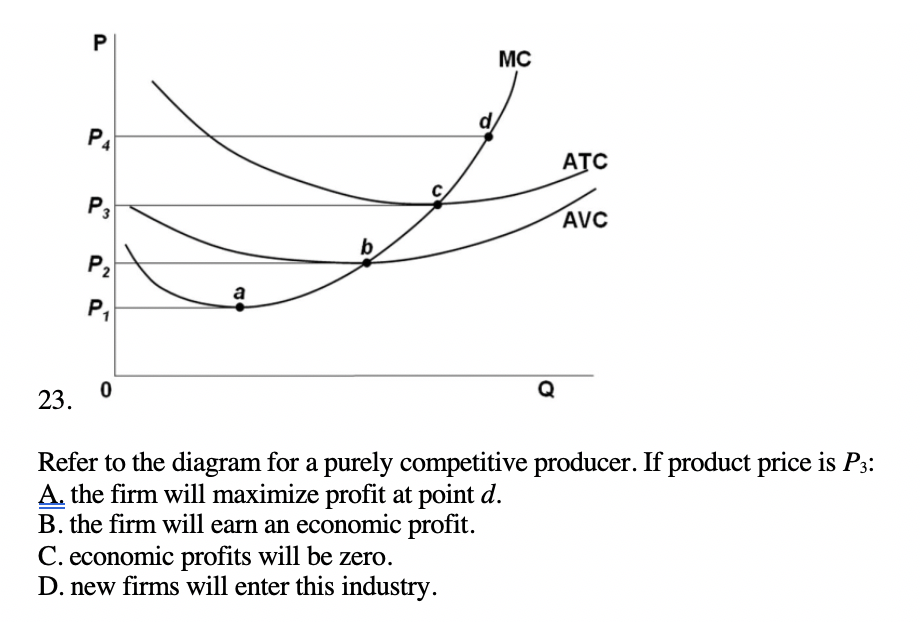
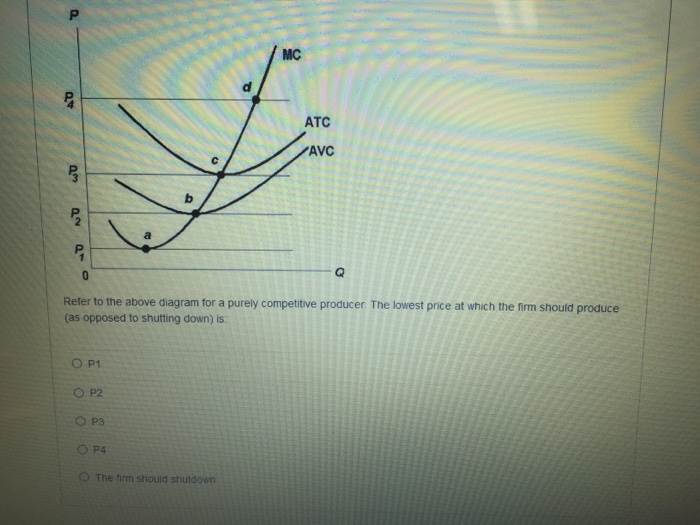
39 refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. if product price is p3,
Comparing to Pure Competition. Recall that purely competitive firms produce where MC is equal to price and that industry supply is obtained by horizontally adding the MC curves of the firms in an industry. In equilibrium, the industry supply curve (the sum of the MC curves) crosses the demand curve. Suppose a firm in a purely competitive market discovers that the price of its product is above its minimum AVC point but everywhere below ATC. Given this, the firm ... Refer to the diagrams, ... If production is occurring where marginal cost exceeds price, the purely competitive firm will. answer choices
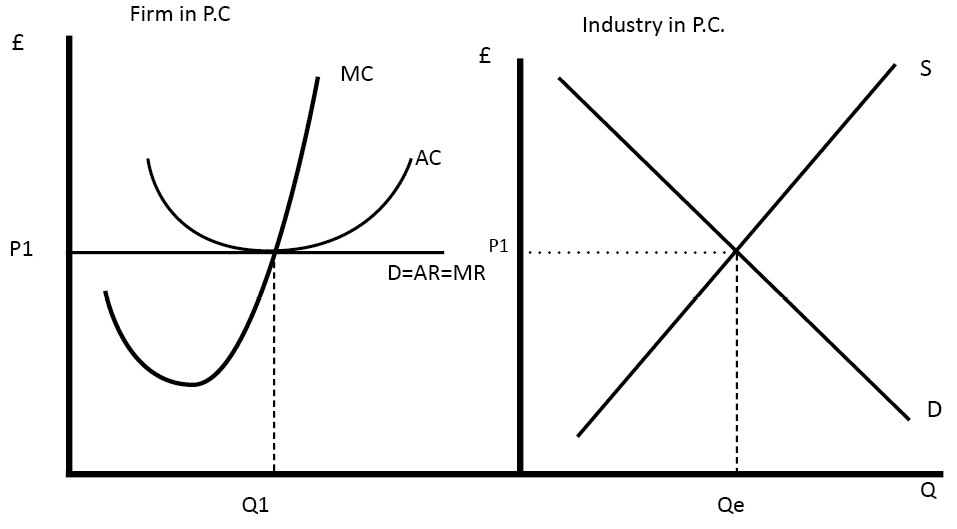
(a) The industry is purely competitive—this firm is a "price taker." The firm is so small relative to the size of the market that it can change its level of output without affecting the market price. (b) See graph. (c) The firm's demand curve is perfectly elastic; MR is constant and equal to P. Therefore, the marginal

Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. if product price is p3,
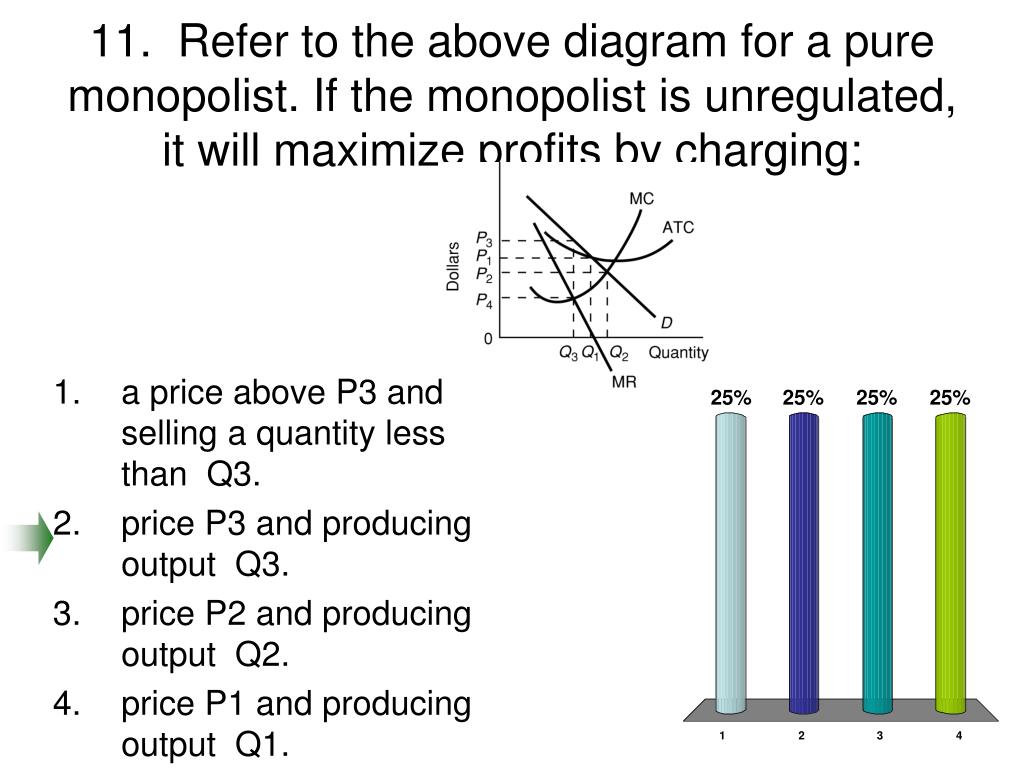
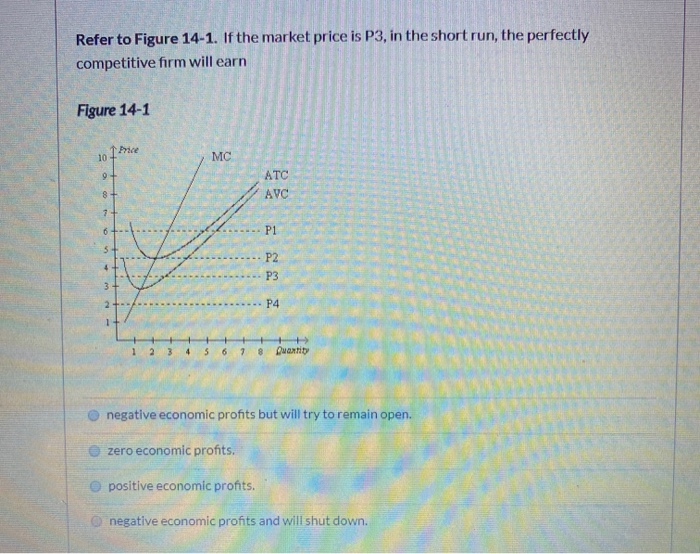
47. Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. If product price is P3: A. the firm will maximize profit at point dB. the firm will earn an economic profit. C. economic profits will be zero.D. new firms will enter this industry. . 72. Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. If product price is P 3: A) the firm will maximize profit at point d. C) economic profits will be zero. B) the firm will earn an economic profit. D) new firms will enter this industry. Answer: C Question 1 0.09524 out of 0.09524 points Correct Picture The diagram shows the short-run average total cost curves for five different plant sizes of a firm. If in the long run the firm should produce output 0x, it should do it with a plant of size: Selected Answer: Correct #2. Answers: #4.
Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. if product price is p3,. 72. Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. If product price is P3: A) the firm will maximize profit at point d. C) economic profits will be zero. B) the firm will earn an economic profit. D) new firms will enter this industry. Answer: C. 73. Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. If product price is between P2 and P3. Multiple Choice O the firm will earn an economic profit. O the firm will earn an economic loss. c ) new firms will enter this industry. Question: Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. If product price is between P2 and P3. Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. If product price is P3: ... Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. The firm will produce at a loss at all prices: between P2 and P3. Refer to the diagram. At P3, this firm will: produce 40 units and incur a loss. econ130 ch 10 hw & quiz. Refer to the data. If the market price for the firm's product is $32, the competitive firm will produce: Correct A.8 units at an economic profit of $16. B.6 units at an economic profit of $7.98. C.10 units at an economic profit of $4. D.7 units at an economic profit of $41.50. A.8 units at an economic profit of $16.
47. Although individual purely competitive firms can influence the price of their product, these firms as a group cannot influence market price. True False 48. In a purely competitive industry competition centers more on advertising and sales promotion than on price. True False 49. E) The nature of the product. 1) Consider the following short-run cost curves for a perfectly competitive firm. FIGURE 9-1 2) Refer to Figure 9-1. The diagram shows cost curves for a perfectly competitive firm. If the market price is P3, the profit-maximizing firm in the short run should A) produce output A. A) Both purely competitive and monopolistic firms are "price takers." B) Both purely competitive and monopolistic firms are "price makers." C) A purely competitive firm is a "price taker," while a monopolist is a "price maker." D) A purely competitive firm is a "price maker," while a monopolist is a "price taker." refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. The lowest price at which the firm should produce (as opposed to shutting down) is a) P1 b) P2 c) P3 d) P4. b. refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. The firm's short-run supply curve is ... the accompanying table gives cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely ...
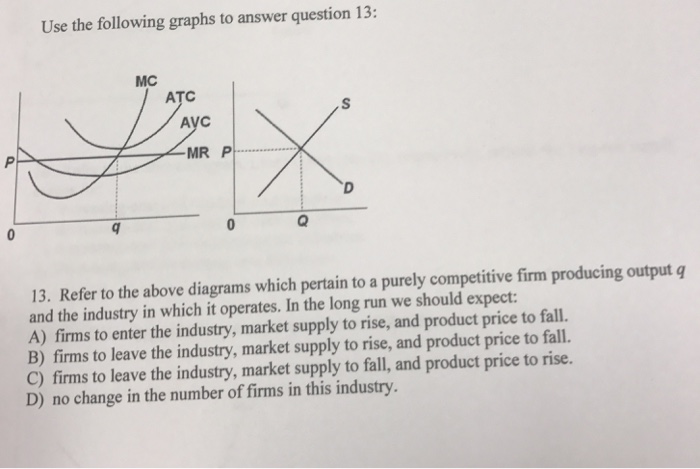
Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. If product price is P3: A. the firm will maximize profit at point d B. the firm will earn an economic profit C. economic profits will be zero D. new firms will enter this industry If product price is p3. Refer to the diagram. P1 p2 p3 p4 the firm should shutdown the lowest price at which the firm should produce as opposed to shutting down is. Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. If product price is p3. Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. 72. Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. If product price is P3: A) the firm will maximize profit at point d. C) economic profits will be zero. B) the firm will earn an economic profit. D) new firms will enter this industry. Answer: C. Type: G Topic: 3 E: 424 MI: 180 73. Refer to the above diagram for a purely ... 2. Refer to the above diagrams, which pertain to a purely competitive firm producing output q and the industry in which it operates. In the long run we should expect: 1. firms to enter the industry, market supply to rise, and product price to fall. 2. firms to leave the industry, market supply to rise, and product price to fall.
Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. The firm will produce at a loss at all pricesbetween p 2 and p 3. If product price is p 3 economic profits will be zero. The lowest price at which the firm should produce as opposed to shutting down is. In the long run we should expect.
more elastic than that of either a pure monopolist or a purely competitive seller. 4. R-1 F25030. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm in short-run equilibrium. This firm's profit-maximizing price will be: A. $10. B. $13. C. $16. D. $19. 5. R-1 F25030. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive ...
Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. If product price is P3: A. the firm will maximize profit at point d. B. the firm will earn an economic profit. C. economic profits will be zero. D. new firms will enter this industry. 16. If a purely competitive firm is producing at some level less than the profit-maximizing output ...

Given A Price Of P2 This Firm In A Purely Competitive Industry Should Produce Q1 Produce Q3 With A Minimum Loss Produce Q5 With An Economic Profit
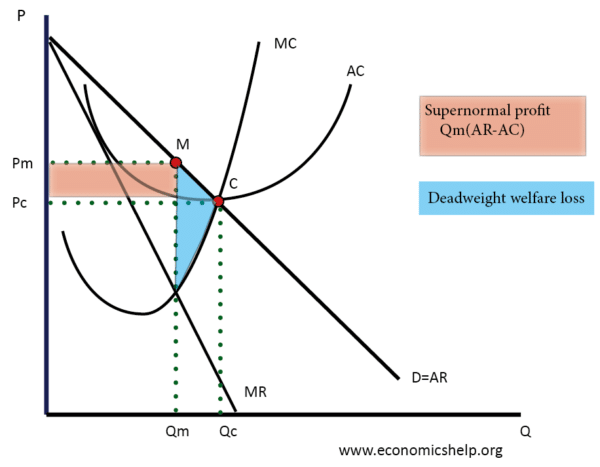
Refer to the above diagram. To maximize profits or minimize losses this firm should produce: ... Comparing a pure monopoly and a purely competitive firm with identical costs, we would find in long-run equilibrium that the pure monopolist's: A. price, output, and average total cost would all be higher. ... Product Price: 0: $ 250: $ 500: 1: 260 ...

Can Price Regulation Increase Land Use Intensity Evidence From China S Industrial Land Market Sciencedirect
Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. The lowest price at which the firm should produce as opposed to shutting down is:
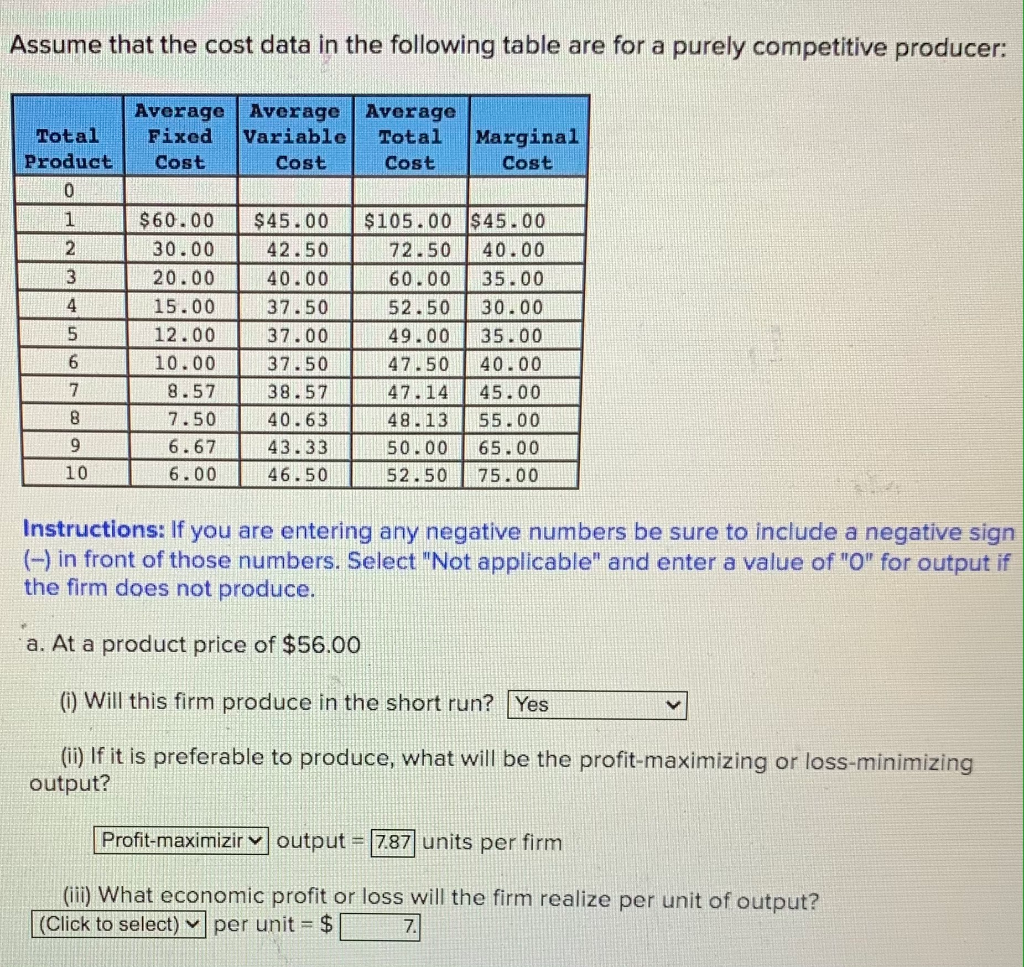
120 seconds. Q. The accompanying table gives cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market. If the market price for the firm's product is $12, the competitive firm should produce. answer choices. 4 units at a loss of $109. 4 units at an economic profit of $31.75. 8 units at a loss of $48.80.
If a firm is confronted with economic losses in the. 20. If a firm is confronted with economic losses in the short run, it will decide whether or not to produce by comparing: A. marginal revenue and marginal cost. B. price and minimum average variable cost.C. total revenue and total cost.D. total revenue and total fixed cost. 21.
b. Answer the questions of 4a assuming that product price is $41. c. Answer the questions of 4a assuming that product price is $32. d. In the table below, complete the short-run supply schedule for the firm (columns 1 to 3) and indicate the profit or loss incurred at each output (column 3). (1) Price (2) Quantity supplied, single firm (3 ...
The accompanying table gives cost data for a firm that is selling in a purely competitive market. If the market price for the firm's product is $32, the competitive firm will produce At P 1 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will produce At P 1 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will produce At P 3 in the accompanying diagram, this firm will At P 3 in the accompanying diagram, this ...
Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. The firm will produce at a loss at all prices: A. Above P1. B. Above P3. C. Above P4. D. Between P2 and P3. 21. Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. If product price is P 3: A. The firm will maximize profit at point d. B. The firm will earn an economic profit. C.
Solved Refer To The Above Diagram For A Purely Competitive Producer If Product Price Is P 3 The Firm Will Maximize Profit At Point D The Firm Wi Course Hero
Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. If product price is P3, Multiple Choice A. economic profits will be zero. B. new firms will enter this industry. C. the firm will maximize profit at point d. D. the firm will earn an economic profit.

Econhw11sols38 Pdf 104 Award 1 00 Point Refer To The Accompanying Diagram This Rm Will Earn Only A Normal Prot If Product Price Is P1 P2 P3 P4 Course Hero
Question 1 0.09524 out of 0.09524 points Correct Picture The diagram shows the short-run average total cost curves for five different plant sizes of a firm. If in the long run the firm should produce output 0x, it should do it with a plant of size: Selected Answer: Correct #2. Answers: #4.
72. Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. If product price is P 3: A) the firm will maximize profit at point d. C) economic profits will be zero. B) the firm will earn an economic profit. D) new firms will enter this industry. Answer: C
47. Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. If product price is P3: A. the firm will maximize profit at point dB. the firm will earn an economic profit. C. economic profits will be zero.D. new firms will enter this industry. .

Realizable Utility Maximization As A Mechanism For The Stability Of Competitive General Equilibrium In A Scarf Economy Request Pdf

Sustainability Free Full Text Multi Criteria Decision Making For Sustainability And Value Assessment In Early Pss Design Html

Refer To The Diagram For A Purely Competitive Producer The Firm Will Produce With An Economic Homeworklib













0 Response to "39 refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. if product price is p3,"
Post a Comment