39 memory diagram c++
The values contained in each variable after the execution of this are shown in the following diagram: First, we have assigned the value 25 to myvar (a variable whose address in memory we assumed to be 1776). The second statement assigns foo the address of myvar, which we have assumed to be 1776. Finally, the third statement, assigns the value contained in myvar to bar. • Every byte inside the primary memory of a machine is identified by a numeric address. The addresses begin at 0 and extend up to the number of bytes in the machine, as shown in the diagram on the right. • Memory diagrams that show individual bytes are not as useful as those that are organized into words.
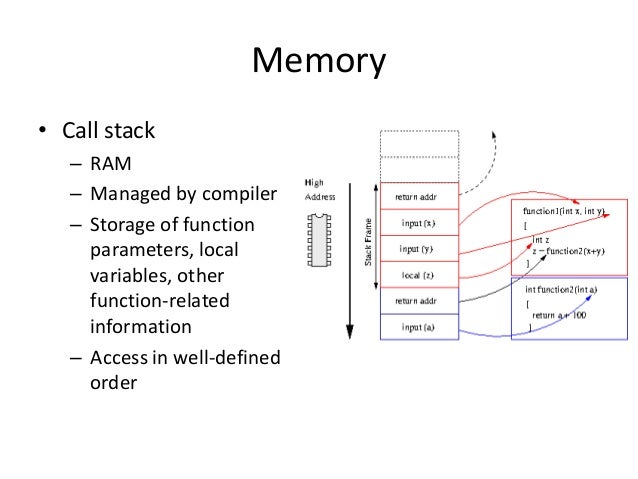
A memory diagram is a picture of the state of the computer's memory at a specific point in time. There are three areas of memory, only two of which are relevant now: Global memory, for global constants (we don't allow you to use global variables in CS 11). You'll sometimes here global memory referred to as static.; Stack memory, for storing variables (and parameters) and some other information ...
Memory diagram c++
Memory can be allocated from different areas. C and C++ can get memory either from the built-in freestore (malloc/free or new/delete), or from the OS via mmap or other system calls, and, in the case of C++, from get_temporary_buffer or return_temporary_buffer. The programs might also get memory from some third-party library. It is important to note that the memory is dynamically allocated on the Heap. The non-static memory and local variables get memory allocated on Stack. Now, let us try to understand the memory map of C++. From the above diagram, it is evident that there are 4 distinct regions of memory in C++. 1. Program: This region holds the compiled code of ... Sep 11, 2019 · Memory Layout of C++ Object in Different Scenarios. Reading Time: 6 minutes. In this article, we will see the memory layout of different C++ Object. And how different storage & access specifiers affect this memory footprint. I am not going to discuss compiler augmented code, name mangling & working of any C++ mechanism related to memory as it ...
Memory diagram c++. Memory Allocation. Many times, you are not aware in advance how much memory you will need to store particular information in a defined variable and the size of required memory can be determined at run time. You can allocate memory at run time within the heap for the variable of a given type using a special operator in C++ which returns the ... 1. Use a block of squared (quadrille rather than graph) paper and a decent pencil* if you want your diagrams to look nice. Also useful for representing memory cells, letters in strings, and so on. You can even get quadrille moleskines, if you want to be hip and square at the same time. CppMem: Interactive C/C++ memory model. help For de-allocating dynamic memory, we use the delete operator. In other words, dynamic memory Allocation refers to performing memory management for dynamic memory allocation manually. Memory in your C++ program is divided into two parts: stack: All variables declared inside any function takes up memory from the stack.
A typical memory layout of a running process. 1. Text Segment: A text segment, also known as a code segment or simply as text, is one of the sections of a program in an object file or in memory, which contains executable instructions. As a memory region, a text segment may be placed below the heap or stack in order to prevent heaps and stack ... Before we begin the problems, we'll step through the basics here so you can get a feel for how to create these diagrams on your own. Recall that the memory of our program is divided into the stack, the portion of memory dedicated to local variables and function stack frames, and the heap, the portion of memory dedicated to dynamic allocation via malloc. Thus whenever we declare a local variable, we are actually allocating space on the stack (and associating that space with a local variable) and when we call malloc, we are actually allocating space on the heap (and receiving a pointer to that memory). Take a look at the following code, which has both local variables (which go on the stack) and dynamically allocated memory (which is put on the heap). After this block of code executes, we will have the following stack: Some things to note in this diagram: 1. Each declaration allocates some storage on either the stack or heap. In the case of xs, we allocate contiguous storage (i.e., arr... C realloc() method "realloc" or "re-allocation" method in C is used to dynamically change the memory allocation of a previously allocated memory. In other words, if the memory previously allocated with the help of malloc or calloc is insufficient, realloc can be used to dynamically re-allocate memory. re-allocation of memory maintains the already present value and new blocks will be ... A more accurate term might be memory diagram, however, as we use stack diagrams to show dynamically allocated memory as well. In C++, dynamic allocation is accomplished using new (while deallocation occurs with delete and delete[]). We draw dynamically allocated memory to the right of the stack diagram and show pointers to that memory using arrows.
Memory in your C++ program is divided into two parts − The stack − All variables declared inside the function will take up memory from the stack. The heap − This is unused memory of the program and can be used to allocate the memory dynamically when program runs. The following diagram illustrate the relationship between computers' memory address and content; and variable's name, type and value used by the programmers. Pointer Variables (or Pointers) A pointer variable (or pointer in short) is basically the same as the other variables, which can store a piece of data. Jan 18, 2015 · A memory diagram is a drawing that represents the state of the memory used by a program at a particular point in execution. Of course, it is an abstraction of the actual memory usage, but contains enough detail to be very useful. A memory diagram usually contains two major sections: 1) stack memory, and 2) heap memory. In C++, when you use the new operator to allocate memory, this memory is allocated in the application's heap segment. int *ptr = new int; // ptr is assigned 4 bytes in the heap int *array = new int[10]; // array is assigned 40 bytes in the heap. The address of this memory is passed back by operator new, and can then be stored in a pointer.
Understanding Memory Leak in C++. Memory leak happens due to the mismanagement of memory allocations and deallocations. It mostly happens in case of dynamic memory allocation.There is no automatic garbage collection in C++ as in Java, so programmer is responsible for deallocating the memory used by pointers.. Misuse of an elevator in a building in real life is an example of memory leak.
In memory there will not be any separation between the rows. We have to code in such a way that we have to count the number of elements in each row depending on its column index. But in memory all the rows and their columns will be contiguous. Below diagram will illustrate the same for a 2D array of size 3X3 i.e.; 3 rows and 3 columns.
An introduction to using dynamic memory in C++. Concepts: Why we may need to allocate memory dynamically?new operatorheap (free store)pointers to reference d...
Program Memory. Computers don't do very good without access to memory. Without access to memory and storage, they are just boxes of wires. When you write C++ code, you are writing real programs ...
As mentioned, stack memory is the default memory for all variables in C++ to be placed. So, we haven't done anything special. We know our variable is going to be in stack memory. Stack memory is a specifically associated with the current function, and the lifecycle of this memory is the lifecycle of the function.
In C and C++, it can be very convenient to allocate and de-allocate blocks of memory as and when needed. This is certainly standard practice in both languages and almost unavoidable in C++. However, the handling of such dynamic memory can be problematic and inefficient. For desktop applications, where memory is freely available, these difficulties can be ignored.
Pointers in C - Simple Examples and Memory Location Diagrams Learn Pointers in C/C++ with examples Memory concepts, Addresses and set a solid foundation of Pointers Rating: 4.3 out of 5 4.3 (33 ratings)
The following diagram shows the memory layout of a 3D array with , in row-major: Note how the last dimension (depth, in this case) changes the fastest and the first (row) changes the slowest. The offset for a given element is: For example, the offset of the element with indices 2,1,1 is 22. ... On the other hand, C and C++ use row-major layout ...
A computer has the following three main components:. 1. Input/output Unit 2. Central Processing Unit 3. Memory Unit. 1. Input and Output Unit. Input : The computer accepts input data from the user via an input device like keyboard.The input data can be characters, word, text, sound, images, document, etc.
Even though the data segment maps a file, it is a private memory mapping, which means that updates to memory are not reflected in the underlying file. This must be the case, otherwise assignments to global variables would change your on-disk binary image. Inconceivable! The data example in the diagram is trickier because it uses a pointer.
C++ Notes: Array Memory Diagrams Here is an array declaration and code to initialize it. int a[5]; // Allocates memory for 5 ints. . . . a[0] = 1; for (int i=1; i<5; i++) { a[i] = a[i-1] * 2; } Arrays are often represented with diagrams that represent their memory use. The diagram below is one typical way to represent the memory used by an array.
Pointers in C: $10 Only - 85% Off Udemy Course https://www.udemy.com/pointers-in-c-simple-examples-and-memory-location-diagrams/?couponCode=T_ONLY10
Sep 11, 2019 · Memory Layout of C++ Object in Different Scenarios. Reading Time: 6 minutes. In this article, we will see the memory layout of different C++ Object. And how different storage & access specifiers affect this memory footprint. I am not going to discuss compiler augmented code, name mangling & working of any C++ mechanism related to memory as it ...
It is important to note that the memory is dynamically allocated on the Heap. The non-static memory and local variables get memory allocated on Stack. Now, let us try to understand the memory map of C++. From the above diagram, it is evident that there are 4 distinct regions of memory in C++. 1. Program: This region holds the compiled code of ...
Memory can be allocated from different areas. C and C++ can get memory either from the built-in freestore (malloc/free or new/delete), or from the OS via mmap or other system calls, and, in the case of C++, from get_temporary_buffer or return_temporary_buffer. The programs might also get memory from some third-party library.



0 Response to "39 memory diagram c++"
Post a Comment