42 orbital diagram for s
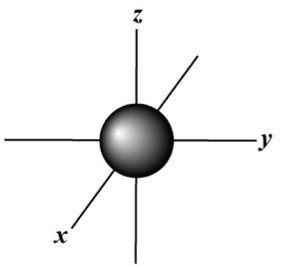
CN- lewis structure, molecular orbital diagram, and, bond ... Also, using the Molecular orbital diagram of CN-we can also find its bond order which helps us to predict its bond length and stability as well. Procedure to draw the molecular orbital diagram of CN. 1. Find the valence electron of each atom in the CN molecule. Clearly, carbon has 4 valence electrons and nitrogen has 5. 2. Find if the molecule homo-nuclear diatomic molecular orbital … Orbitals Chemistry (Shapes of Atomic Orbitals) - Shape of ... The Shape of s Orbitals The boundary surface diagram for the s orbital looks like a sphere having the nucleus as its centre which in two dimensions can be seen as a circle. Hence, we can say that s-orbitals are spherically symmetric having the probability of finding the electron at a given distance equal in all the directions.
Atomic orbital - Wikipedia In atomic theory and quantum mechanics, an atomic orbital is a mathematical function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus.The term atomic orbital may also refer to the physical region or space …

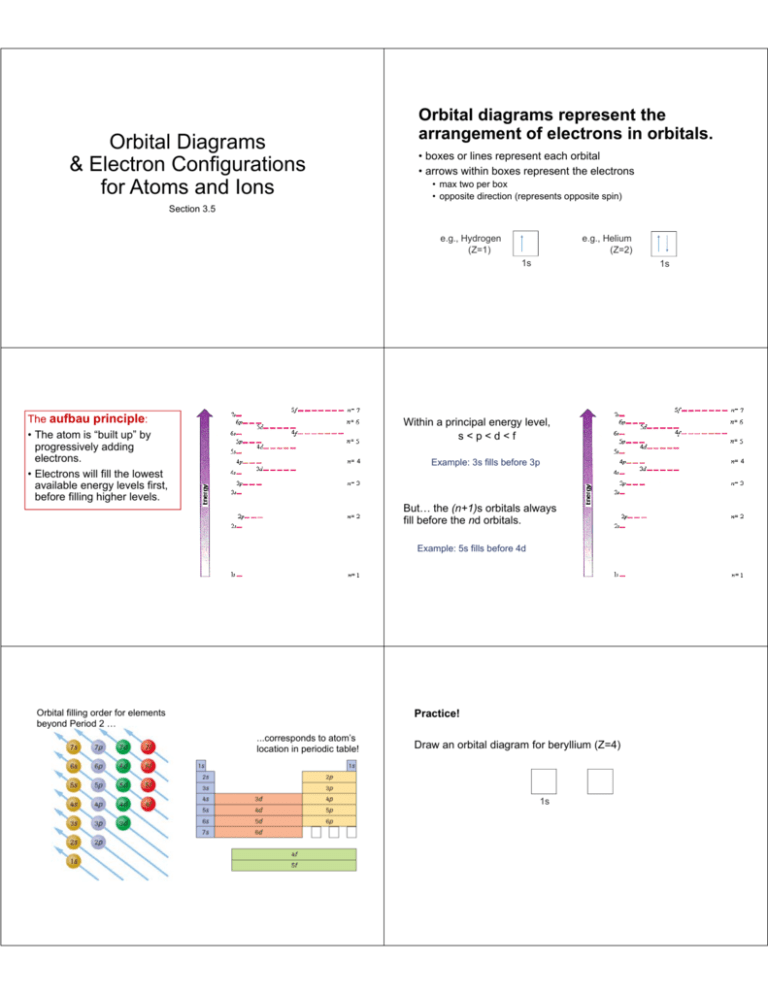
Orbital diagram for s
Orbital Diagrams Flashcards | Quizlet The order in which orbitals are listed on an orbital diagram follows: The Aufbau principal. Hund's rule states that the electron configuration with the lowest-energy will have the maximum possible number of unpaired electrons. Which of the elements below would require special attention to this rule to correctly depict the orbital diagram? Degenerate Orbitals - Explanation With Diagram, Examples ... p orbital has 3 degenerate orbitals. All three have the same energy levels. Each orbital is first assigned with only one electron. The second electron will be of opposite spin. Each orbital is filled and the total is six electrons. Explanation of Degenerate Orbitals with Diagram. Orbitals in the 2p sublevel are degenerate orbitals – Which means that the 2p x, 2p y, and 2p z orbitals have … 8 - Drawing Molecular Orbital Diagrams — Flux Science Molecular orbital diagrams are complex, involving two additional orbitals, electronegativity, atomic symmetries and atomic energies. Although more complex, these diagrams reveal a more realistic case for bonding, allowing electrons to travel about a molecule, rather than in between one.
Orbital diagram for s. Orbital Diagrams - Concept - Chemistry Video by Brightstorm Orbital diagrams are pictorial descriptions of the electrons in an atom. Three rules are useful in forming orbital diagrams. According to the Auf Bau Principle, each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital. The Pauli Exclusion Principle says that only two electrons can fit into an single orbital. Hund s rule states that electrons go into ... Cobalt(Co) electron configuration and orbital diagram To create an orbital diagram of an atom, you first need to know Hund’s principle and Pauli’s exclusion principle. Hund’s principle is that electrons in different orbitals with the same energy would be positioned in such a way that they could be in the unpaired state of maximum number and the spin of the unpaired electrons will be one-way. And Pauli’s exclusion principle is that … Copper(Cu) electron configuration and orbital diagram Therefore, an electron of 4s orbital completes a full-filled 3d orbital by jumping into a 3d orbital. So, the copper(Cu) electron configuration will be 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 10 4s 1. How to write the orbital diagram for copper(Cu)? To create an orbital diagram of an atom, you first need to know Hund's principle and Pauli's exclusion ... Earth Orbital Diagram - xkcd This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 2.5 License. This means you're free to copy and share these comics (but not to sell them). More details..
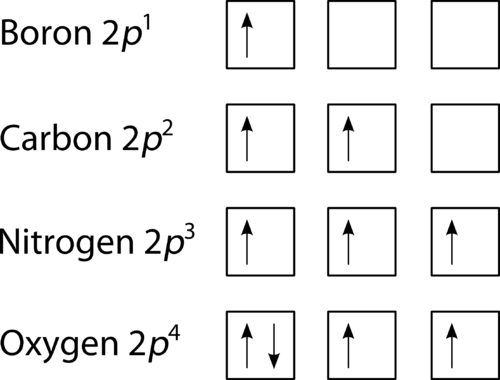
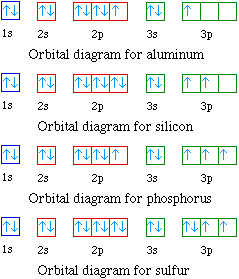
PDF Electron Configurations and Orbital Diagrams key 2. The lobes of a p orbital disappear at the nucleus. What does this tell us about electrons in p orbitals? The probability of finding an electron at the nucleus is 0 (you will never find an electron in the nucleus). 3. 2The electron configuration for phosphorus, written in core notation, is [Ne] 3s 3p 3. What two things does Hund's rule tell us PDF Orbital Diagrams, Noble Gas Configuration, Lewis Dot Diagrams Orbital Filling Diagrams •Each box represents an orbital which can hold a max of 2 e- •Aufbau principal -each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available; German for "build up" •Electrons are notated with an arrow -Up arrow goes first then, down arrow -Arrows represent the opposing spin of electrons 5.2 Quantum Theory & The Atom xkcd.com › 1356Orbital Mechanics - xkcd This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 2.5 License. This means you're free to copy and share these comics (but not to sell them). More details. Orbital Diagram of All Elements (Diagrams given Inside) Orbital diagram of Hydrogen (H) 2: Orbital diagram of Helium (He) 3: Orbital diagram of Lithium (Li) 4: Orbital diagram of Beryllium (Be) 5: Orbital diagram of Boron (B) 6: Orbital diagram of Carbon (C) 7: Orbital diagram of Nitrogen (N) 8: Orbital diagram of Oxygen (O) 9: Orbital diagram of Fluorine (F) 10: Orbital diagram of Neon (Ne) 11 ...
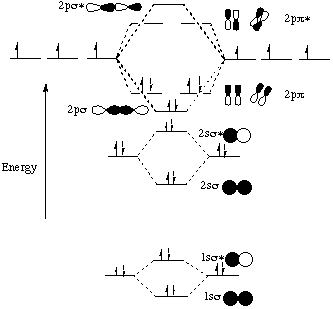
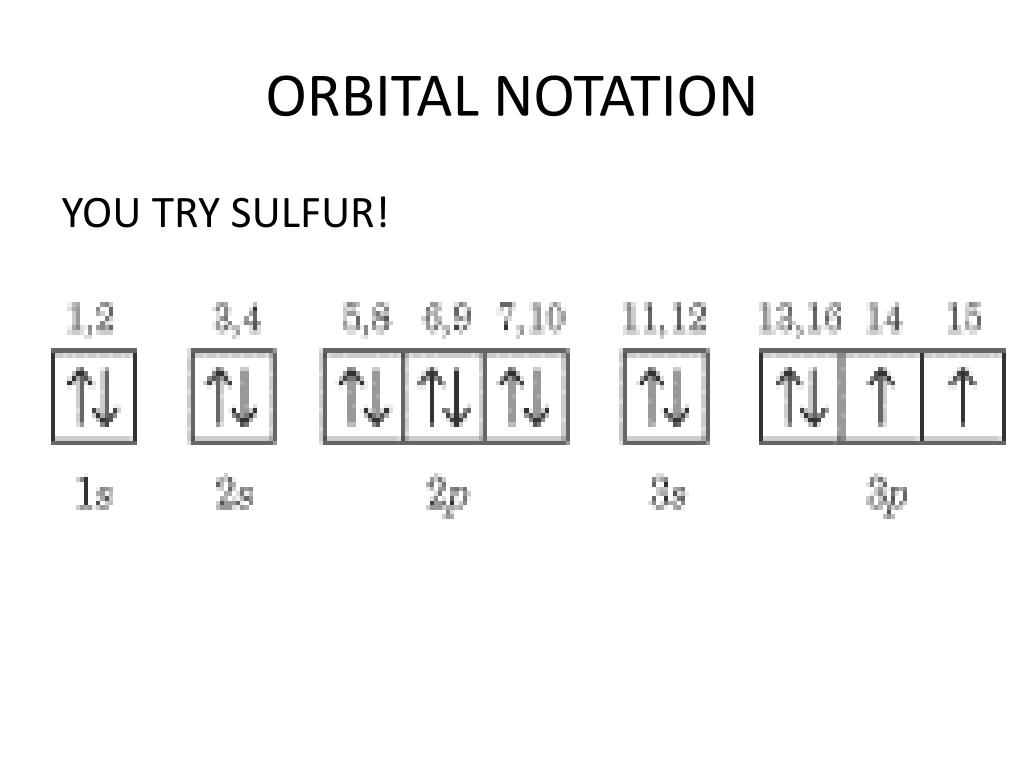
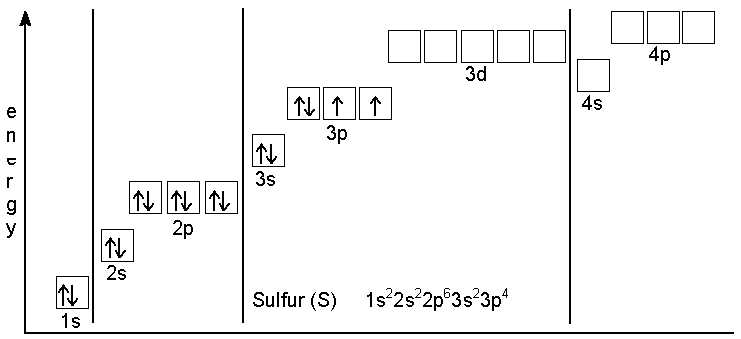
7.7 Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry Fundamentals This is the molecular orbital diagram for the homonuclear diatomic Be 2+, showing the molecular orbitals of the valence shell only. The molecular orbitals are filled in the same manner as atomic orbitals, using the Aufbau principle and Hund's rule. Bond Order. Orbital Filling Diagram For Sulfur The orbital diagram for sulfur has seven boxes with two arrows pointing in opposite directions and two boxes with one arrow pointing up in each. The arrows represent the 16 electrons of the sulfur atom, and the directions represent their spins. The boxes represent sulfur's orbitals. Sulfur's electron configuration is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 4. 39 formaldehyde molecular orbital diagram - Diagram Online ... A) draw a molecular orbital (mo) diagram for co and show the filling of electrons. Let's take [co (nh3)6]3+ as an example. For the homonuclear diatomic #o_2#, we simply have two copies of this atomic orbital diagram far apart at first. Electronic configuration of co molecule is: Draw the orbital diagram for the ion co2+. Electron Configuration for Sulfur (S) - TerpConnect In writing the electron configuration for Sulfur the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons ...24 Oct 2016 · Uploaded by Wayne Breslyn
s,p,d,f Orbitals - Chemistry | Socratic An s orbital is spherically symmetric around the nucleus of the atom, like a hollow ball made of rather fluffy material with the nucleus at its centre. As the energy levels increase, the electrons are located further from the nucleus, so the orbitals get bigger. The order of size is 1s < 2s < 3s < …, as shown below.
PDF Hund©s Rule & Orbital Filling Diagram Hund©s Rule & Orbital Filling Diagram Complete the orbital diagram for each element. 2) calcium 1s 2s 4s 3s 3d 2p 4p 3p 1) sodium 1s 2s 4s 3s 3d 2p 4p 3p 3) nickel 1s 2s 4s 3s 3d 2p 4p 3p 4) silicon 1s 2s 4s 3s 3d 2p 4p 3p 5) iron 6) copper 1s 2s 4s 3s 3d 2p 4p Answer key 3p 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 1s 2s 4s 3s 2p 4p 3p 3d. Created Date:
Orbital Diagrams and Electron Configuration - Basic ... This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into orbital diagrams and electron configuration. It explains how to write the orbital diagram n...
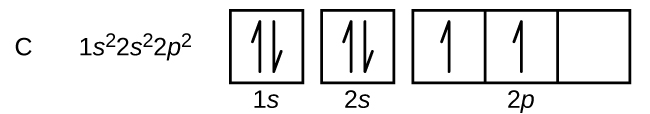
Carbon Orbital diagram, Electron configuration, and ... The orbital diagram for Carbon is drawn with 3 orbitals. The orbitals are 1s, 2s, and 2p. The Carbon orbital diagram contains 2 electrons in 1s orbital, 2 electrons in 2s orbital, and the rest two electrons in 2p orbital. Orbital diagram for a ground-state electron configuration of Carbon atom is shown below-.
Hund's Rule and Orbital Filling Diagrams | Chemistry for ... Orbital filling diagrams for hydrogen, helium, and lithium. According to the Aufbau process, sublevels and orbitals are filled with electrons in order of increasing energy. Since the s sublevel consists of just one orbital, the second electron simply pairs up with the first electron as in helium.
Molecular orbital diagram - Wikipedia A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ...
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Orbital_elementsOrbital elements - Wikipedia In this diagram, the orbital plane (yellow) intersects a reference plane (gray). For Earth-orbiting satellites, the reference plane is usually the Earth's equatorial plane, and for satellites in solar orbits it is the ecliptic plane .
What is orbital diagram in chemistry? - Frequentlyasked An orbital filling diagram is the more visual way to represent the arrangement of all the electrons in a particular atom. In an orbital filling diagram, the individual orbitals are shown as circles (or squares) and orbitals within a sublevel are drawn next to each other horizontally.
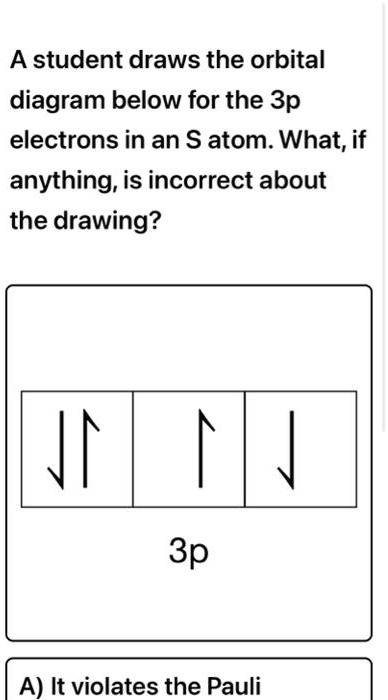
What Is the Orbital Diagram for Sulfur? - Reference.com The orbital diagram for sulfur has seven boxes with two arrows pointing in opposite directions and two boxes with one arrow pointing up in each. The arrows represent the 16 electrons of the sulfur atom, and the directions represent their spins. The boxes represent sulfur's orbitals.
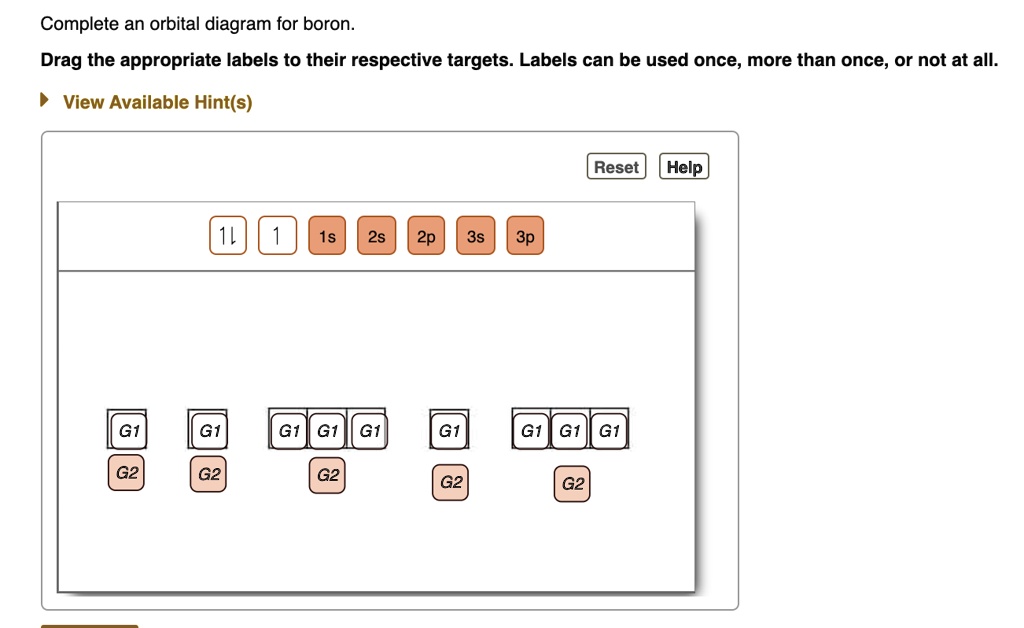
Solved Show the orbital-filling diagram for S (sulfur ... Show the orbital-filling diagram for S (sulfur). Order subshells by energy, with the lowest-energy subshell at the left. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. View Available Hint(s) Reset Help 11 1 15 2s 2p 3s 3p G1 G1 G1 G1G1 G1 G1 G1 | G1 G2 G2 G2 G2 G2 Submit Part D Show the orbital-filling diagram for Br (bromine).
Diagram - Wikipedia A diagram is a symbolic representation of information using visualization techniques. Diagrams have been used since prehistoric times on walls of caves, but became more prevalent during the Enlightenment. Sometimes, the technique uses a three-dimensional visualization which is then projected onto a two-dimensional surface. The word graph is sometimes used as a synonym …
Sulfur(S) electron configuration and orbital diagram Orbital diagram for sulfur (S) Sulfur (S) excited state electron configuration Atoms can jump from one orbital to another orbital by excited state. This is called quantum jump. Ground state electron configuration of sulfur is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 4. The valency of the element is determined by electron configuration in the excited state.
PDF Using Symmetry to Generate Molecular Orbital Diagrams s-orbital rotation about the C ∞, and C 2 axes leaves the s-orbital unchanged ∞ C 2 thus the "1" character in the row highlighted for the s-orbital, and under the columns headed C ∞, and ∞C 2 1 -1
How To Draw Molecular Orbital Diagram Of Co - Drawing ... A) draw a molecular orbital (mo) diagram for co and show the filling of electrons. Let's take [co (nh3)6]3+ as an example. For the homonuclear diatomic #o_2#, we simply have two copies of this atomic orbital diagram far apart at first. Electronic configuration of co molecule is: Draw the orbital diagram for the ion co2+.
Detailing and Solid Surface Products - Gem Industries ... Polisher Parts Diagram: Sanding/Finishing Steps: MICRON vs. GRIT CHART: GEM Industries invented the Orbital Polisher for car, boat, and plane detailing almost 50 years ago and has been in uninterrupted production ever since. The GEM Orbital Polisher is currently sold throughout the world and recognized as the premier quality buffer for the professional detailer. In 2001, GEM …
9.8: Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry LibreTexts 20.02.2022 · The lithium 1s orbital is the lowest-energy orbital on the diagram. Because this orbital is so small and retains its electrons so tightly, it does not contribute to bonding; we need consider only the 2 s orbital of lithium which combines with the 1 s orbital of hydrogen to form the usual pair of sigma bonding and antibonding orbitals.
What Are The 3 Rules For Orbital Diagrams An orbital diagram is a clear way of showing exactly how many paired and unpaired electrons there are in a particular atom's electronic configuration. How do you label orbitals? An integer called the principal quantum number, also designated by the symbol n, is used to label each orbital. The larger the value of n, the greater the energy of ...
Orbital filling diagrams - The Cavalcade o' Chemistry The orbital filling diagram for helium. The electron configuration for helium is 1s². This means that we have two electrons in the 1s orbital, which looks like this: This diagram is exactly the same as the one for hydrogen, except that there's a second arrow added to the 1s orbital. This represents the second electron in the 1s orbital, and ...
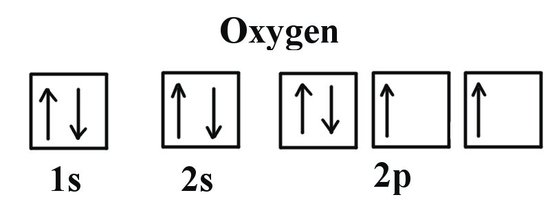
Oxygen(O) electron configuration and orbital diagram The s-orbital can have a maximum of two electrons. Therefore, the next two electrons enter the 2s orbital. The p-orbital can have a maximum of six electrons. So, the remaining four electrons enter the 2p orbital. Therefore, the oxygen(O) electron configuration will be 1s 2 2s 2 2p 4. How to write the orbital diagram for oxygen(O)? To create an orbital diagram of an atom, you first …
What is the full orbital diagram of S? - Answers one full s-orbital. The rest all have at least one of each orbital full. What is an orbital diagram with arrows? An orbital is a region of space that an electron can exist in. so on. Each orbital...
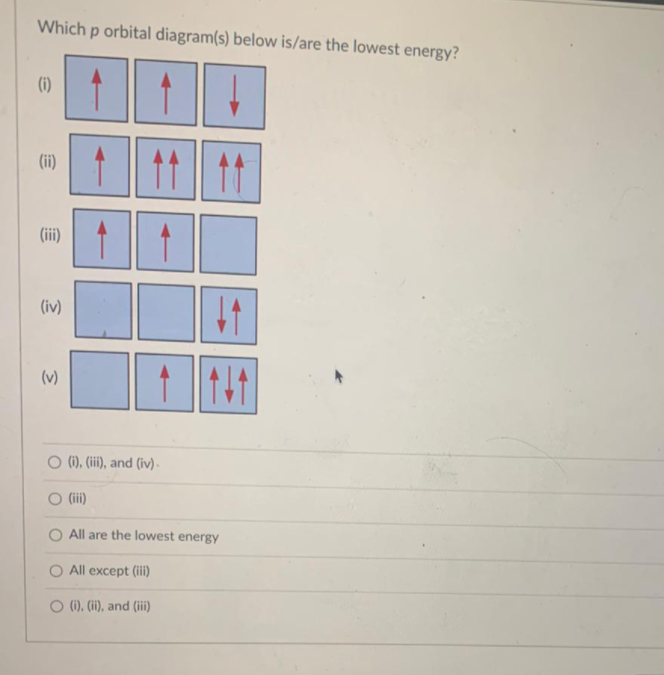
The orbital diagram in which the Hund's rule is violated is Solution. Verified by Toppr. Correct option is A) option {a} consists of the orbital diagram in which the Hund's rule is violated . You can't pair electron unless degenerate orbitals are singly occupied. Solve any question of Structure of Atom with:-. Patterns of problems.
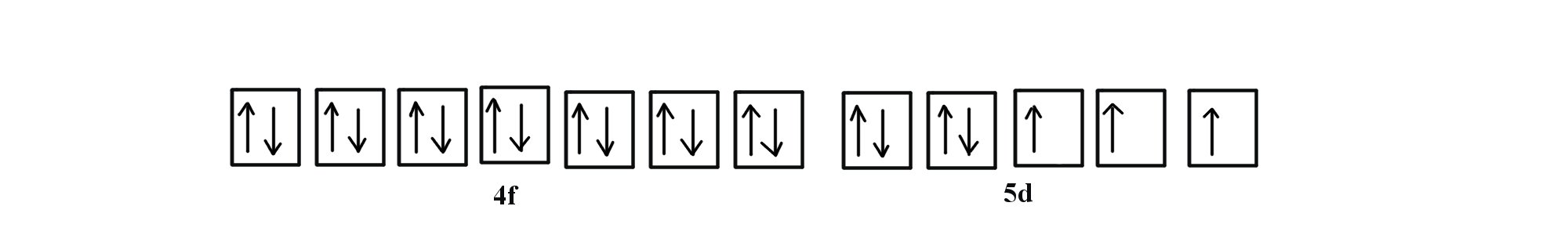
Magnesium Orbital diagram, Electron configuration, and ... Basics of Orbital diagram:- There are different types of orbitals - s, p, d, and, f. These orbitals contain a number of boxes that can hold a number of electrons. Let's see. Each box will hold a maximum of 2 electrons with opposite spin. S orbital contain 1 box that can hold a maximum of 2 electrons.
How to Draw Orbital Diagrams and Hund's Rule | Study ... This video goes over how to properly draw orbital diagrams for an element, after determining the electron configuration. You will also learn how to use hund'...
8 - Drawing Molecular Orbital Diagrams — Flux Science Molecular orbital diagrams are complex, involving two additional orbitals, electronegativity, atomic symmetries and atomic energies. Although more complex, these diagrams reveal a more realistic case for bonding, allowing electrons to travel about a molecule, rather than in between one.
Degenerate Orbitals - Explanation With Diagram, Examples ... p orbital has 3 degenerate orbitals. All three have the same energy levels. Each orbital is first assigned with only one electron. The second electron will be of opposite spin. Each orbital is filled and the total is six electrons. Explanation of Degenerate Orbitals with Diagram. Orbitals in the 2p sublevel are degenerate orbitals – Which means that the 2p x, 2p y, and 2p z orbitals have …
Orbital Diagrams Flashcards | Quizlet The order in which orbitals are listed on an orbital diagram follows: The Aufbau principal. Hund's rule states that the electron configuration with the lowest-energy will have the maximum possible number of unpaired electrons. Which of the elements below would require special attention to this rule to correctly depict the orbital diagram?



/800px-Orbital_representation_diagram.svg-589bd6285f9b58819cfd8460.png)


















0 Response to "42 orbital diagram for s"
Post a Comment