36 which part of the diagram is considered nerve fiber?
Myelin is a lipid-rich (fatty) substance that surrounds nerve cell axons (the nervous system's "wires") to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) are passed along the axon. The myelinated axon can be likened to an electrical wire (the axon) with insulating material (myelin) around it. However, unlike the plastic covering on an electrical ...
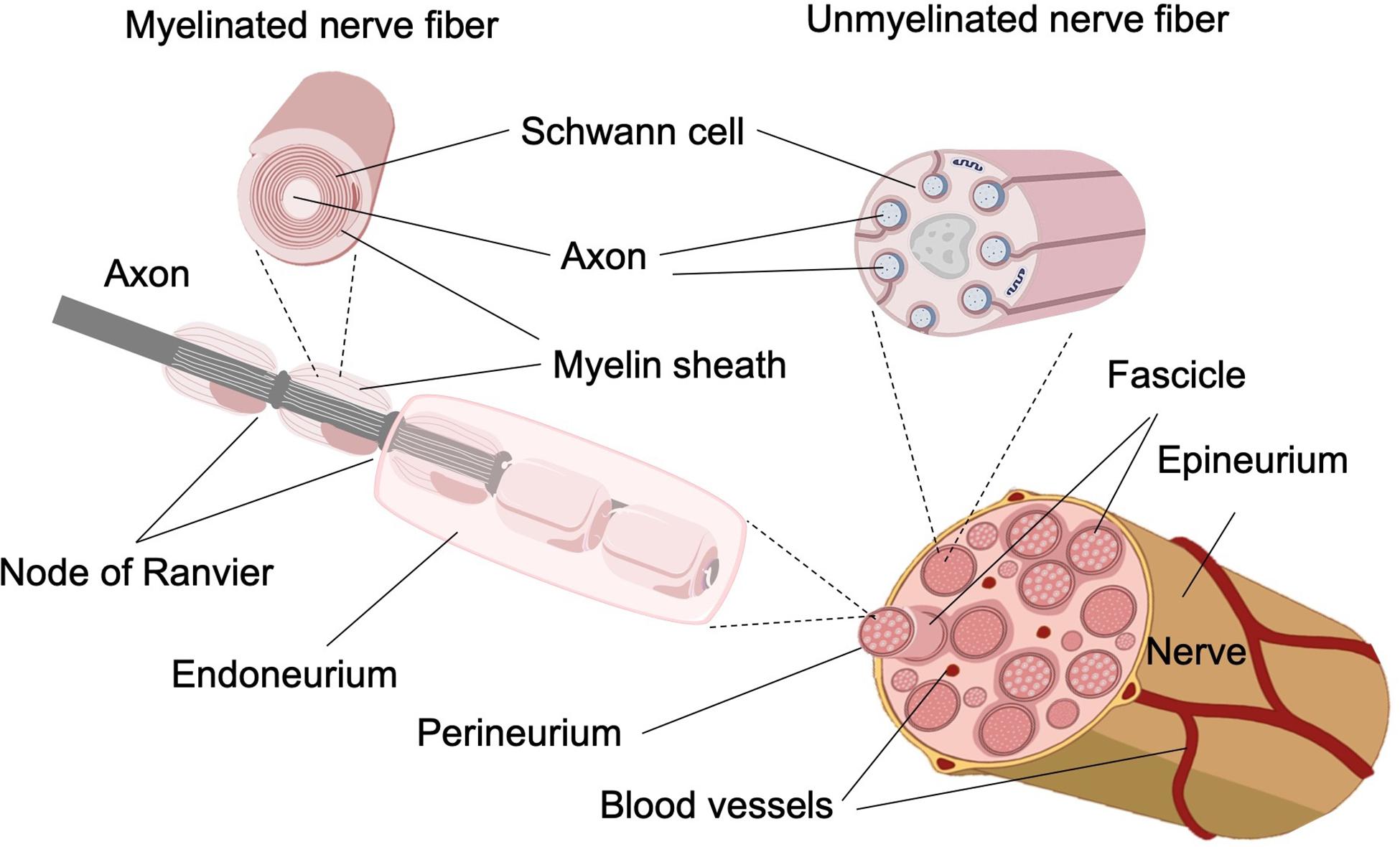
The myelin membranes originate from and are a part of the Schwann cells in the ... Electron micrograph of a single peripheral nerve fiber from rabbit.
The optic nerve is made up of millions of nerve fibers that transmit these impulses to the visual cortex — the part of the brain responsible for our sight. Read an overview of general eye anatomy to learn how the parts of the eye work together .
Which part of the diagram is considered nerve fiber?
An axon or nerve fiber is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, ... The axon hillock is the area formed from the cell body of the neuron as ...
Thus, they can be considered one pathway. The spinothalamic tract is part of the anterolateral system, which also encompasses the spinoreticulothalamic tract (SRTT) and the spinotectal tract (SpTT). Three types of sensory fibers are associated with the spinothalamic tract: type III fibers, unmyelinated c-fibers, and myelinated A-delta fibers.
Visceral sensory nerves transmit pain, stretch, temperature, and chemical change in visceral organs which gets interpreted as sensations like nausea, hunger, gas, cramping, etc. General visceral afferent fibers are considered part of the autonomic nervous system, but unlike the efferent arm, GVA fibers do not classify as sympathetic or ...
Which part of the diagram is considered nerve fiber?.
The human brain weighs about 3 lbs. (1.4 kilograms) and makes up about 2% of a human's body weight. On average, male brains are about 10% larger than female brains, according to Northwestern ...
The mandibular nerve provides sensation and motion to the lower jaw and mouth, and it also provides sensory input from some areas of the scalp. Of these three, the mandibular nerve is the only one that serves both sensory and motor functions. However, the lingual nerve itself is only sensory. The lingual nerve provides sensation to the floor of ...
The enteric nervous system is a complex network of nerve fibers that innervate the abdomen's organs like the gastrointestinal tract, pancreas, gall bladder, etc. It contains nearly 100 million nerves.
Nerves. DRG neurons are considered pseudo-unipolar neurons, with a single axon that bifurcates into two separate branches resulting in a distal process and proximal process. Dorsal root neurons, when conjoined with ventral root neurons, make up the spinal nerves.
Olfactory nerve fibers extend from the mucous membrane, through the cribriform plate, to the olfactory bulbs. Olfactory bulbs: bulb-shaped structures in the forebrain where olfactory nerves end and the olfactory tract begins. Olfactory tract: band of nerve fibers that extend from each olfactory bulb to the olfactory cortex of the brain.
Taste buds are microscopic sensory organs containing chemosensory cells which synapse with afferent fibers of gustatory nerves. The number of taste buds in the oral cavity and uppermost gastrointestinal tract is subject to a high degree of interindividual variation (500-5000) while the number of cells in one taste bud can be up to 150 Due to the abrasive environment of the oral cavity ...
Types of neurons and synapse (diagram) Depending on the type of target tissue, there are central and peripheral synapses. Central synapses are between two neurons in the central nervous system, while peripheral synapses occur between a neuron and muscle fiber, peripheral nerve, or gland. Each synapse consists of the:
Optogenetic stimulation, an effective stimulation technique, is applied to the treatment of Parkinson's disease (PD) to compete with the current neuromodulation technology that focuses on the electrical stimulation. Using the cortical-thalamic-basal ganglia model, we systematically study the effect of optogenetic stimulation on pathological parkinsonian rhythmic neural activity. Based on the ...
The axillary nerve, which is also called the circumflex nerve, emerges from the posterior cord of a network of nerves called the brachial plexus right at the level of the armpit. It's a major peripheral nerve of the arm, carrying fibers from the fifth and sixth cervical vertebrae (C5 and C6), which are in near the base of the neck.
The root of the penis is the most proximal part of the penis. It is located in the urogenital triangle of the perineum, where it is fixed to the pubic symphysis via the two suspensory ligaments of the penis.The root consists of the two muscles (ischiocavernosus and bulbospongiosus muscles) and proximal expansions of the erectile tissues; the two crura of penis and the bulb of penis.
Cardiopulmonary splanchnic nerves carry the postsynaptic fibers destined for the thoracic cavity. Nerves that will innervate the abdominal and pelvic viscera pass through the paravertebral without synapsing, becoming abdominopelvic splanchnic nerves. These nerves include the greater, lesser, least, and lumbar splanchnic nerves.
The diagram above shows the locations where the nerves of the parasympathetic nervous system exit the brain and spinal cord. It also shows the locations where they form synapses with effector ...
31) Which part of the diagram is considered nerve fiber? a) A b) D ; 32) This part of the neuron contains the nucleus and Nissl bodies. a) A b) B ; 33) This part ...
Within the endoneurium, individual nerve fibers are surrounded by a liquid called the endoneurial ... Diagram A shows the primary structures of a nerve.
Ten of the twelve cranial nerves may also be considered part of the PNS. General components of the PNS are: Sensory and autonomic ganglia, myelinated nerve fibers, and unmyelinated nerve fibers.
All basic life functions originate in the brain stem, including heartbeat, blood pressure and breathing. In humans, this area contains the medulla, midbrain and pons. This is commonly referred to as the simplest part of the brain, as most creatures on the evolutionary scale have some form of brain creation that resembles the brain stem.
Mixed cranial nerves are the cranial nerves that contain sensory and motor nerve fibers. There are four of such nerves in our peripheral nervous system ; Trigeminal nerve (CN V) Facial nerve (CN VII) Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) Vagus nerve (CN X)
The enteric nervous system is often considered our 'second brain'. It's a complex network of more than a hundred million neurons that cover specific areas such as the small intestine and colon. Additionally, this system is capable of acting independently of the brain itself.
Find the answer to this question here. Super convenient online flashcards for studying and checking your answers! · Which Part Of The Diagram Is Considered Nerve ...
Objective This is the first double-blind randomized controlled trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of IV immunoglobulin (IVIG) vs placebo in patients with idiopathic small fiber neuropathy (I-SFN). Methods Between July 2016 and November 2018, 60 Dutch patients with skin biopsy-proven I-SFN randomly received a starting dose of IVIG (2 g/kg body weight) or matching placebo (0.9% saline).
Nerve fibers connecting cortical area in one hemisphere with cortical area in ... The diagrams are based on monopolar recording of a moist nerve in air.
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision.It is the most complex organ in a vertebrate's body. In a human, the cerebral cortex contains approximately 14-16 billion neurons, and the estimated number of neurons in the cerebellum is ...
In physiology, an action potential (AP) occurs when the membrane potential of a specific cell location rapidly rises and falls: this depolarization then causes adjacent locations to similarly depolarize. Action potentials occur in several types of animal cells, called excitable cells, which include neurons, muscle cells, endocrine cells and in some plant cells.
Your brain is made up of millions of cells called neurons. Neurons make connections with each other to create pathways that control all aspects of life, such as bodily functions, emotions, and...
Motor Neuron: Function, Types, and Structure. By Olivia Guy-Evans, published June 24, 2021. Motor neurons (also referred to as efferent neurons) are the nerve cells responsible for carrying signals away from the central nervous system towards muscles to cause movement. They release neurotransmitters to trigger responses leading to muscle movement.
Innervation is the supply of nerves to a body part. In the case of the trapezius muscle, it is innervated by the spinal accessory nerve, or cranial nerve XI. This nerve extends from the skull to the trapezius muscle and controls the muscle's movement.
Which part of the diagram is considered nerve fiber? ... This part of the diagram contains organelles and Nissl bodies. ... This portion of the diagram contains ...
The end of optical fiber was connected to the semiconductor laser, and the output power of the optical fiber was detected. The distance between the fiber and the spinal cord is approximately 1 cm. Finally, the wound is covered with sterile silicone gauze and transparent dressing (Fig. 1a, is the schematic diagram of the experiment). On the ...
They are sometimes referred to as fibers. Dendrites are usually, but not always, short and branching, which increases their surface area to receive signals from ...
The endothelium of the cornea, sclera, and choroid arise from the neural crest cells. The neuroectoderm produces the posterior part of the iris, optic nerve, and retina. The remaining fibrous network and vasculature of the eye arise from the mesodermal layer.
Cranial nerve XI innervates the motor function of the trapezius. The function of the trapezius is to stabilize and move the scapula. The upper fibers can elevate and upwardly rotate the scapula and extend the neck. The middle fibers adduct (retract) the scapula. The lower fibers depress and aid the upper fibers in upwardly rotating the scapula.
0 Response to "36 which part of the diagram is considered nerve fiber?"
Post a Comment