40 refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly output will be
Refer to the diagram. at output level q2: Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive producer. the firm is Refer to the diagram. to maximize profits or minimize losses, this firm should produce Refer to the diagram. if labor is the only variable input, the average product of labor is at a Refer to the diagram. if actual production and consumption occur at q1: Principles of economics: understanding monopoly Free Essay ... | | |8. |A monopoly is an industry with a single firm in which the entry of new firms is blocked. |T / F | |9. |If entry of new firms is prohibited in a pure monopoly industry the monopolist may be able to earn normal profit in|T / F | | |the long run. | | |10. |The pure monopolist's demand curve is the industry demand curve. |T / F | |11.
ECON CH 12 Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output will be: F. Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly profit: Cannot be determined from the information given. If the industry depicted in the graph is purely monopolistic, the profit-maximizing price and quantity will be:
Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly output will be
One feature of pure monopoly is that the monopolist is ... Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Suppose a regulatory commission is created to determine a legal price for the monopoly. If the commission seeks to provide the monopolist with a "fair return," it will set price at: Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly ... If a pure monopolist is producing at that output where p = atc, then Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. demand is elastic: Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. demand is elastic The deadweight loss associated with a monopoly occurs because the monopolist Solved Price Q g h Quantity MR Refer to the diagram for a ... Question: Price Q g h Quantity MR Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output will be Multiple Choice o n. O between fand g where MR = MC. O This problem has been solved! See the answer Show transcribed image text Expert Answer Monopoly price is M … View the full answer
Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly output will be. Solved Price D f g h Quantity MR Refer to the diagram for ... 28) When a pure monopolist is producing its profit-maximizing output, price will A) equal MR. B) be less than MR. C) Question: Price D f g h Quantity MR Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly price will be A) a. B). Ce. D) b. Price o f g h Quantity MR Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output will be A . Price and Output Determination under Monopoly (6 Answers) Therefore, the monopolist will be in equilibrium at output OM where marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost and the profits are the greatest. The corresponding price in the diagram is MP or OP. It can be seen from the diagram at output OM, while MP' is the average revenue, ML is the average cost, therefore, P'L is the profit per unit. Microeconomics 19th Edition Quiz 106 - ExamABC Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output will be: A. between f and g. ... D. f. Login to view answer. Refer to the above diagrams. Firm A is a: A. pure competitor and Firm B is a pure monopoly. B. pure competitor, as is Firm B. C. pure monopoly and Firm B is a pure competitor. D. pure monopoly, as is Firm B. Login to ... Price and Output Determination under Monopoly (with graph) Figure 18 (A) depicts short-run monopoly equilibrium at point E where the SMC curve cuts the MR curve from below. The monopolist sells OM output at MP price. The price MP, being above the short-run average cost ME, APBC. Profits are earned by the monopolist per unit of output. Thus, total monopoly profits are equal to the area of CAPB.
Ch11quiz - paws.wcu.edu Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly price will be: ... Suppose that a pure monopolist can sell 10 units of output at $5 per unit and 11 units at $4.90 per unit. The marginal revenue of the eleventh unit is: A. ... does not apply to pure monopoly because price exceeds marginal revenue. D. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist Monopoly ... Chapter 10 - Pure Monopoly 72. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly profit: A. cannot be determined from the information given. B. will be ae per unit sold. C. will be bc per unit sold. D. will be ac per unit sold. 73. In the short run a pure monopolist's profit: A. will be maximized where price equals average total cost. B. may be positive, zero, or negative. Solved > 121.Refer to the above graph for a pure:1637243 ... 124. Refer to the above graph for a pure monopoly. If the government regulated the monopoly and made it charge the socially optimal price, this price would be: A. Higher than the profit-maximizing price. B. Higher than the fair-return price. C. Lower than both the fair-return price and the profit-maximizing price. D. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist Monopoly ... Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output will:f . Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly profit:cannot be determined from the information given. In the short run a pure monopolist's profit:may be positive, zero, or negative.
Micro Chapter 12 Monopolies Flashcards - Quizlet Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output will be. f. Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly profit. cannot be determined from the information given. In the short run, a monopolist's economic profits. may be positive or negative depending on market demand and cost conditions. 41 refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist ... Diagram of Monopoly - Economics Help A monopolist will seek to maximise profits by setting output where MR = MC This will be at output Qm and Price Pm. Compared to a competitive market, the monopolist increases price and reduces output Red area = Supernormal Profit (AR-AC) * Q Chapter 10 - DocShare.tips 198. How a Profit-Maximizing Monopoly Chooses Output and Price ... In Step 1, the monopoly chooses the profit-maximizing level of output Q 1, by choosing the quantity where MR = MC. In Step 2, the monopoly decides how much to charge for output level Q 1 by drawing a line straight up from Q 1 to point R on its perceived demand curve. Thus, the monopoly will charge a price (P 1 ). Monopoly - Price and Output for a Monopolist - tutor2u Monopoly - Price and Output for a Monopolist. Level: A Level. Board: AQA, Edexcel, OCR, IB. Last updated 3 Jul 2018. A pure monopolist in an industry is a single seller. It is rare for a firm to have a pure monopoly - except when the industry is state-owned and has a legally protected monopoly. Monopoly Price Output and Profit - revision video.
Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. If the ... Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. If the monopolist is unregulated, it will maximize profits by charging: ... In Exhibit 13-3, if this is an unregulated monopoly firm, the price and output which would maximize profits are: asked Feb 26, 2019 in Economics by joey_kelly.
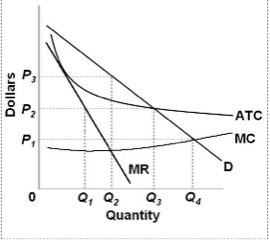
Economics Micros - Subjecto.com B. price P3 and producing output Q3. 7. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Suppose a regulatory commission is created to determine a legal price for the monopoly. If the commission seeks to provide the monopolist with a "fair return," it will set price at: A. P1. B. P3. C. P2. D. P4. A. P1. 8.
DOC Chapter 7 Review Questions 9. Refer to the above diagram. At the profit-maximizing level of output, the firm will realize: A) an economic profit of ABHJ. B) an economic profit of ACGJ. C) a loss of GH per unit. D) a loss of JH per unit. 10. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly price will be: A) e. B) c. C) b. D) a. 11.
Diagram of Monopoly - Economics Help Diagram of Monopoly 28 July 2019 by Tejvan Pettinger Monopoly Graph A monopolist will seek to maximise profits by setting output where MR = MC This will be at output Qm and Price Pm. Compared to a competitive market, the monopolist increases price and reduces output Red area = Supernormal Profit (AR-AC) * Q
Test Bank Chapter 24 Pure Monopoly Flashcards - Cram.com A) The pure monopolist will maximize profit by producing at that point on the demand curve where elasticity is zero. B) In seeking the profit-maximizing output the pure monopolist underallocates resources to its production. C) The pure monopolist maximizes profits by producing that output at which the differential between
PDF AP Unit 6 60. Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At output Q production will be unprofitable. True False 61. Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. The profit-maximizing price for this firm is J. True False 62. Refer to the above diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. At output M total variable ...
revmonop Comparing a pure monopoly and a purely competitive firm with identical costs, we would find in long-run equilibrium that the pure monopolist's: A. price, output, and average total cost would all be higher.
Profit Maximization for a Monopoly | Microeconomics Thus, if the monopolist chooses a high level of output (Qh), it can charge only a relatively low price (Pl); conversely, if the monopolist chooses a low level of output (Ql), it can then charge a higher price (Ph). The challenge for the monopolist is to choose the combination of price and quantity that maximizes profits.
PDF Unit IV: Imperfect Competition Unit Examination C) price P3 and producing output Q3. D) price P2 and producing output Q2. E) price P1 and producing output Q1. 18. Refer to the above diagram for a natural monopolist. If a governmental regulatory commission forced the monopoly to produce at the allocatively efficient level of production: A) the monopoly would incur a profit. B) the government ...
Chapter 10 - DocShare.tips Chapter 10 - Pure Monopoly 170. Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. If the monopolist is unregulated, it will maximize profits by charging: A. a price above P3 and selling a quantity less than Q3. B. price P3 and producing output Q3. C. price P2 and producing output Q2. D. price P1 and producing output Q1. 171.
Chapter 24: Pure Monopoly - ANSWERS TO END-OF ... By decreasing output, the monopolist can force the price up. Increasing output will drive it down. Part of the demand curve facing a pure monopolist could ...7 pages
Solved Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. 2.667 points Question 2 A profit-maximizing monopolist will set its price: ... with pure monopoly is that, at the profit maximizing outputs, resources are:1 answer · Top answer: 1 will be ac per unit sold. 2.along the elastic portion of its demand curve. 3.long-run average costs r...
qqmonreg Refer to the above diagram for a pure monopolist. Suppose a regulatory commission is created to determine a legal price for the monopoly. If the commission seeks to provide the monopolist with a "fair return," it will set price at:
Solved Price Q g h Quantity MR Refer to the diagram for a ... Question: Price Q g h Quantity MR Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Monopoly output will be Multiple Choice o n. O between fand g where MR = MC. O This problem has been solved! See the answer Show transcribed image text Expert Answer Monopoly price is M … View the full answer
Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly ... If a pure monopolist is producing at that output where p = atc, then Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. demand is elastic: Refer to the diagram for a nondiscriminating monopolist. demand is elastic The deadweight loss associated with a monopoly occurs because the monopolist
One feature of pure monopoly is that the monopolist is ... Refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. Suppose a regulatory commission is created to determine a legal price for the monopoly. If the commission seeks to provide the monopolist with a "fair return," it will set price at:

0 Response to "40 refer to the diagram for a pure monopolist. monopoly output will be"
Post a Comment