37 co molecular orbital diagram
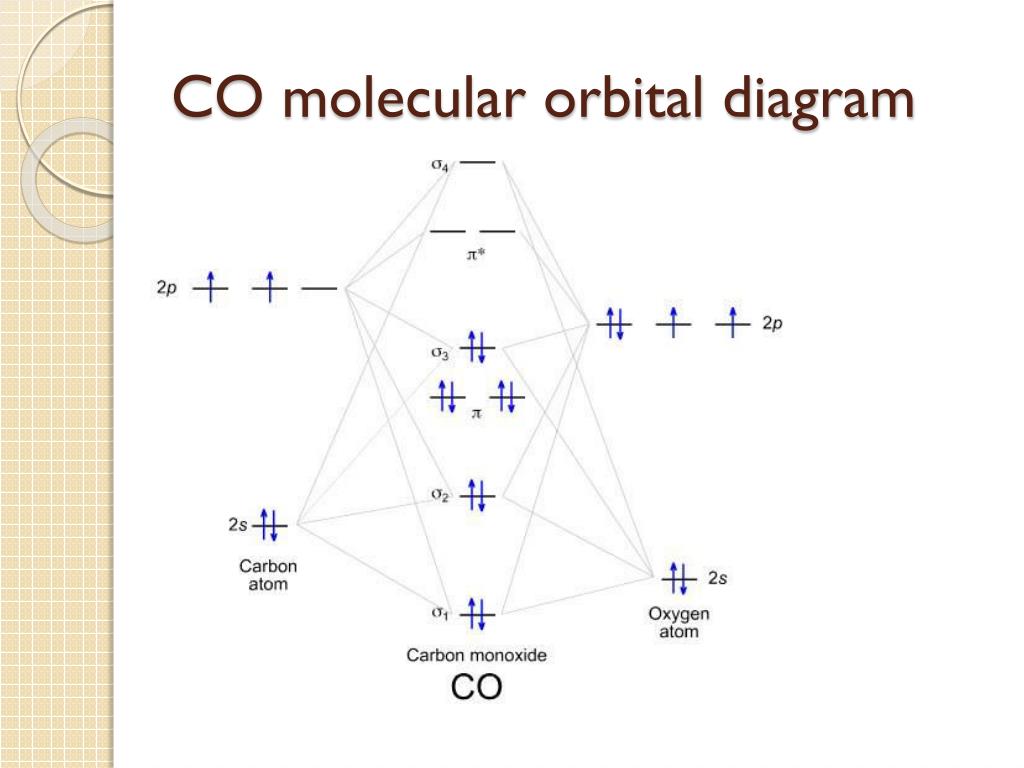
CO molecule has 10 valence electrons,four from carbon atom (2s²2p²) and six from oxygen atom (2s²2p⁴).According to molecular orbital diagram, molecular orbital configuration is given as. σ2s² σ*2s² πx² πy² σz² π*x⁰ πy⁰ σ*z⁰. Thus , bond order = 1/2 (8-2)=3. 78.5K views. Molecular Orbitals for CO. Jmol models of wavefunctions calculated at the RHF/3-21G* level. To view a model, click on a molecular orbital in the energy level correlation diagram shown The results displayed may be switched between those from a low level of calculation and those from a high level.
Carbon Monoxide Molecular Orbital Diagram Explanation. generic s-p valence MO diagram for carbon monoxide CO chain one can reasonably explain, that the HOMO of carbon monoxide must be of. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining MO diagrams can explain why some molecules exist and others do not.
Co molecular orbital diagram
7.3: How to Build Molecular Orbitals. The molecular orbital (MO) theory is a powerful and extensive approach which describes electrons as delocalized moieties over adjacent atoms. The applications of the MO theory extend beyond the limitations of the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) model and the Valence Bond theory. 12-12 This video describes the molecular orbital theory diagram of CO, placing emphasis on how MO theory differs for homo and heteronuclear diatomics Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in
Co molecular orbital diagram. Home / Structure and Bonding / Atomic Orbitals / Molecular orbitals in Carbon Monoxide. Molecular orbitals in Carbon Monoxide. CONTROLS > Click on the CO molecular orbitals in the energy level diagram to display the shapes of the orbitals. Explore bonding orbitals in other small molecules. Molecular Orbital diagram for CO. The course introduces the three key spectroscopic methods used by chemists and biochemists to analyse the molecular and electronic structure of atoms and molecules. These are UV/Visible , Infra-red (IR) and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopies. The content is presented using short focussed and ... Printable O2 molecular orbital diagrams are available for you to guide your study in the molecular orbital lesson.This diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of a molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular. Responsible for the dipole moment is the highest occupied molecular orbital, a $\pmb{\sigma}$ orbital, which has its largest coefficient at the carbon atom. In first order approximation, this orbital can be considered the lone pair of carbon. All other valence orbitals are more strongly polarised towards the oxygen.
Relationship between electronic configuration and Molecular behaviour. 1) Stability of molecules in terms of bonding and antibonding electrons . Number of electrons present in the bonding orbitals is represented by N b and the number of electrons present in antibonding orbitals by Na.. 1) If N b > Na,the molecule is stable because greater number of bonding orbitals are occupied than ... Also see here... Bond order for "NO"^+ Order by bond length: "NO", "NO"^(+), "NO"^(-) Is "CO" a Lewis acid? "O"_2 is well-known to be paramagnetic, and it is one of the successes of molecular orbital theory. You can see that "CO" is not (as it has zero unpaired electrons), but "NO" is (it has one unpaired electron). Well, the MO diagram for "O"_2 is: The bond order is already calculated in the ... Figure 3-1 Molecular orbitals of Cr(CO) 6 (Only interactions between Ligand (σ- and π*) orbitals and metal d-orbitals are shown.) Simplified MO energy level diagram for Cr(CO) 6. Note the empty π* orbitals. Only three are involved in overlap with metal d orbitals. The molecular orbital diagram of carbon monoxide, CO, is show below. Which overlap is strongest? During the axial overlap of p-p orbitals, the electron density increases around the axis, so the bond formed is the strongest. Therefore, the strongest bond formed is when p-p orbital overlap occurs. Final answer: The correct answer is Option B- 2p ...
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ... The Molecule · CO is a very stable 10-valence-electron molecule, isoelectronic with [CN]– and with N2, which has a slightly lower bond dissociation energy than ... A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining MO diagrams can explain why some molecules exist and others do not. . combinations such as CO and NO show that the 3σg MO is higher in energy. Mulliken came up with theory known as Molecular Orbital Theory to explain questions like above. Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ...
Molecular Orbital Diagram of CO. By. All About Chemistry - July 2, 2020. 1. 225. Molecular Orbital Diagram of CO. more. more. TAGS; Molecular Orbital Diagram; Previous article Wohl-Ziegler Bromination. Next article Molecular Orbital Diagram of NO. All About Chemistry. https://allaboutchemistry.net. Hello Reader! Thanking for reading this post ...
Watch the video solution for the question: Draw the orbital diagram for ion Co 2+.. . can be accommodated in the metal d orbitals. • d0 ions •d7 ions - Fe1+, Ru1+, Co2+, Rh2+, Ni3+, etc. . σ-ML4 Tetrahedral MO Diagram e. Answer to Write orbital diagram for Co2+. Use the buttons at the top of the tool to add orbitals.
Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified. Megan Lim. Oct 26, 2016 · 3 min read. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding ...
Figure 9.7. 3: Molecular Orbital Energy-Level Diagrams for Diatomic Molecules with Only 1 s Atomic Orbitals. (a) The H 2+ ion, (b) the He 2+ ion, and (c) the He 2 molecule are shown here. Figure 9.7. 3 a shows the energy-level diagram for the H 2+ ion, which contains two protons and only one electron.
Formation of Molecular Orbitals. An atomic orbital is an electron wave; the waves of the two atomic orbitals may be in phase or out of phase. Suppose Ψ A and Ψ B represent the amplitude of the electron wave of the atomic orbitals of the two atoms A and B. Case 1: When the two waves are in phase so that they add up and amplitude of the wave is ...
Molecular Orbital Description of the CO Ligand The CO LUMO orbitals are antibonding of * symmetry. These are empty orbitalsand canaccept electron density from a metal centre via ‐ backbonding with the metal d(xy), d(xz) and d(yz), orbitals The CO HOMO orbital is a bonding orbital of symmetry with significant electron density on the carbon.
Simple Molecular Orbitals - Sigma and Pi Bonds in Molecules An atomic orbital is located on a single atom. When two (or more) atomic orbitals overlap to make a bond we can change our perspective to include all of the bonded atoms and their overlapping orbitals. Since more than one atom is involved, we refer to these orbitals as molecular orbitals.
The molecular orbital diagram of carbon monoxide is very similar to that of molecular nitrogen. Carbon, with 4 valence electrons, and oxygen with 6 valence electrons, together have the same number of electrons as dinitrogen.
a) Draw a molecular orbital (MO) diagram for CO and show the filling of electrons. Label orbitals {eq}\sigma, \sigma^{\ast }, \pi {/eq} or {eq}\pi^{\ast } {/eq}.
Magnetic Behavior: If all the molecular orbitals in species are spin paired, the substance is diamagneti. But if one or more molecular orbitals are singly occupied it is paramagnetic. For Example, if we look at CO Molecule, it is diamagnetic as all the electron in CO are paired as in the figure below: Fig. No. 9 Molecular Orbital Diagram for CO
in this video i have discussed about the molecular orbital diagram of co which is the most important ligand in organometalics and coordination chemistry.con...
Molecular orbital diagram of co. The s orbitals and p z orbitals of both atoms are the correct symmetry to form σ interactions. Molecular electron configuration for o2 σ2σ2σ2π4π2 we can also calculate the oo bond order. You have the here on this side you would have the energy so the energy is going up there.
Mar 19, 2021 — Carbon monoxide MO diagram ... Carbon monoxide is an example of a heteronuclear diatomic molecule where both atoms are second-row elements. The ...Molecular orbital diagrams for... · Carbon monoxide MO diagram
Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in
12-12 This video describes the molecular orbital theory diagram of CO, placing emphasis on how MO theory differs for homo and heteronuclear diatomics
7.3: How to Build Molecular Orbitals. The molecular orbital (MO) theory is a powerful and extensive approach which describes electrons as delocalized moieties over adjacent atoms. The applications of the MO theory extend beyond the limitations of the Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) model and the Valence Bond theory.



0 Response to "37 co molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment