39 nitric oxide molecular orbital diagram
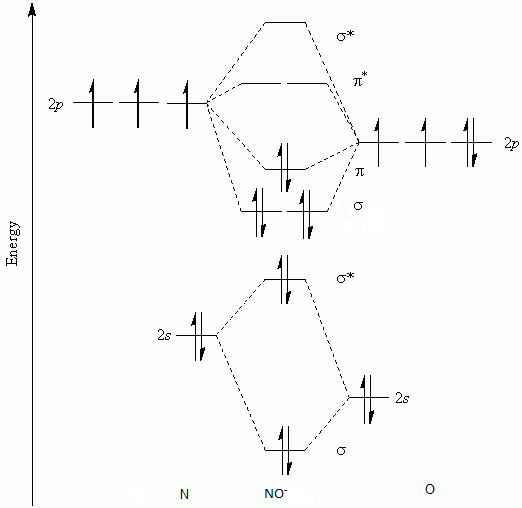
How to write the molecular orbital diagram for NO, nitric oxide a heteronuclear molecule. As we discussed before, NO is polar. This is because the non-bonding orbitals give rise to partial + and - charges on O and N sides. Conclusion. An elaborate explanation has been given about nitric oxide and its bonding nature. We have drawn the most suitable Lewis Structure and found out the Molecular geometry i.e. the three-dimensional ...
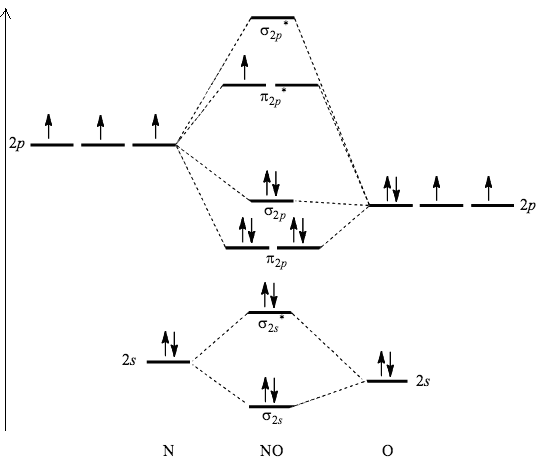
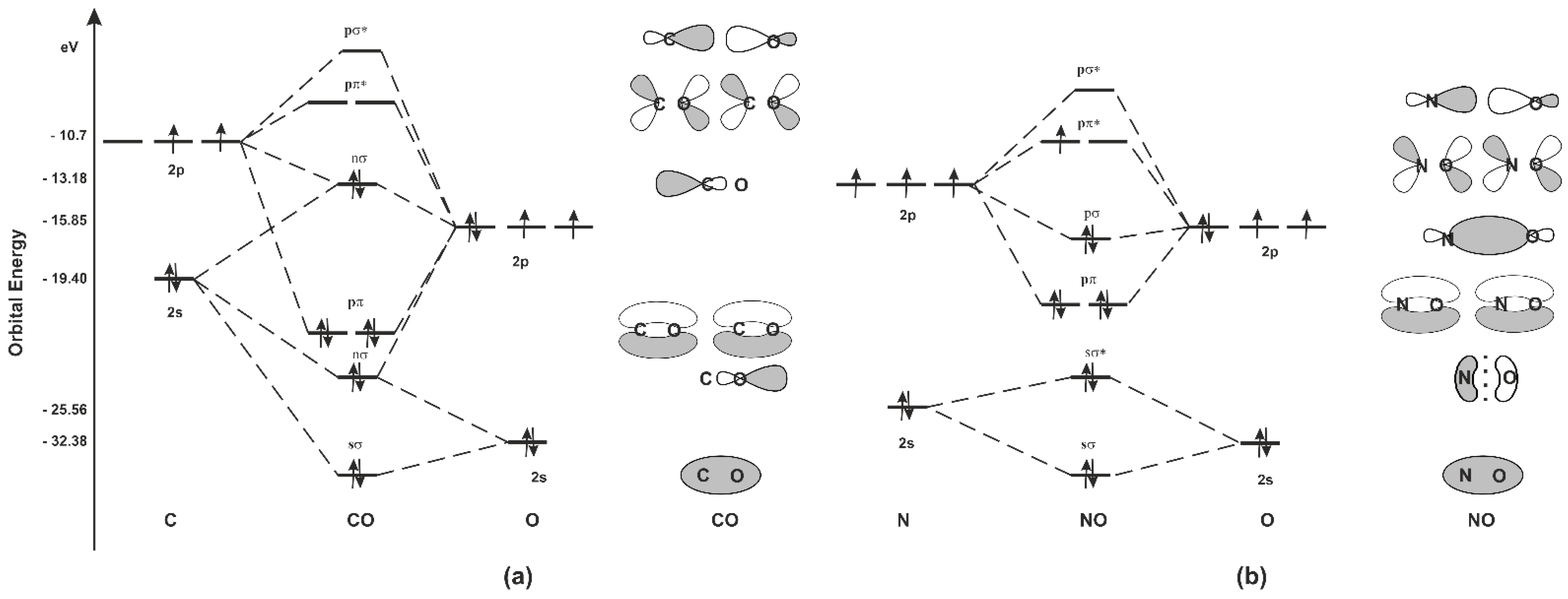
Given: Molecular orbital diagram of nitric oxide. 9.1 Name the eight molecular orbitals that result from the overlap of N's atomic orbitals with that of O and indicate which molecular orbital is bonding (BMO), non-bonding (NBMO) and anti-bonding (ABMO).
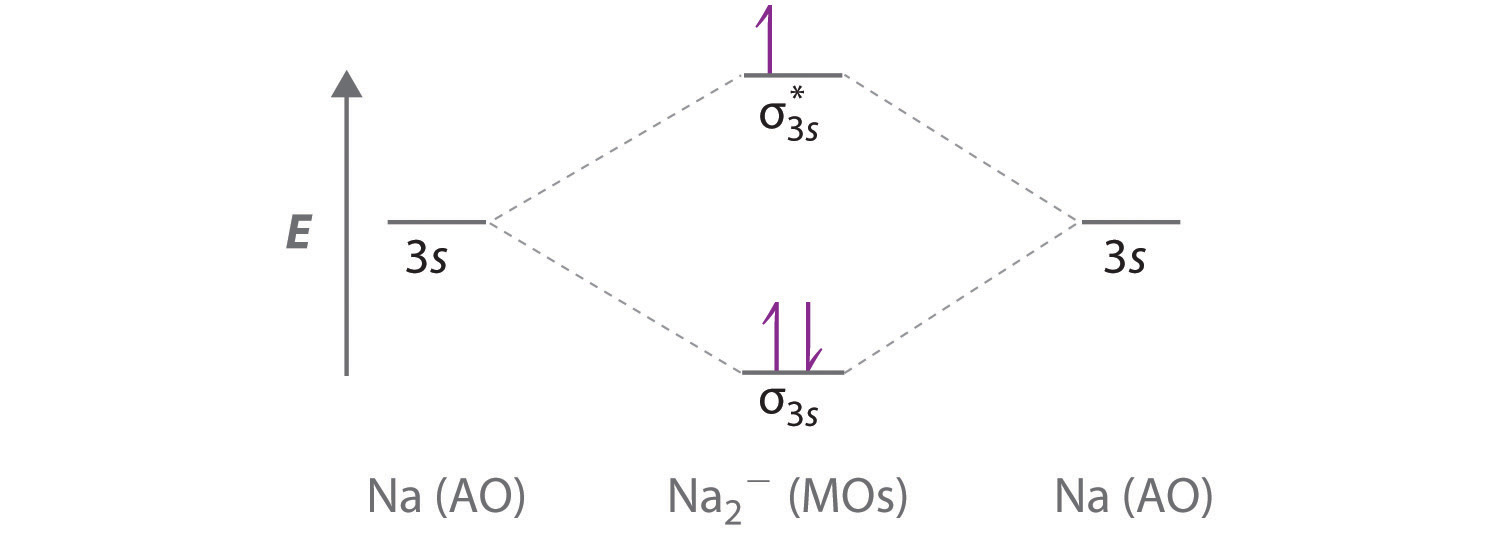
Nitric oxide molecular orbital diagram
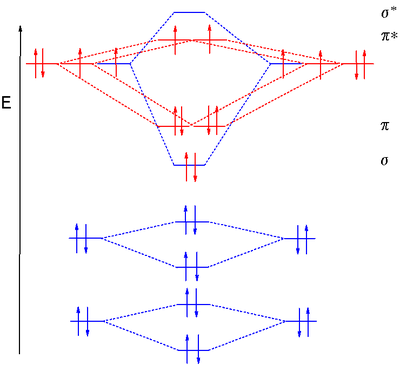
Consider the molecular orbital diagram below: It's to say, that As the modern theory of molecular orbitals considers, there is some inter-atomic space between two atoms, where is the bonding electron allocation is the most likely situated in by the moment. A molecular orbital diagram describes the bonding in terms of constructive and destructive overlap of atomic orbitals. A MO diagram dispenses with the need for resonance. May 24, · Nitric oxide was labeled as the molecule of the year in and a Noble prize was awarded in for research regarding its role in cardiovascular systems. Among the biological molecules with unpaired electrons, molecular oxygen (O 2) is pre-eminent.Although O 2 has an even total number of electrons, in the most common form (the ground state) two of the electrons are unpaired (occupy separate molecular orbitals) and so the reaction of •NO with O 2 (Figure 1 A) is without doubt the single most studied reaction of •NO.
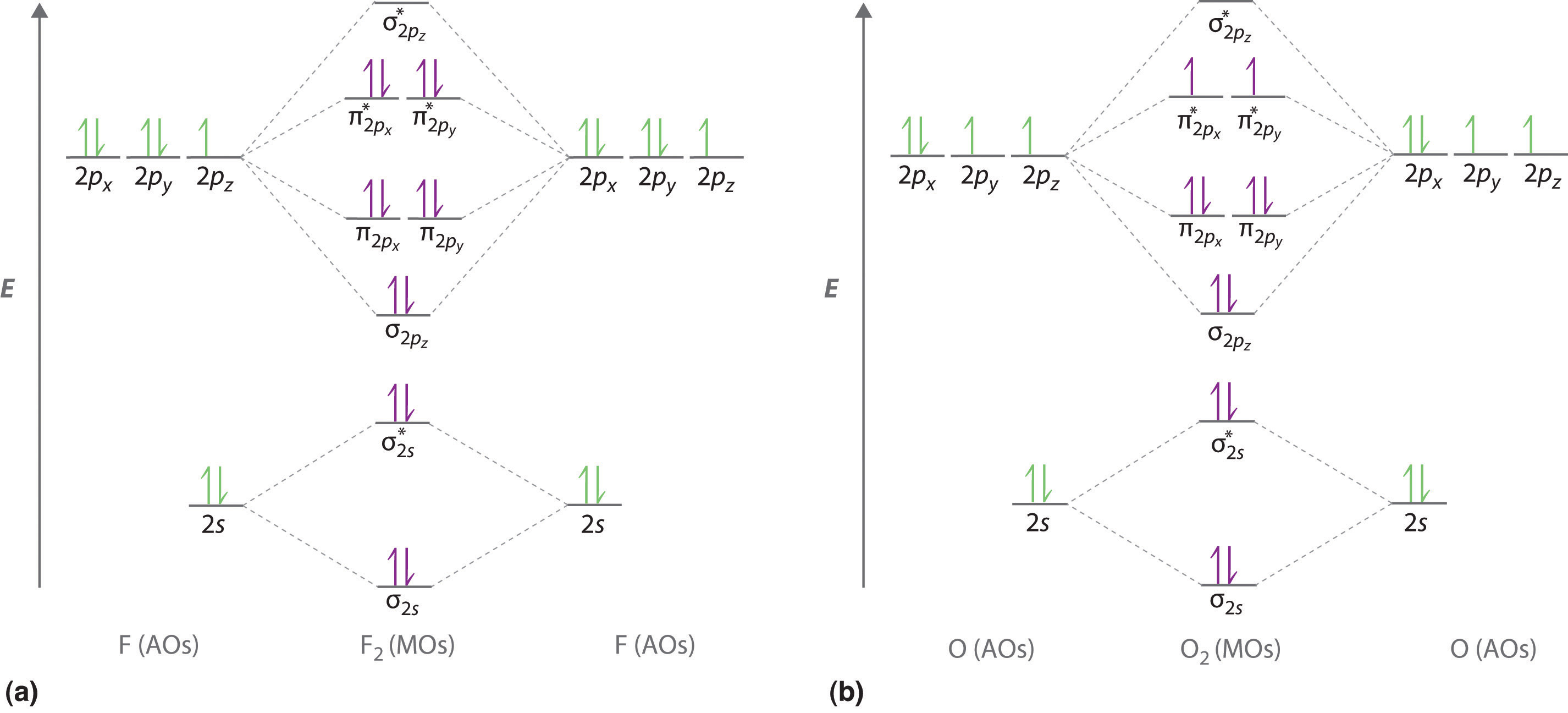
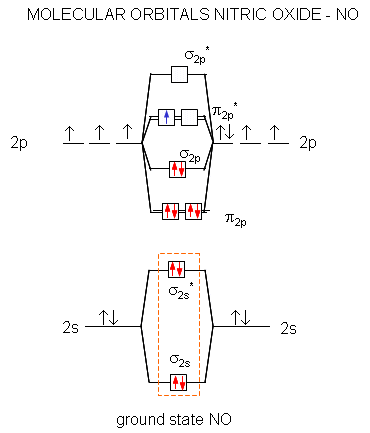
Nitric oxide molecular orbital diagram. A molecular orbital diagram of .NO shows it to have a bond order of 2.5 and one unpaired electron in a π2p* antibonding orbital (hence the notation .NO). ... This protein induces synthesis of nitric oxide synthase, producing .NO, which through the reactions listed above, can damage bacterial macromolecules. Nitric oxide is a heteronuclear molecule that exhibits mixing. Answer to a) Draw a molecular orbital diagram for the nitric oxide (NO) molecule labeling the energy axis, the AOs and MOs on the. Nitric oxide was labeled as the molecule of the year in and a The goal of this section is to introduce molecular orbital diagrams for. understand molecular orbital diagram for the nitrosyl ligand first. Figure 15. The molecular orbital diagram of nitric oxide (NO). After looking at the molecular orbital diagram for NO, one can immediately recognize the difference from the carbonyl ligand that there is one extra electron in the π*-orbital. This suggests that NO ligand can be A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. A fundamental principle of these theories is that as atoms bond to form molecules, a certain number of atomic orbitals combine to form the same number of ...
see more informative videos of chemistryhttps://youtu.be/iZhZRWNonVshttps://youtu.be/3bQ2YZVCRqUhttps://youtu.be/PEkZoDgbMdIhttps://youtu.be/FMsg4LDrjkohttps... Chemistry questions and answers. 12D.4. Nitric oxide (NO) has the following molecular orbital energy-level diagram. σ2p σ2p Energy | π2p -tt- σ2s a) What is its bond order? b) Is it diamagnetic or paramagnetic? c) Write the molecular orbital electron configuration of NO. Now the next topic to cover is the molecular orbital diagram of nitrous oxide. N2O Molecular Orbital Diagram. Molecular orbital diagrams say about the mixing of orbitals in a compound. Using a MO diagram, the bond order of a compound can be determined which gives us an idea about bond length, bond stability as well. Answer (1 of 2): This image shows the molecular orbitals of nitric oxide and the types of bonds present.
Heteroatomic molecular orbitals Heteroatomic molecular orbitals Mix atomic orbitals For discussion, treated simplistically as one orbital from each center Often close to correct because a single orbital predominates Must mix orbitals of Similar energy Same symmetry Molecular orbital energies Rough estimation by diagram File:Nitric oxide MO diagram.svg. Size of this PNG preview of this SVG file: 531 × 354 pixels. Other resolutions: 320 × 213 pixels | 640 × 427 pixels | 800 × 533 pixels | 1,024 × 683 pixels | 1,280 × 853 pixels. Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in Among the biological molecules with unpaired electrons, molecular oxygen (O 2) is pre-eminent.Although O 2 has an even total number of electrons, in the most common form (the ground state) two of the electrons are unpaired (occupy separate molecular orbitals) and so the reaction of •NO with O 2 (Figure 1 A) is without doubt the single most studied reaction of •NO.
A molecular orbital diagram describes the bonding in terms of constructive and destructive overlap of atomic orbitals. A MO diagram dispenses with the need for resonance. May 24, · Nitric oxide was labeled as the molecule of the year in and a Noble prize was awarded in for research regarding its role in cardiovascular systems.
Consider the molecular orbital diagram below: It's to say, that As the modern theory of molecular orbitals considers, there is some inter-atomic space between two atoms, where is the bonding electron allocation is the most likely situated in by the moment.


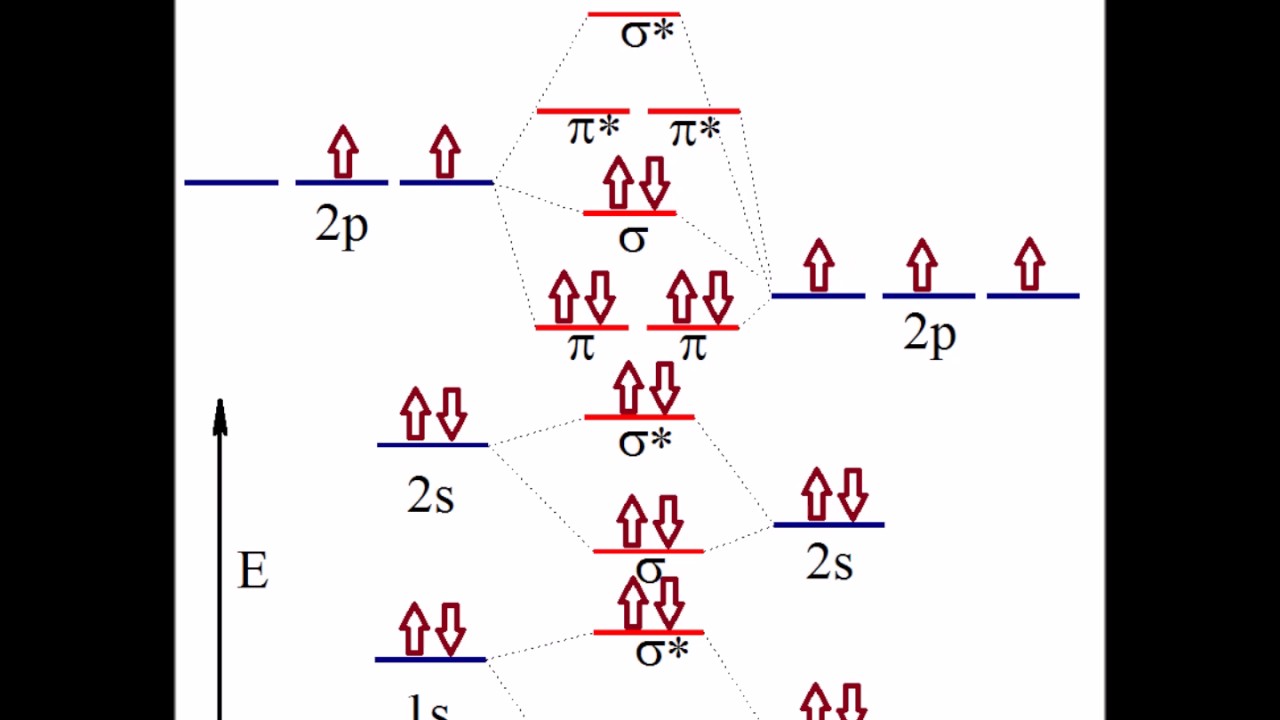





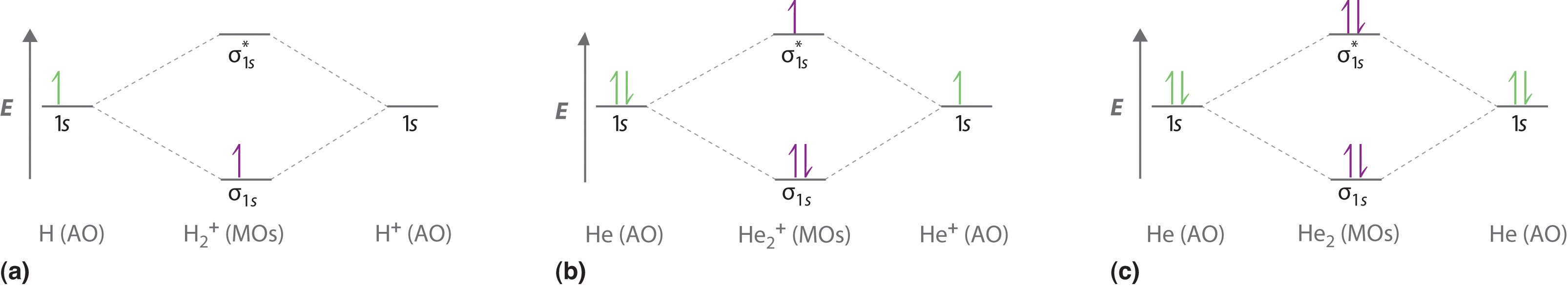















0 Response to "39 nitric oxide molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment