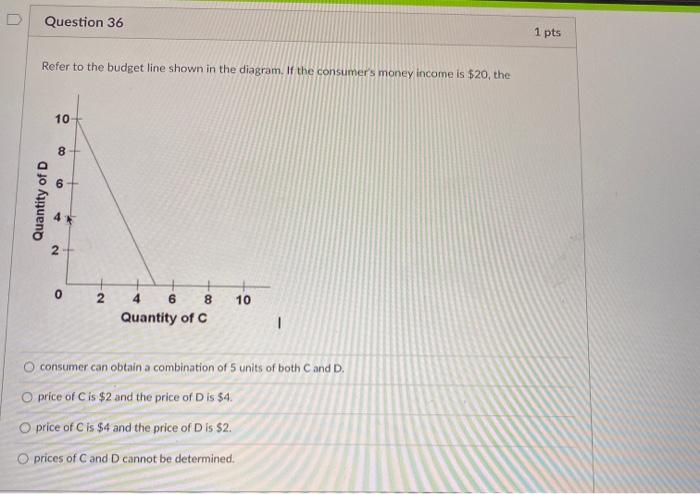
37 refer to the budget line shown in the diagram. if the consumer's money income is $20, the
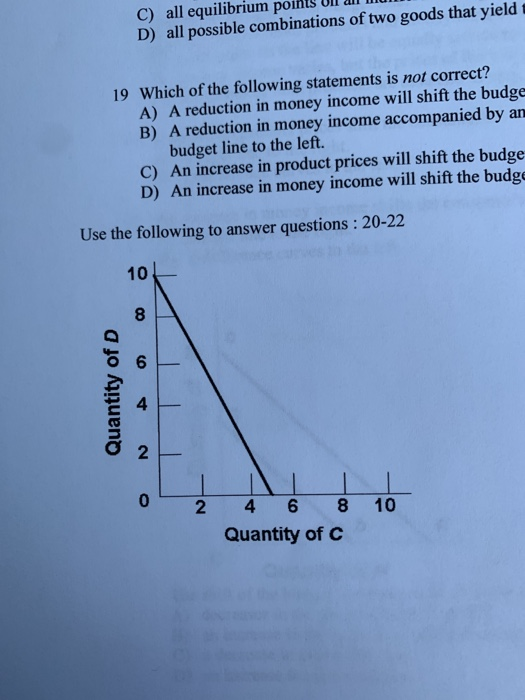
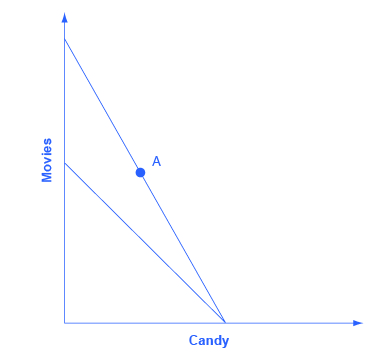
Refer to the budget line shown in the diagram. If the consumer's money income is $20, which of the following combinations of goods is unattainable? asked Aug 11, 2018 in Economics by VonDutch. A. 4 units of C and 6 units of D. B. 5 units of C and no units of D. Important Points about Budget line (Refer Fig. 2.8): 1. Budget line AB slopes downwards as more of one good can be bought by decreasing some units of the other good. 2. Bundles which cost exactly equal to consumer's money income (like combinations E to J) lie on the budget line. 3. Bundles which cost less than consumer's money income (like ...
Refer to the budget line shown in the diagram. If the consumer's money income is $20, the: price of C is $4 and the price of D is $2. If the price of A is $12 and the price of B is $3, the budget line tells us that a consumer in effect can trade: 1 unit of A for 4 of B.

Refer to the budget line shown in the diagram. if the consumer's money income is $20, the
Example of a Budget Line. Radha has ₹50 to buy a biscuit. She has a few options to allocate her income so that she receives maximum utility from a limited salary. To get an appropriate budget line, the budget schedule given can be outlined on a graph. The budget set indicates that the combinations of the two commodities are placed within the ... Other things equal, an increase in a consumer's money income: A. increases the amount of utility a consumer receives from a given quantity of a good. B. shifts the individual's budget line rightward because she can now purchase more of both products. C. eliminates the individual's economizing problem. A. Show various combinations of two products which can be purchased with a given money income with knowledge of the prices of the two products. (Figure 1) B. A decrease in money income shifts the budget constraint line inward to the left in Figure 1; an increase in money income shifts the budget constraint line outward to the right in Fig. 1.
Refer to the budget line shown in the diagram. if the consumer's money income is $20, the. Refer to the budget line shown in the diagram above. If the consumer's money income is $20, the: A) prices of C and D cannot be determined. B) price of C is $2 and the price of D is $4. C) consumer can obtain a combination of 5 units of both C and D. D) price of C is $4 and the price of D is $2. 15. Question 36 1 pts Refer to the budget line shown in the diagram. If the consumers money income is $20, the 10 8 Quantity of D N 0 N 10 6 8 Quantity of C 1 consumer can obtain a combination of 5 units of both C and D. O price of C is $2 and the price of Dis $4. O price of C is $4 and the price of Dis $2. O prices of Cand D cannot be determined. Refer to the budget line shown in the diagram. If the consumer's money income is $20, the a) consumer can obtain a combination of 5 units of both C and D, For example, if José's budget drops from $56 to $42, the budget line will shift inward, as he is unable to purchase the same number of goods as before. To plot the new budget line, find the new intercepts: Budget: $42. Price of movies: $7. Price of T-shirts: $14. Maximum number of movies (y-intercept): $42/$7 = 6.
Refer to the budget line shown in the diagram. If the consumer's money income is $50, the. A.prices of C and D cannot be determined. B.price of C is $5 and the price of D is $10. C.consumer can obtain a combination of 5 units of both C and D. D. price of C is $10 and the price of D is $5. D. Price of C is $10 and the price of D is $5 20. Refer to the budget line shown in the diagram above. If the consumer's money income is $20, ti A) prices of C and D cannot be determined. B) price of C is $2 and the price of D is $4. C) consumer can obtain a combination of 5 units of both C and D. D) price of C is $4 and the price of D is $2. n the come money income, reducti C) all ... Refer to the budget line shown in the diagram. If the consumer's money income is $20, which of the following combinations of goods is unattainable? A. 4 units of C and 6 units of D. B. 5 units of C and no units of D. C. 1 unit of C and 8 units of D. D. 2 units of C and 6 units of D. Jul 17, 2019 · Refer to the budget line shown in the diagram above if the consumers income is 20 the. Econ Module 5 Economics 1030 With Addie At Ohio University Studyblue Consumer can obtain a combination of 5 units of both c and d. Refer to the budget line shown in the diagram if the consumers money income is 20 the. The combinations of products m and n ...
The effect of changes in income on the budget line is shown in Fig. 8.18. Let BL be the initial budget line, given certain prices of goods and income.' If the consumer's income increases while the prices of both goods X and Y remain unaltered, the price line shifts upward (say, to B'L') and is parallel to the original budget line BL. If the consumer's income does not change but the prices of goods X and Y change, the slope of his budget line will change. Suppose that consumer's income is Rs.40 and the price of good Y (Re. 1) remains constant and the price of good X falls from Rs.2 to Re. 1, his budget line will rotate outwards from point В to the line L 2 He can now purchase the maximum 40 units of as shown in Fig. 13. - Technique 2 with total costs of $5 Refer to the budget line shown in the diagram. If the consumer's money income is $200, the - price of C is $5 and the price of D is $10. Share this link with a friend: Refer to the budget line shown in the diagram above. If the consumer's money income is $20, the: A. prices of Cand Dcannot be determined. B. price of Cis $2 and the price of Dis $4. C. consumer can obtain a combination of 5 units of both Cand D. D. price of C is $4 and the price of D is $2. 14.
A) a lower budget line. B) a higher budget line. C) a lower indifference curve. D) a higher indifference curve. E) a tangent point on the same indifference curve. Answer: D 23) The substitution effect is the effect of A) a change in income on the quantity bought. B) a change in price on the quantity bought when the consumer moves to a higher ...
9. Refer to the budget line shown in the diagram above. If the consumer's money income is $20, the price/unit for good C is: A. $1. B. $2. C. $10. D. $20. E. None of the above. 10. Refer to the budget line shown in the diagram above. The total opportunity cost of obtaining the 1 st unit of C is: A. 5 units of D. B. 1 unit of C. C. 4 units of D ...
Refer to the budget line shown in the diagram above. If the consumer's money income is $20, the: A. rices of C and D cannot be determined. B. price of C is $2 and the price of D is $4. C. consumer can obtain a combination of 5 units of both C and D. D. price of C is $4 and the price of D is $2. 106. Refer to the budget line shown in the ...
The alternative combinations of two goods which a consumer can purchase with a given money income is shown by. Definition. a budget line: ... Refer to the budget line shown in the diagram above if the consumer's income is $20, the ... Any combination of goods lying outside of the budget line: Definition. is unattainable, given the consumer's ...
View if the consumer's money income is $20.PNG from ECO/365 365T at University of Phoenix. 10 Quantity of D a: 0 2 4 6 8 10 Quantity of C Refer to the budget line shown in the diagram. lfthe
Refer to the budget line shown in the diagram. If the consumer's money income is $50, the. price of C is $10 and the price of D is $5. ... Refer to the diagram. The initial demand for and supply of pesos are shown by D 1 and S 1. ... Net Investment Income +20 (6) Net Transfers −15 (7) Foreign Purchases of Assets in the United States +30 ...
refer to the budget line shown in the diagram. if the consumer's money income is $20, the: price of C is $4 and the price of D is $2. refer to the table. over the $8-$6 range, supply is: inelastic.
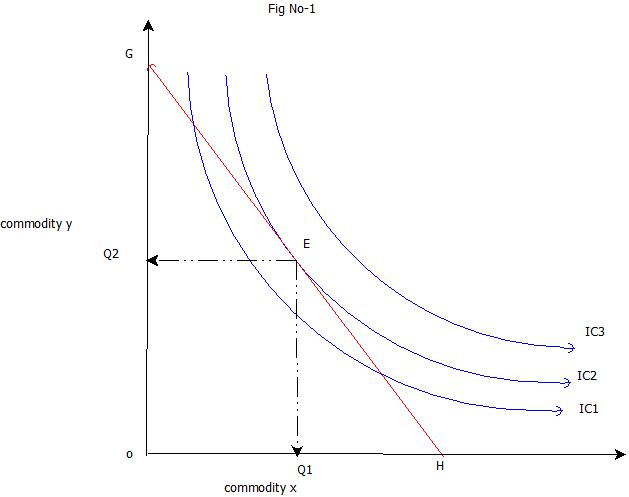
1. A consumer's equilibrium is always formed at a point on the given budget line. 2. A consumer's equilibrium will shift to a higher indifference curve with an increase in consumer's income. Answer: 1. Budget line shows all possible combinations of the two goods that a consumer can buy, given income and prices of commodities.
Consumer Theory - Income and Substitution Effects . Q. X. ... line and graph it in the same diagram as in a). The new budget line is given by the equation 72 = 4X + 6Y is shown as BL2 in the and ... then after the government gives the money back to Abe, his budget constraint will shift back to the one in b), thus Abe will consume (5,5) and ...
Situation 1: Income = $20, Px = $5, Py = $2 . Situation 2: Income = $20, Px = $2, Py = $2 . a) Draw the budget lines for both situations on one graph, labeling them BL1 and BL2. b) Suppose we are told something about the consumer's preferences: in situation 1 she buys X=2 and Y=5, and in situation 2 she buys X=4 and Y=6. Mark and label these ...
Question 13 Refer to the budget line shown in the diagram. If the consumer's money income is $20, the: prices of C and D cannot be determined. price of C is $2 and the price of D is $4. 5/11/17, 9:19 AM Module 1 quiz: (Summer 2017-A) ECO2013: PRINCIPLES OF MACROECONOMICS 802 (30498) Page 10 of 14 consumer can obtain a combination of 5 units of ...
Refer to the budget line shown in the diagram. If the consumer's money income is $20, which of the following combinations of goods is unattainable. 4 units of C and 6 units of D. A point inside the production possibilities curve is ____ while a point outside the curve is ____.
where C is consumption and Y is disposable income. 26. Refer to the above data. The MPC is: A) .45. B) .20. C) .50. D) .90. Answer: D 27. Refer to the above data. At an $800 level of disposable income, the level of saving is: A) $180. B) $740. C) $60. D) $18. Answer: C 28. Which one of the following will cause a movement down along an economy's ...
A. Show various combinations of two products which can be purchased with a given money income with knowledge of the prices of the two products. (Figure 1) B. A decrease in money income shifts the budget constraint line inward to the left in Figure 1; an increase in money income shifts the budget constraint line outward to the right in Fig. 1.
Other things equal, an increase in a consumer's money income: A. increases the amount of utility a consumer receives from a given quantity of a good. B. shifts the individual's budget line rightward because she can now purchase more of both products. C. eliminates the individual's economizing problem.
Example of a Budget Line. Radha has ₹50 to buy a biscuit. She has a few options to allocate her income so that she receives maximum utility from a limited salary. To get an appropriate budget line, the budget schedule given can be outlined on a graph. The budget set indicates that the combinations of the two commodities are placed within the ...













0 Response to "37 refer to the budget line shown in the diagram. if the consumer's money income is $20, the"
Post a Comment