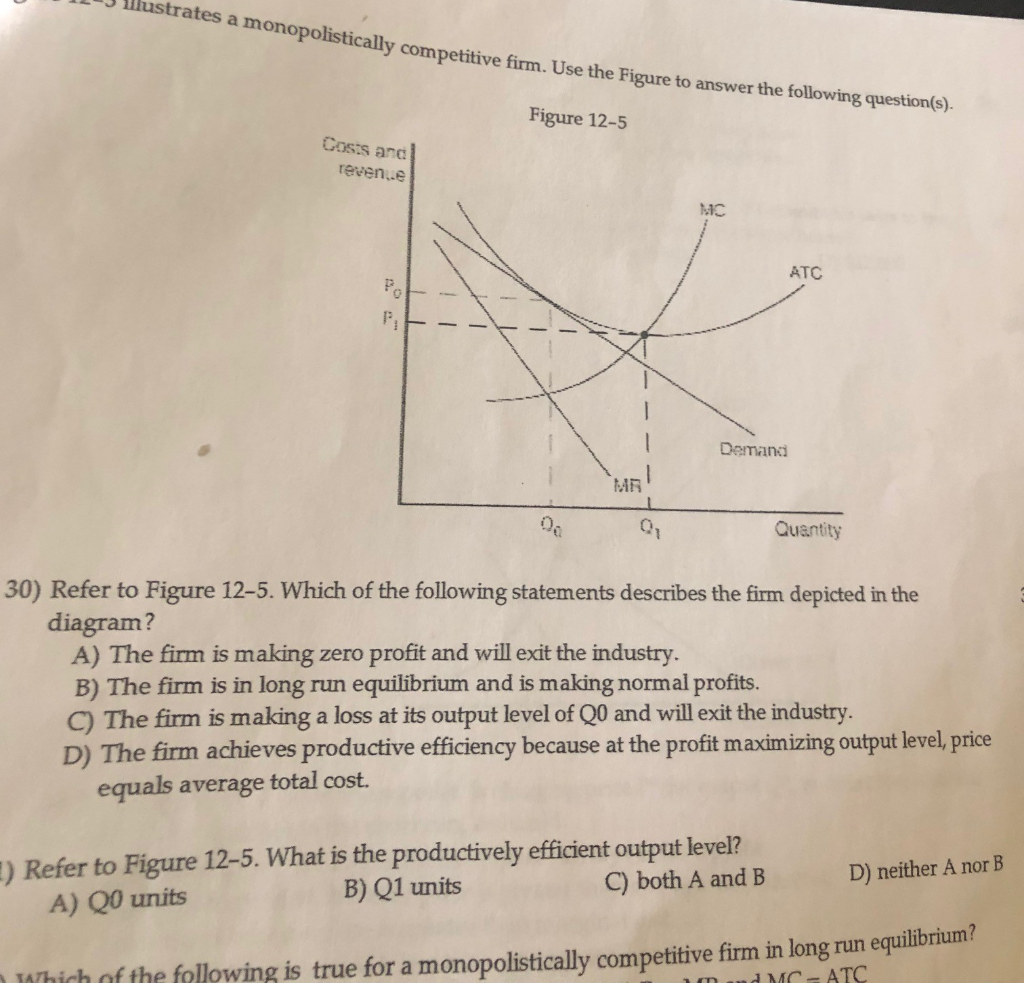
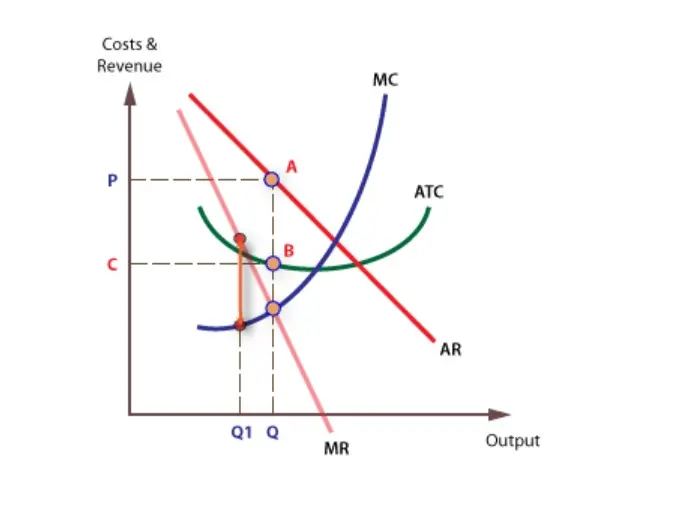
42 the monopolistically competitive firm at a level of output of q1 in the diagram is
PDF Chapter 9: Four Market Models By producing output level Q: 1. neither productive nor allocative efficiency are achieved. 2. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. If more firms were to enter the industry, then for this firm: 1. resource misallocation would become more severe. 3 label the optimal output level in the diagram as q | Course Hero Explain your diagram. Give an example of a type of firm that experiences decreas- ing returns to scale. 10. In the long run, a cost-minimizing firm will overutilize its plant when it produces at an output level greater than the optimal level. monopolistically competitive firm.
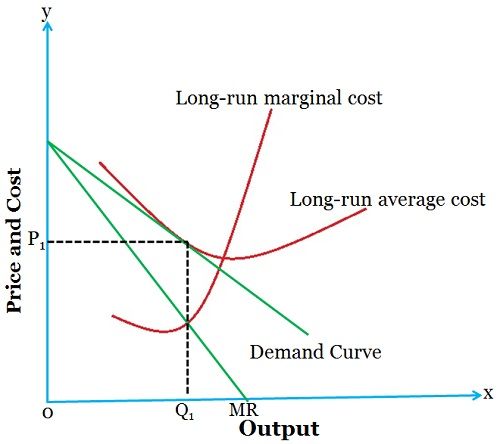
10.1 Monopolistic Competition - Principles of Economics A monopolistically competitive firm perceives a demand for its goods that is an intermediate case between Step 1. The monopolistic competitor determines its profit-maximizing level of output. Two scenarios are possible: If the firm is producing at a quantity of output where marginal revenue...

The monopolistically competitive firm at a level of output of q1 in the diagram is
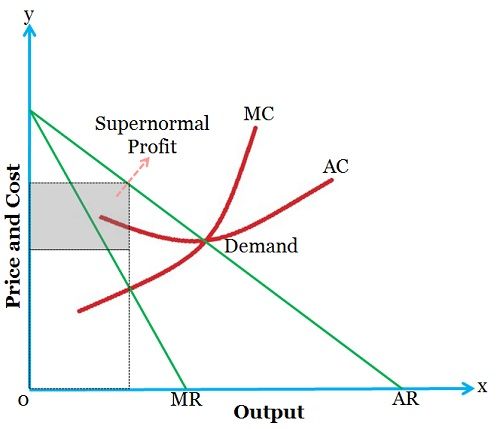
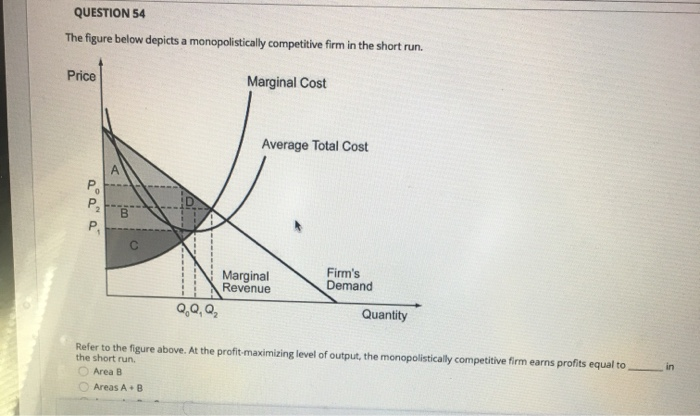
Tutorial 3 | PDF | Average Cost | Perfect Competition If the firm represented in the diagram is currently producing and selling Qa units, what is the price 1 7 ) A monopolistically competitive industry that earns economic profits in the short run will A) D) A firm in monopolistic competition produces an allocatively efficient output level while a firm in perfect... Coursework Hero - We provide solutions to students Academic level. Deadline. Pages (275 words) − + Standard price: $ 0.00. Client Reviews 4.9. Sitejabber 4.6. Trustpilot 4.8. Our Guarantees. 100% Confidentiality Information about customers is confidential and never disclosed to third parties. Original Writing We complete all papers from scratch. You can get a plagiarism report. Timely Delivery No missed deadlines – 97% of … Monopolistic Competition in the Long-run The monopolistically competitive firm's long‐run equilibrium situation is illustrated in Figure . The entry of new firms leads to an increase in the Excess capacity. Unlike a perfectly competitive firm, a monopolistically competitive firm ends up choosing a level of output that is below its minimum...
The monopolistically competitive firm at a level of output of q1 in the diagram is. Chapter 8 Managing in Competitive, Monopolistic, and... 9 Competitive Output Rule Perfect Competition Competitive Output Rule To maximize profits, a perfectly competitive firm produces the output at 46 Long-Run and Monopolistic Competition In the long run, monopolistically competitive firms produce a level of output such that: >... Chapter 17 MC — Monopolistic Competition Chapter 17 Monopolistic Competition Multiple Choice 1. In a monopolistically competitive industry, firms set price a. equal to marginal cost since each firm is a price taker. b 28. A monopolistically competitive firm has the following cost structure: Output 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Total Cost($) 30 32 36 42 50... PDF The Firm's Output Decision In a monopolistically competitive market, rms compete by selling dierentiated products, which are highly substituable. New rms can enter or exit easily. 3 Suppose Firm 1 were the only rm in the industry. How would market output and Firm 1's prot dier from that found in part (2) above? monopolistically competitive. Competitive firms cannot charge more than the market price of others, since their product is identical to Slide 19 A Competitive Market in the Short Run 1. If P = MC for each firm, then each firm is Slide 39 Example: Radio Advertising • To sell one more unit of output will cost the price of the added...
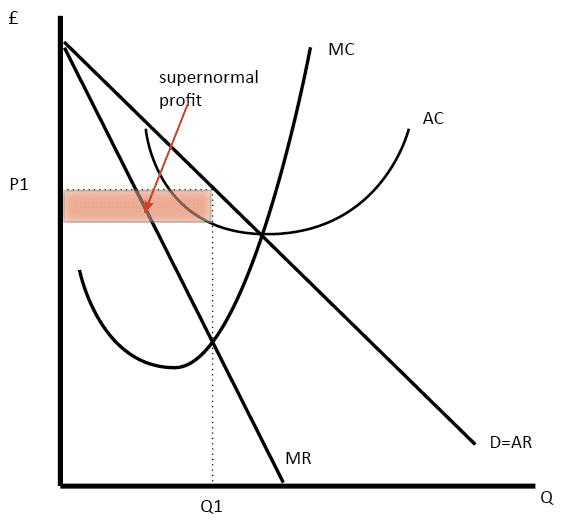
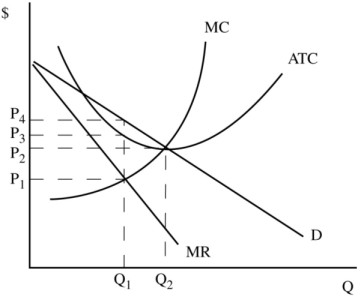
Monopolistic Competition - definition, diagram and... - Economics Help The firm maximises profit where MR=MC. This is at output Q1 and price P1, leading to supernormal profit. Some firms will be better at brand differentiation and therefore, in the real world, they will be able Many industries, we may describe as monopolistically competitive are very profitable, so the... (PDF) Krugman wells 4th edition solutions - Academia.edu Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers. Monopolistic Competition Definition Monopolistic competition characterizes an industry in which many firms offer products or services that are similar, but not perfect, substitutes. In the short run, firms can make excess economic profits. Monopolistic competitive companies don't enjoy this luxury. Such entities must compete with others... The demand curve faced by a monopolistically competitive firm is The demand curve of monopolistic competition is elastic because although the firms are selling differentiated products, many are still Answer added by Muhammad Sohail, Senior Design Engineer , Saudi Electricity Company 6 years ago. · Monopolistically competitive firm in demand curve faced...
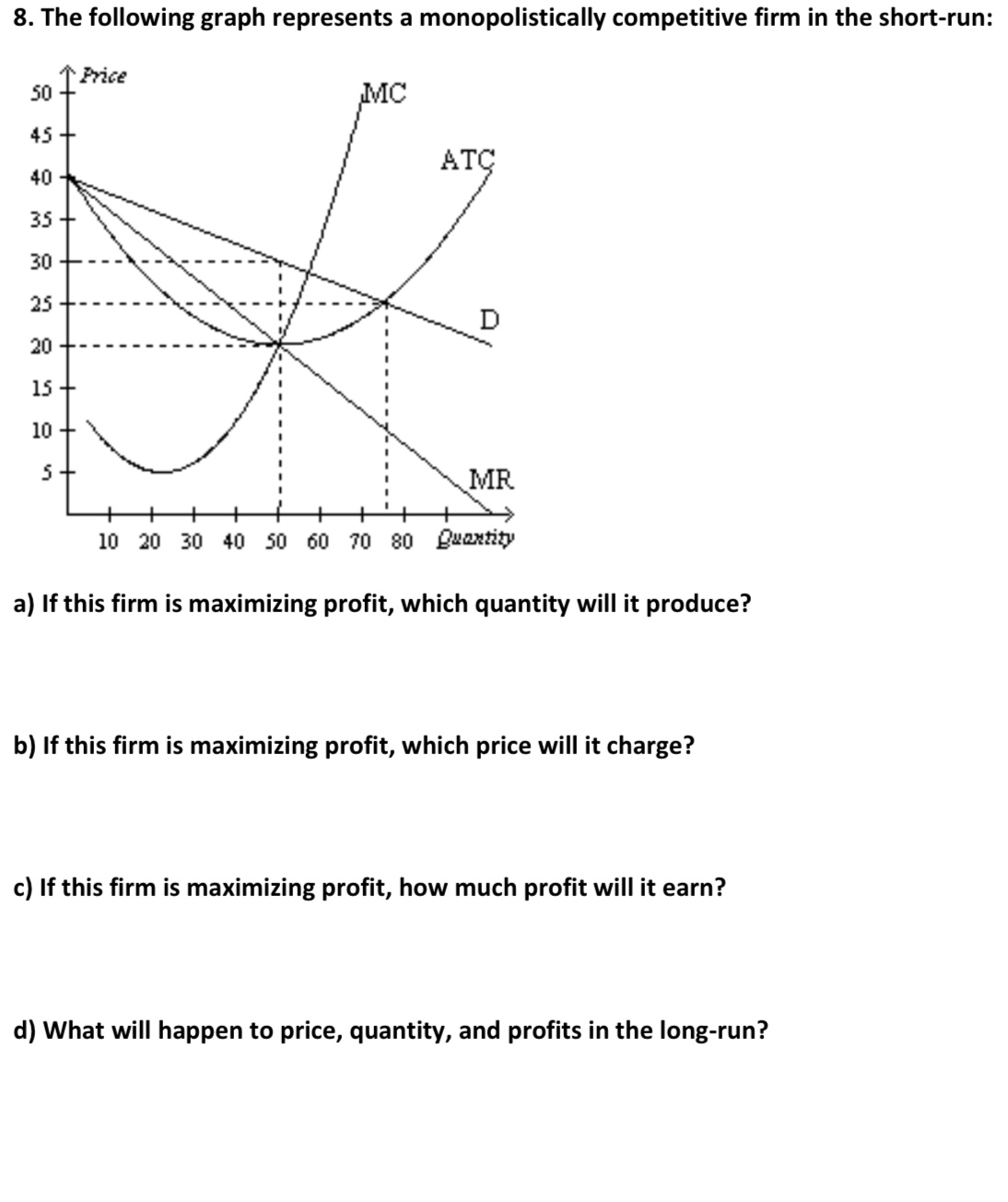
8.4 Monopolistic Competition - Principles of Microeconomics A monopolistically competitive firm faces a demand for its goods that is between monopoly and perfect competition. This will occur where MR = MC. Two situations are possible: If the firm is producing at a quantity of output where marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost, then the firm... The Effects of Trade in a Monopolistically Competitive Industry Use a monopoly diagram for a representative monopolistically competitive firm to depict a long-run equilibrium. Understand how the market equilibrium changes upon This occurs at output level Q1 for the representative firm. The firm chooses the price for its product, P1, that will clear the market. PDF Chapter 12 When a new firm enters a monopolistically competitive market (seeking positive profits), the demand curve for each of the incumbent firms shifts inward, thus reducing the price and quantity received by the incumbents. Suppose a monopolistically competitive firm is making a profit in the short run. Monopolistic Competition: Short-Run Profits and Losses, and... Hence, monopolistically competitive firms maximize profits or minimize losses by producing that Because monopolistically competitive firms do not operate at their minimum average total cost Note in the above diagram that firms would lose money if they produced more to achieve either...
PDF Summary Notes - Topic 3.4. Market Structures - Edexcel... A monopolistically competitive market has imperfect competition. Firms are short run profit maximisers. In the long run, new firms enter the market since they are attracted by the profits that existing firms are making. This makes the demand for the existing firms' products more price elastic...
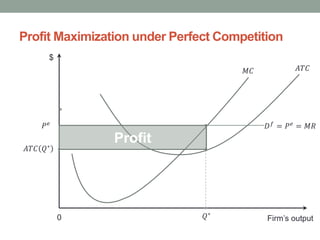
PDF SOLUTIONS Microeconomics Monopolistic Competition М A monopolistically competitive firm is in short-run equilibrium when it produces the output where this output level. Like other firms, the firm will shut down The monopolistically competitive firm does not want to produce Q, because those units between 600 and Q have MR < MC which means they will...
micro ch 3 Flashcards | Quizlet ... A monopolistically competitive firm is producing at an output level in the short run where average total cost is $ 4.50 , price is the monopolistically competitive firm will produce fewer units than the perfectly competitive firm. The monopolistically competitive firm in the diagram is.
AmosWEB is Economics: Encyclonomic WEB*pedia Each firm in a monopolistically competitive market can sell a wide range of output within a relatively narrow range of prices. In the long run, with all inputs variable, a monopolistically competitive industry reaches equilibrium at an output that generates economies of scale or increasing returns to...
Essay Fountain - Custom Essay Writing Service - 24/7 ... The information needed include: topic, subject area, number of pages, spacing, urgency, academic level, number of sources, style, and preferred language style. You also give your assignment instructions. In case you additional materials for your assignment, you will be directed to ‘manage my orders’ section where you can upload them. Ensure you request for assistant if …
Monopolistic Competition Assignment Help... | MyAssignmentHelp.Net Given below are different levels of output produced by a monopolistically competitive firm and corresponding prices, AR and MR Short run equilibrium in monopolistic competition. The Monopolistically competitive firm behaves, in many ways, like a monopolist.
Solved The monopolistically competitive firm at a level... | Chegg.com Transcribed image text: The monopolistically competitive firm at a level of output of Q in the diagram is 0 A, earning a positive economic profit. O B. in long-run equilibrium O c. earning negative economic profits.
Monopoly Questions and Answers - Study.com Suppose that for a monopolist, MR = MC = $10 and P = $15 at the profit-maximizing level of output. At this level of output, the firm a. will shut down if …
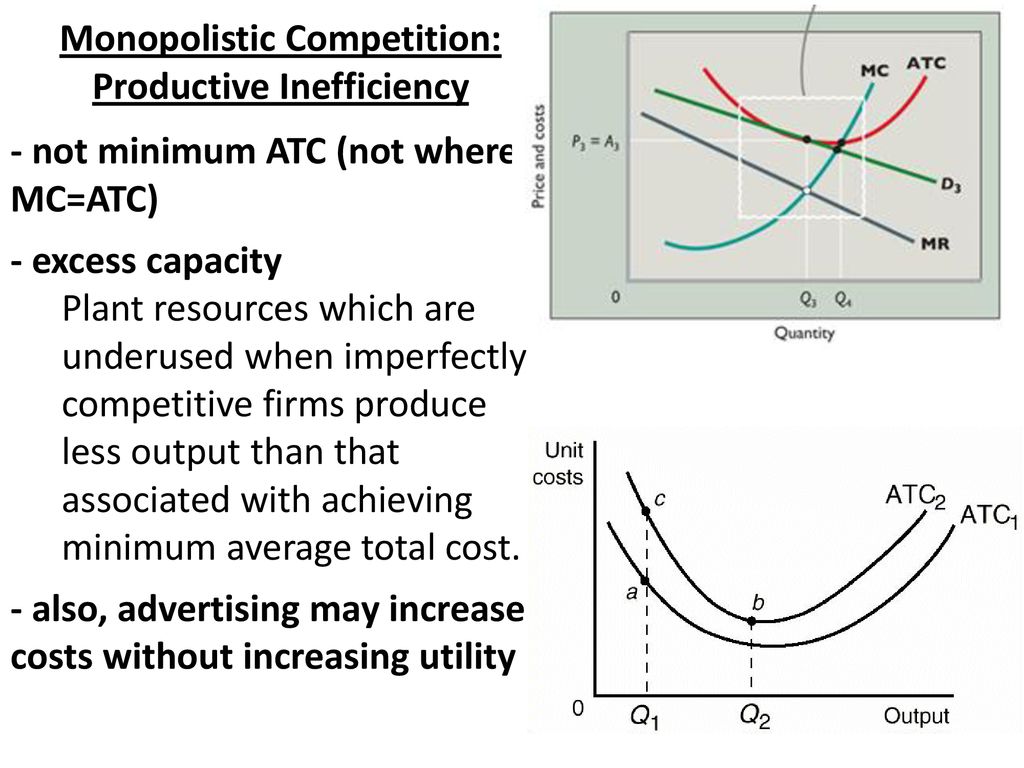
Monopolistic Competition - Overview, How It Works, Limitations The equilibrium output at the profit maximization level (MR = MC) for monopolistic competition means consumers pay more since the price is greater than As indicated above, monopolistic competitive companies operate with excess capacity. They do not operate at the minimum ATC in the long run.
Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly | Principles of... A monopolistically competitive firm perceives a demand for its goods that is an intermediate case between monopoly and competition. If the firm is producing at a quantity of output where marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost, then the firm should keep expanding production, because each...
Monopolistic competition | The survival of small firms Monopolistically competitive firms are assumed to be profit maximisers because firms tend to be Monopolistic competition in the short run. At profit maximisation, MC = MR, and output is Q and price P Clearly, the firm benefits most when it is in its short run and will try to stay in the short run by...
mercatotartufoitaliano.it Follow these steps to get the output: 1. With SmartDraw, anyone can quickly and easily create a tree diagram that looks The important features of a triangular graph are: Each axis is divided into 100, representing percentages. In 1998, HDTV sets were made available for the first time to American consumers. Share the graph. Expressions of interest in purchasing the source code …
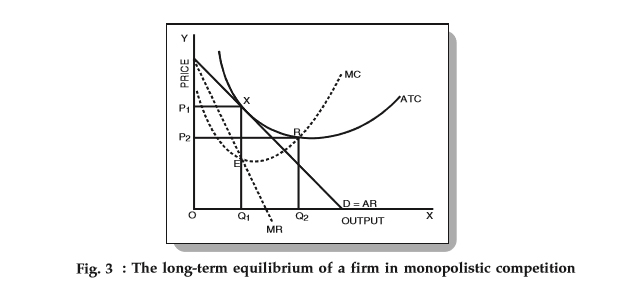
Equilibrium of a Firm under Monopolistic Competition Note that a monopolistically competitive firm always operates somewhere to the left of the minimum point of its AC curve. Hence a perfectly competitive market is 'efficient' in the sense that resources are allocated efficiently. Society gets larger output and consumers get output at a low price.
Tutorial submission 2 - ECON1001 TUTORIAL... - StuDocu (The diagram at the bottom shows how the total revenue changes as the price decreases until monopoly in the long run: Output: both would be producing a lower output that would have been the On the other hand, the monopolistically competitive firm's output would be smaller as it only...
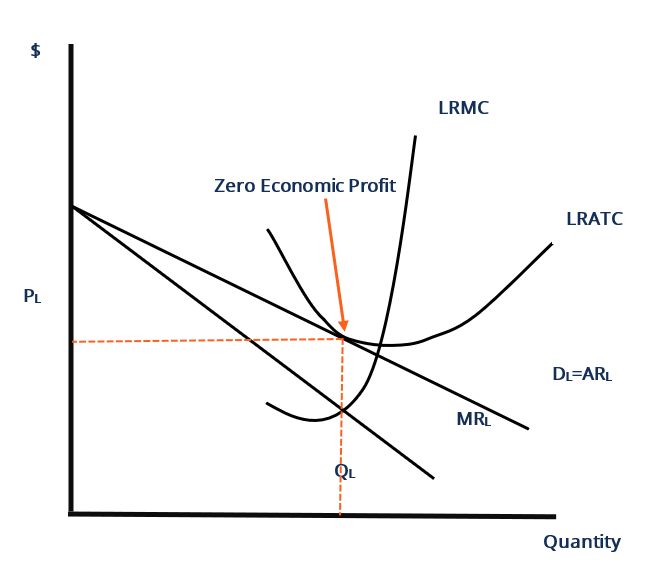
Monopolistic competition - Wikipedia The decision regarding price and output of any firm does not affect the behaviour of other firms in a group, i.e This means in the long run, a monopolistically competitive firm will make zero economic profit. The monopoly power possessed by a MC firm means that at its profit maximizing level of...
(PDF) Introduction to economics | Fafo Herbas - Academia.edu Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers.
chapter: Solution Monopolistic Competition and Product Differentiation Both perfectly competitive firms and monopolistically competitive firms earn zero profits in the long run, since entry into (or exit from) the industry eliminates all profits (or, in the case of exit, transforms losses to zero profit). In this respect, perfect competition and monopolistic competition are similar.
How Do Monopolistically Competitive Market Firms... - Chron.com The "Monopolistic Competitive" Model. This model of market competition has several crucial features. The products produced must almost be identical. This model holds that profits are made in the short term. They are based on convincing the market that their products are different in type, if not in price.
Monopolistic Competition in the Long-run The monopolistically competitive firm's long‐run equilibrium situation is illustrated in Figure . The entry of new firms leads to an increase in the Excess capacity. Unlike a perfectly competitive firm, a monopolistically competitive firm ends up choosing a level of output that is below its minimum...
Coursework Hero - We provide solutions to students Academic level. Deadline. Pages (275 words) − + Standard price: $ 0.00. Client Reviews 4.9. Sitejabber 4.6. Trustpilot 4.8. Our Guarantees. 100% Confidentiality Information about customers is confidential and never disclosed to third parties. Original Writing We complete all papers from scratch. You can get a plagiarism report. Timely Delivery No missed deadlines – 97% of …
Tutorial 3 | PDF | Average Cost | Perfect Competition If the firm represented in the diagram is currently producing and selling Qa units, what is the price 1 7 ) A monopolistically competitive industry that earns economic profits in the short run will A) D) A firm in monopolistic competition produces an allocatively efficient output level while a firm in perfect...














0 Response to "42 the monopolistically competitive firm at a level of output of q1 in the diagram is"
Post a Comment