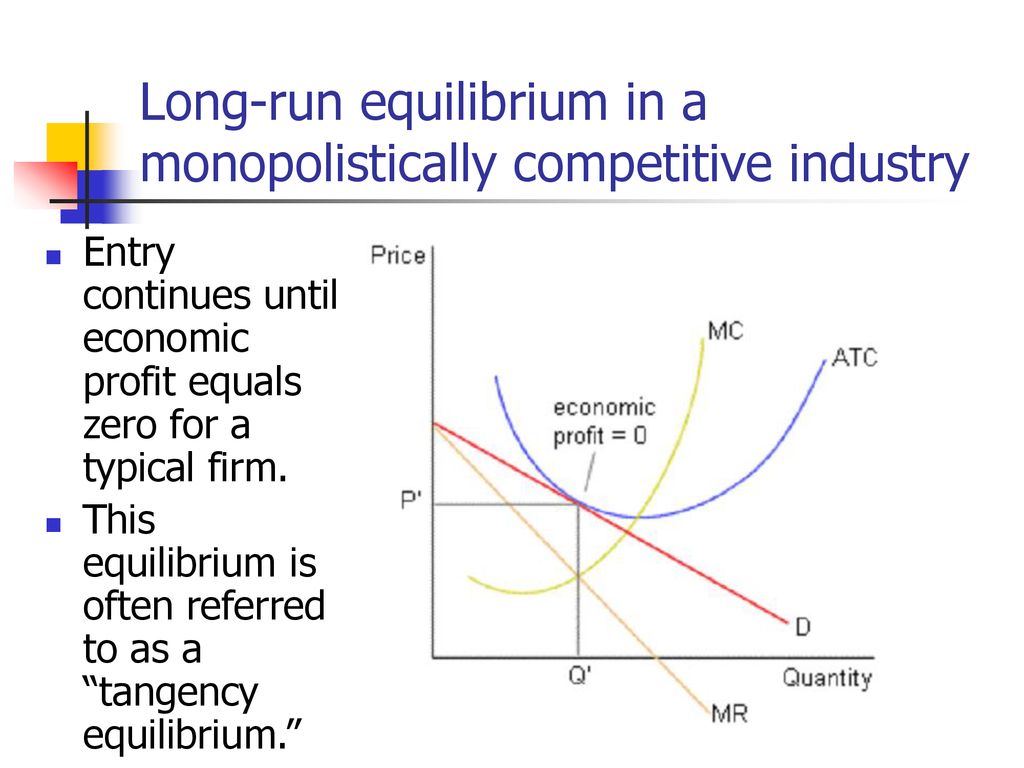
Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. long-run equilibrium price will be
8.4 Monopolistic Competition - Principles of Microeconomics In the long run, what price will this firm charge for its output? a) $10. b) A price less than $10 and greater than $6. c) $6. d) A price less than $6 and greater than $4. The following TWO questions refer to the diagram below. 3. Which of the four diagrams illustrates a long run equilibrium for a monopolistically competitive firm? a) Figure 1 ... 44 Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive ... Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive producer. The firm is - realizing a normal profit in the long run. 45. This industry shown in this table illustrates Firm Market Share (%) A 40 B 30 C 20 D 5 E 5 - Oligopoly. 46. If the industry depicted in this graph were purely competitive, then the market price would be - $25, which is ... Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive ... Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm will realize an economic: asked Aug 17, 2018 in Economics by Commodore64
Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. long-run equilibrium price will be. PDF ECO 211 Microeconomics Yellow Pages ANSWERS Unit 3 2. the equilibrium position of a competitive firm in the long run. 3. a competitive firm that is realizing an economic profit. 4. the loss-minimizing position of a competitive firm in the short run. 9. Refer to the above diagram. If this competitive firm produces output Q, it will: 1. suffer an economic loss. 2. earn a normal profit. In long-run equilibrium, a monopolistically competitive ... In long-run equilibrium, both purely competitive and monopolistically competitive firms will Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive producer. the firm is Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive producer. this firm is experiencing PDF Chap 13 Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly MULTIPLE ... 40)In the long run, a firm in a monopolistically competitive industry produces where its marginal cost A)equals its price. B)is less than its average cost. C)equals its average cost. D)exceeds its average cost. 40) 41)In the long run, a firm in monopolistic competition produces where the slope of the average total cost curve is A)zero. Solved > 11) Long-run equilibrium under monopolistic ... 11) Long-run equilibrium under monopolistic competition and perfect competition similar : 1926971. 11) Long-run equilibrium under monopolistic competition and perfect competition is similar in that. A) firms produce at the minimum point of their average cost curves. B) price equals marginal cost. C) firms break even.
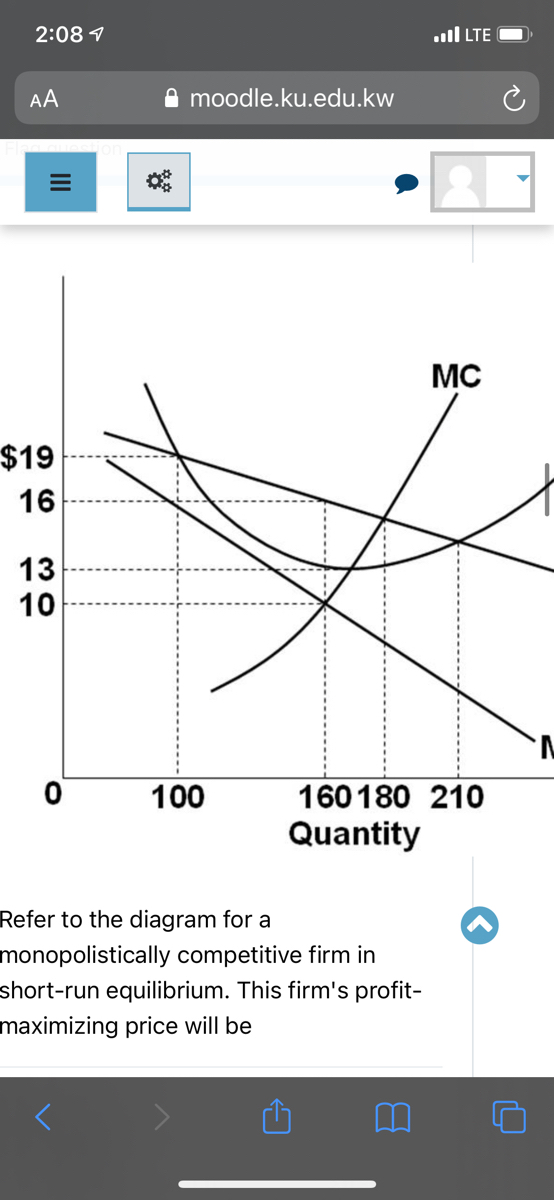
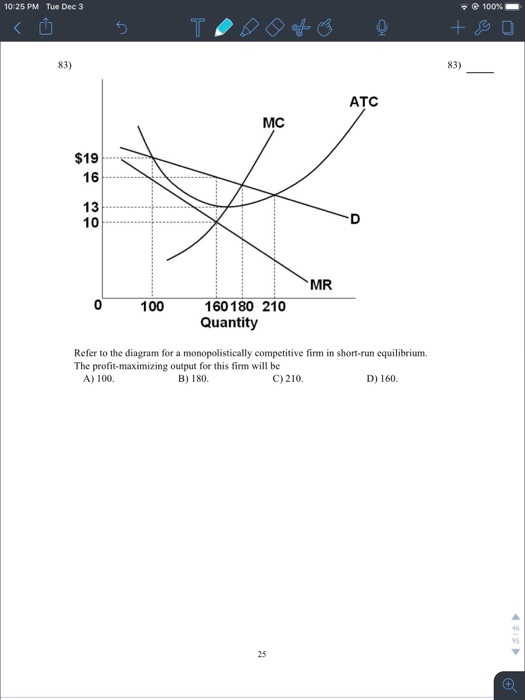
PDF Unit IV: Imperfect Competition Unit Examination C) differential between price and marginal costs which characterizes monopolistically competitive firms. D) fact that most monopolistically competitive firms encounter diseconomies of scale. E) fact that firms produce more than the socially optimal output 9. When a monopolistically competitive firm is in long-run equilibrium: Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive ... Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. The profit-maximizing output for this firm will be: A. 100. B. 160. C. 180. D. 210. 27. When a monopolistically competitive firm is in long-run equilibrium: A. production takes place where ATC is minimized. B. marginal revenue equals marginal cost and price ... Micro Chapter 25 Flashcards - Quizlet A) equilibrium output would rise and equilibrium price would fall. B) the demand curve would become more elastic. C) equilibrium output would decline and equilibrium price would rise. D) none of these above. B. Refer to the diagram below for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly Multiple Choice ... 35. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm's profit-maximizing price will be: A) $10. B) $13. C) $16. D) $19. Ans: 36. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. The profit-maximizing output for this firm will be: A) 210. B) 180 ...
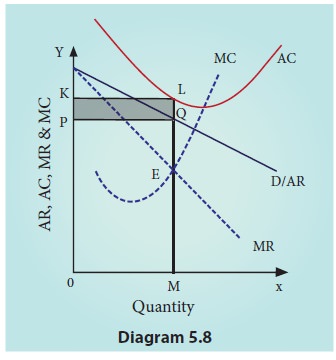
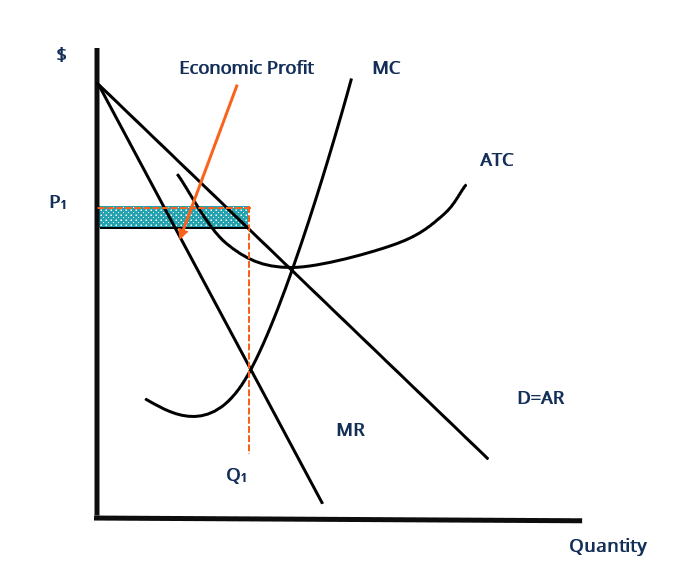
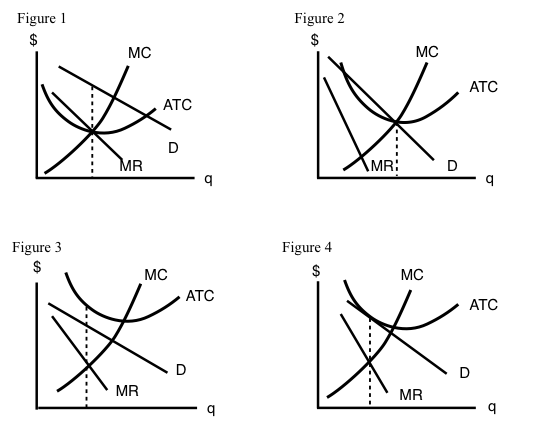
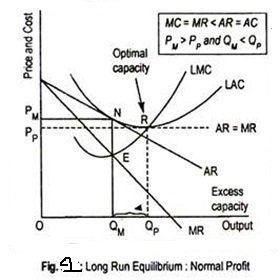
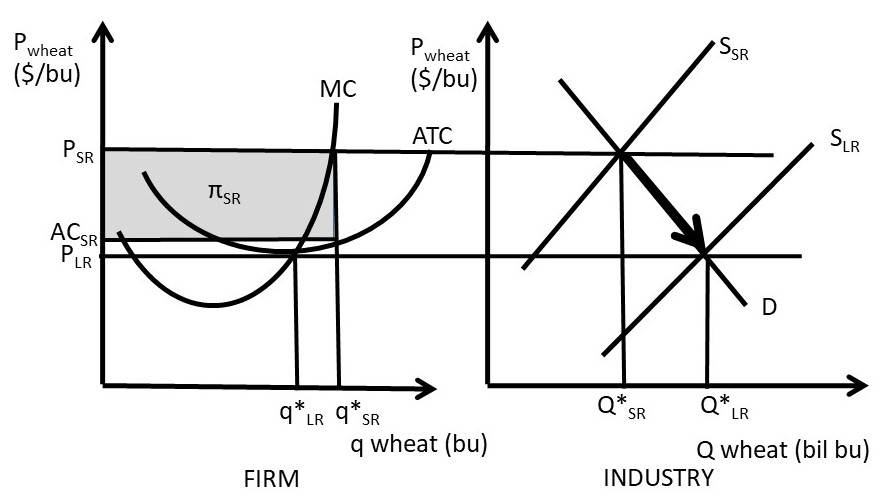
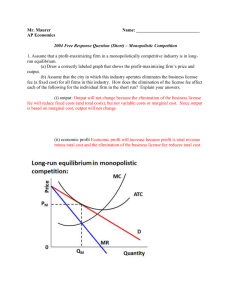
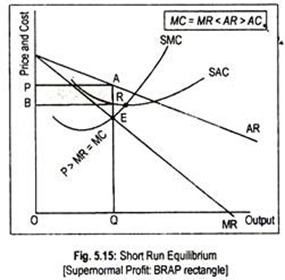
When a monopolistically competitive firm is in long-run ... A monopolistically competitive firm in a long-run equilibrium produces where Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium Both monopolistically competitive firms and perfectly competitive firms maximize profits Monopolistic Competition in the Long-run The monopolistically competitive firm's long‐run equilibrium situation is illustrated in Figure .. The entry of new firms leads to an increase in the supply of differentiated products, which causes the firm's market demand curve to shift to the left. As entry into the market increases, the firm's demand curve will continue shifting to the left until it is just tangent to the average total ... Chapter 13 Study Set - Subjecto.com In the long run, economic theory predicts that a monopolistically competitive firm will: micro econ Ch. 13 - Subjecto.com Monopolistically competitive firms: may realize either profits or losses in the short run but realize normal profits in the long run. Refer to the diagrams, which pertain to monopolistically competitive firms. Short-run equilibrium entailing economic loss is shown by: diagram c only. Solved > 31) Refer to Figure 11-2. Diagram C depicts ... C) a monopolistically competitive industry. D) an oligopolistic industry. E) None of the above - it is not a long-run equilibrium. 33) Refer to Figure 11-2. The position of a typical firm when the industry is in long -run equilibrium with free entry and exit and product differentiation is exhibited in diagram A) A. B) B. C) C. D) D. 34) In long ... Refer To The Diagram For A Monopolistically Competitive ... Purely competitive firms monopolistically competitive firms and pure monopolies all earn zero economic profits in the long run. 1refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. Let us learn about the short run and long run equilibrium of a firm under monopolistic competition. 4both diagrams b and c. 3refer to the diagram above. Solved 1.Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically ... 1.Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. Long-run equilibrium output will be: a. b. d. 2.Refer to the diagram. In short-run equilibrium, the monopolistically competitive firm shown will set its price: a. below ATC. 10.1 Monopolistic Competition - Principles of Economics If the firms in a monopolistically competitive industry are suffering economic losses, then the industry will experience exit of firms until economic profits are driven up to zero in the long run. A monopolistically competitive firm is not productively efficient because it does not produce at the minimum of its average cost curve. Answered: Refer to the diagrams, which pertain to… | bartleby Business Economics Q&A Library Refer to the diagrams, which pertain to monopolistically competitive firms. Long-run equilibrium is shown by diagram b only. diagram a only. none of these diagrams. diagram c only. Refer to the diagrams, which pertain to monopolistically competitive firms. Section 2: Short-Run and Long-Run Profit Maximization for ... Long-Run Equilibrium. In the long run, a monopolistically competitive firm earns zero economic profits. A firm looks at its cost of production and then marks up its price to obtain a reasonable profit. If firm A marks up its price too much, competing firm B will take advantage of it by charging a lower price. revmncmp Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm's profit-maximizing price will be: A. $10. B. $13. C. $16. D. $19. 5. R-1 F25030 ... In long-run equilibrium a monopolistically competitive firm will: A. earn an economic profit. ... Equilibrium of a Firm under Monopolistic Competition Long run equilibrium is achieved at point E where LMC equals MR (Fig. 5.16). The equilibrium output thus determined is OQ M. At this output, AR equals AC. The firm gets normal profit by selling OQ M output at the price OP M. Note that a monopolistically competitive firm always operates somewhere to the left of the minimum point of its AC curve. Pricing in Theory (With Diagram) - Economics Discussion (6) Under perfect competition the firm in the long run makes only normal profits but under monopoly the firm can get super-normal profits even in the long run. (7) Since, even in the long run, the monopolist's demand curve remains downward sloping, it cannot be tangent to average cost curve at AC min . DOCX Livingston Public Schools / LPS Homepage 56.When a monopolistically competitive firm is in long-run equilibrium: A)production takes place where ATC is minimized. B)marginal revenue equals marginal cost and price equals average total cost. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive ... Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm will realize an economic: asked Aug 17, 2018 in Economics by Commodore64 44 Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive ... Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive producer. The firm is - realizing a normal profit in the long run. 45. This industry shown in this table illustrates Firm Market Share (%) A 40 B 30 C 20 D 5 E 5 - Oligopoly. 46. If the industry depicted in this graph were purely competitive, then the market price would be - $25, which is ... 8.4 Monopolistic Competition - Principles of Microeconomics In the long run, what price will this firm charge for its output? a) $10. b) A price less than $10 and greater than $6. c) $6. d) A price less than $6 and greater than $4. The following TWO questions refer to the diagram below. 3. Which of the four diagrams illustrates a long run equilibrium for a monopolistically competitive firm? a) Figure 1 ...
![Solved] The Diagram Below Shows Demand and Cost Curves for a ...](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5441/11ea71cb_f380_68da_91e5_a7c4098536ab_TB5441_00_TB5441_00_TB5441_00_TB5441_00_TB5441_00_TB5441_00.jpg)
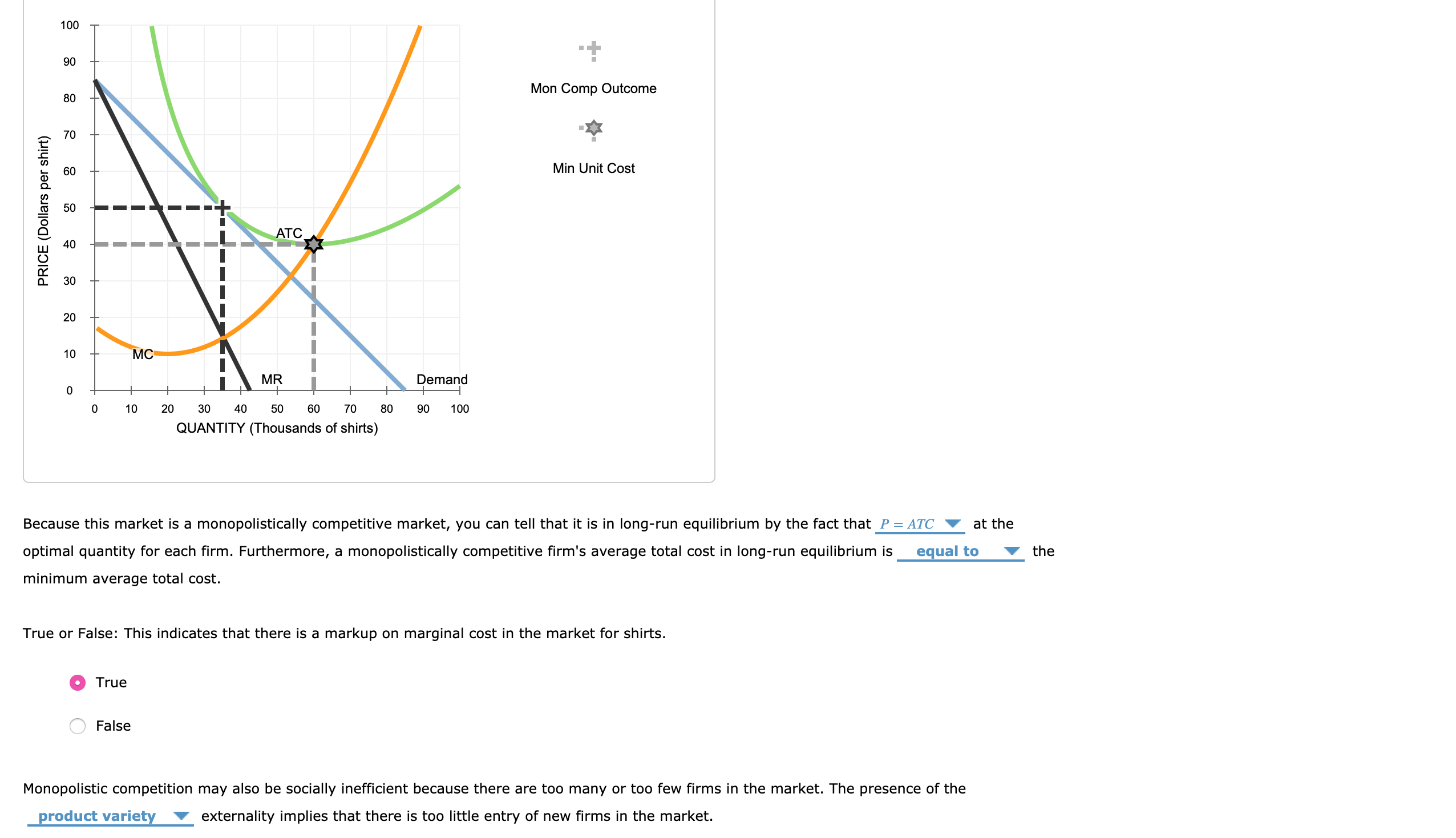
















0 Response to "41 refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. long-run equilibrium price will be"
Post a Comment