41 is the potential-energy diagram for a 20 g particle that is released from rest at x = 1.0 m.
Often, you can get a good deal of useful information about the dynamical behavior of a mechanical system just by interpreting a graph of its potential energy as a function of position, called a potential energy diagram.This is most easily accomplished for a one-dimensional system, whose potential energy can be plotted in one two-dimensional graph—for example, U(x) versus x—on a piece of ... Jul 14, 2021 — || FIGURE EX10.24 is the potential-energy diagram for a 20 g particle that is released from rest at x = 1.0 m. a. Will the particle move ...1 answer · Top answer: a. From the graph, we have PE (Potential energy) = Total energy = 4 J (since the particle is released from rest, hence the kinetic energy will be zero) ...
A 100 g particle experiences the one-dimensional, conservative force F x shown in FIGURE P10.59. a. Let the zero of potential energy be at x = 0 m. What is the potential energy at x = 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, and 4.0 m?b. Suppose the particle is shot to the right from x = 1.0 m with a speed of 25 m/s.
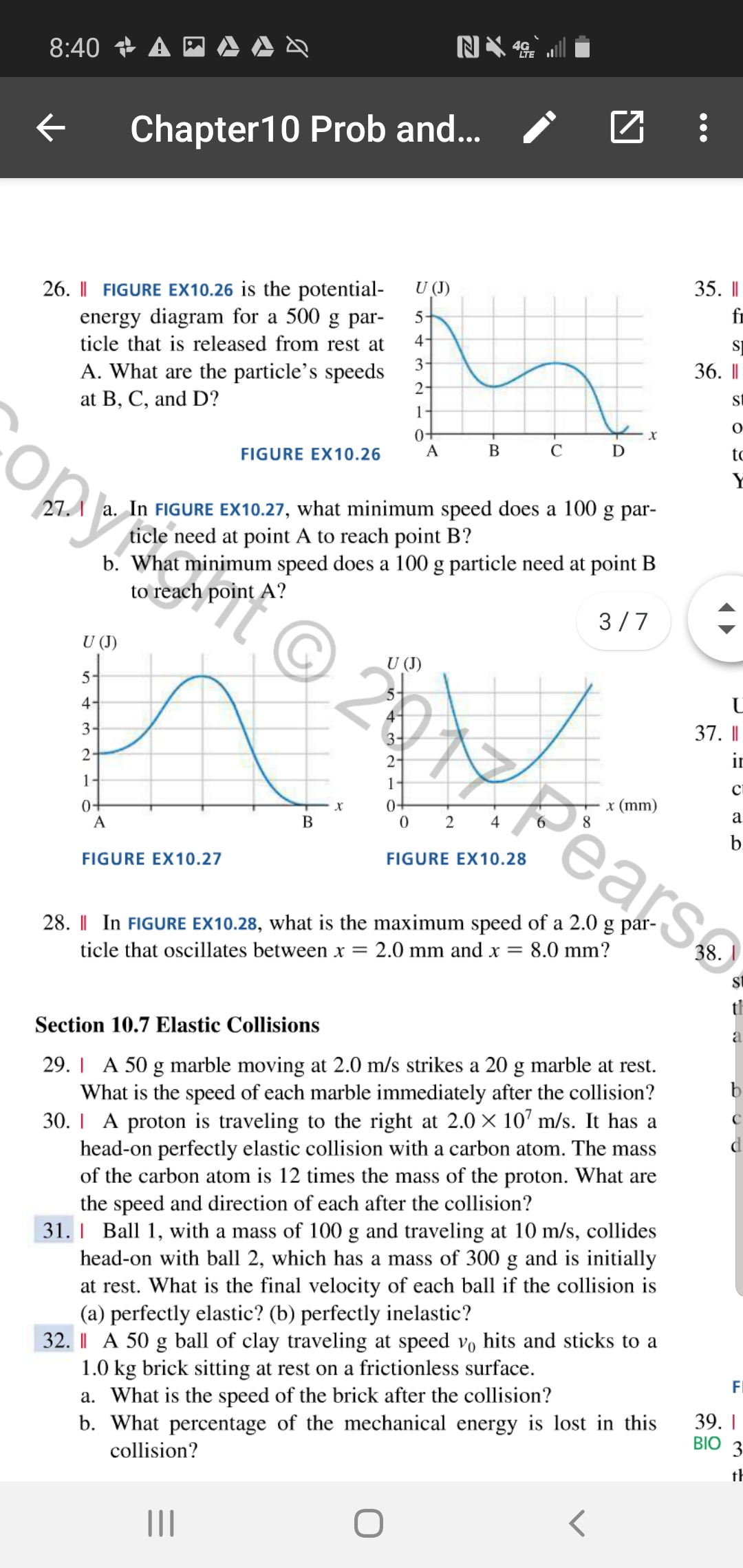
Is the potential-energy diagram for a 20 g particle that is released from rest at x = 1.0 m.
Exercise 1 (10.24, p. 256) The figure below is the potential-energy diagram for a 20 g particle that is released from rest at x = 1.0 m. a. Will the particle move to the right or to the left? b. What is the particle's maximum speed? At what position does it have this speed? c. Where are the turning points of the motion? Exercise 2 (10.28, p ... Model:For an energy diagram, the sum of the kinetic and potential energy is a constant. Visualize: The particle with a mass of 500 g is released from rest at A. That is, at A. Since we can draw a horizontal TE line through The distance from the PE curve to the TE line is the particle's kinetic energy. your hand moving at 20.0 m/s. The ball reaches a maximum height y 2. What is the speed of the ball when it is at a height of y 2 /2? Ignore air resistance. A. 10.0 m/s B. less than 10.0 m/s but greater than zero C. greater than 10.0 m/s D. not enough information given to decide Q7.2 m = 0.150 kg v 1 = 20.0 m/s v 2 = 0 y 1 = 0 y 2
Is the potential-energy diagram for a 20 g particle that is released from rest at x = 1.0 m.. gained as a potential energy is lost as a kinetic energy and vice versa. Kinetic energy is at its maximum when potential energy is at its minimum. E pot = 1 2 kx2 + mgx The minium is to be found by the condition : dE pot(x) dx = 0 kx+ mg = 0 x = mg k = 27:5 9:81 25500 = 10:6mm The position x = 10.6mm found above is the point of maximum kinetic ... Problem: The figure(Figure 1) is the potential-energy diagram for a 20 g particle that is released from rest at x=1.0m.1. Will the particle move to the right or ...1 answer · Top answer: 1.The particle will move to the right.2.ΔK.E = - ΔUThe decrease in potential energy is equal to the gain in kinetic energy.At x = 1m, the potential ... Answer to: The figure shows the potential energy diagram for a 500 g particle that is released from rest at A. a. What is the particle's speed at... Transcribed image text: The potential-energy diagram for a 20 g particle that is released from rest at x = 1.0 m. Will the particle move to the right or to ...
Physics. For the potential-energy diagram in (Figure 1), what is the maximum speed of a 5.0 g particle that oscillates between x = 2.0 mm and x = 8.0 mm? parabola starts at 5,2 and ends at 5,8 with the bottom at 1,4. 👍. [51] Figure P10.51 is the potential-energy diagram for a 20 g particle that is released from the rest at x =1.0 m. a. Will the particle move to the right or to the left? Problem 25E. Figure EX10.25 is the potential-energy diagram for a 20 g particle that is released from rest at x = 1.0 m. a. Will the particle move to the ...1 answer · Top answer: ?Solution 25E Part (a) Step 1 of 4: Our aim is to find the direction of the particle which is left free from the point x = 1 m. The total energy ... The force corresponds to the potential-energy function graphed in Fig. 7.45. The particle is released from rest at point A. (a) What is the direction of the force on the particle when it is at point A? (b) At point B? (c) At what value of x is the kinetic energy of the particle a maximum? (d) What is the force on the particle when it is at point C?
(B) The potential energy of the spring is at a minimum at x = A. (C) The kinetic energy of the block is at a minimum at x =0. (D) The kinetic energy of the block is at a maximum at x = A. 23. A simple pendulum consists of a l.0 kilogram brass bob on a string about 1.0 meter long. It has a period of 2.0 seconds. The pendulum would have a period ... Answer to the potential energy diagram for a 20 g particle that is released from rest at x 10 m. The particle is released from rest at x 10 m. Adsorption Of Ethanol Molecules On The Al 1 1 1 Surface A The diagram shows a plot of the potential energy as a function of x for a particle moving along the x axis. The energy E in the system is proportional to the square of the amplitude. E = ½kA 2. It is a continuously changing mixture of kinetic energy and potential energy. For any object executing simple harmonic motion with angular frequency ω, the restoring force F = -mω 2 x obeys Hooke's law, and therefore is a conservative force. We can define a ... (4 ed) 13.2 A 50-g mass connected to a spring of force constant 35 N/m oscillates on a horizontal, frictionless surface with anamplitude of 4.0 cm. Find (a) the total energy of the system and (b) the speed of the mass when the displacement is 1.0 cm. When the displacement is 3.0 cm, find (c) the kinetic energy and (d) the potential energy.
8.52 A 200-g particle is released from rest at point A along the horizontal diameter on the inside of a frictionless, hemispherical bowl of radius R = 30.0 cm (Figure P8.52). ... so the potential energy is. U A = m g h A = m g R (b) At point B, the height is zero, ... v = v x = 1.0 m /0.505 s
The mass of the particle m 20 g 002 kg the mechanical energy e 4 j at x 1 m when it is released the particle will get its maximum speed only when the potential energy u is minimum or zero. Is the potential energy diagram for a 20 g particle that is released from rest at x = 1.0 m.. Will the particle move to the. The potential energy of a 020 kg ...
The potential energy of a particle m = 0.20 kg moving along the x axis is given by U(x) = 8x2 + 2x4, where U is in joules and x is in meters. Use a calculator to solve the equation. If the particle has a speed of 5.0 m/s when it is at x = 1.0 m. Find the speed of the particle when it is at the origin.
If the object is released from rest at this point, what is its velocity when it is a large distance from the three charges? (Take 5 8 , L9 x 10 =) Answer: This portion of the question requires recognizing that, far from the surface, the potential energy of a particle initially placed at position A will all be converted to kinetic energy, and ...
Chapter 20 Electric Potential and Electrical Potential Energy Q.21P IP A particle with a mass of 3.8 g and a charge of +0.045 μC is released from rest at point A in Figure 20-20. (a) In which direction will this charge move? ... Charge 1 is +q and is located at x = −1.0 m; charge 2 is −2q and is located at x = 1.0 m. ...
is the potential-energy diagram for a 20 g particle that is released from rest at x = 1.0 m. Will the particle move to the right or to the left? What is the particle's maximum speed? Where are the turning points of the motion? try again. 10.6.
is the potential-energy diagram for a 20g particle that is released from rest at x=1.0m a. Will the particle move to the right or to the left?4 answers · Top answer: Okay, so there in chapter 10 Problem 29 here. So we have this craft here that shows the potential ...
The potential energy of a system, U, is the interaction ... diagram for a positively charged particle in a uniform electric field. The potential energy increases linearly with ... released from rest in vacuum. They move toward each other. As they do, QuickCheck 25.5 A. A positive potential energy becomes more positive.
PE grav. = m * h * g. Where: m - mass; h - height; g - the gravitational field strength (9.81 on Earth) The formula is relatively simple. An object which is not raised above the ground will have a height of zero and therefore zero potential energy. When you double the mass or the height of an object, its potential energy will also double.
Answer to: The figure is the potential-energy diagram for a 15 g particle that is released from rest at x = 6 m. (a) Will By signing up, you'll get...1 answer · Top answer: We are given: • Mass of the particle: m = 15 g m = 15 g • Initial position of the particle: x0 = 6m x0 = 6m Part(a): A...
Potential energy U is energy that can be associated with ... 1 0 −x 2 1 2 1 0 2 0 ... A charge q(q= 6.24 μC)is released from rest at the positive plate and reaches the negative plate with a speed of 3.4 m/s. The plates are connected to a 12-V battery Calculate: (a) the mass of the charge. ...
Jul 14, 2021 — The figure (Intro 1 figure) is the potential-energy diagram for a 20 g particle that is released from rest at x = 1.0 m.
Transcribed image text: Is the potential-energy diagram for a 20 g particle that is released from rest at x = 1.0 m. Part A Will the particle move to the right or to the left? Part B What is the particle's maximum speed? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units.
A particle with the potential energy shown in the graph is moving to the right. It has 1 J of kinetic energy at x = 1 m. Where is the particle's turning point? A. x = 1 m B. x = 2 m C. x = 5 m D. x = 6 m E. x = 7.5 m
kinetic energy required to clear the D potential energy barrier is (31 + 10) × 20 = 820 µJ. (This is the same as the "activation energy" needed by two chemical reactants to clear a potential energy barrier before taking part in an exothermic reaction.) The kinetic energy of the particle when it arrives at point B is ΔKU=−qΔV=−20× ...
Problem: is the potential-energy diagram for a 20 g particle that is released from rest at x = 1.0 m.a. What is the particles maximum speed? At what position does it have this speed?b. Where are the turning points of the motion?c. Will the particle move to the right or to the left?
your hand moving at 20.0 m/s. The ball reaches a maximum height y 2. What is the speed of the ball when it is at a height of y 2 /2? Ignore air resistance. A. 10.0 m/s B. less than 10.0 m/s but greater than zero C. greater than 10.0 m/s D. not enough information given to decide Q7.2 m = 0.150 kg v 1 = 20.0 m/s v 2 = 0 y 1 = 0 y 2
Model:For an energy diagram, the sum of the kinetic and potential energy is a constant. Visualize: The particle with a mass of 500 g is released from rest at A. That is, at A. Since we can draw a horizontal TE line through The distance from the PE curve to the TE line is the particle's kinetic energy.
Exercise 1 (10.24, p. 256) The figure below is the potential-energy diagram for a 20 g particle that is released from rest at x = 1.0 m. a. Will the particle move to the right or to the left? b. What is the particle's maximum speed? At what position does it have this speed? c. Where are the turning points of the motion? Exercise 2 (10.28, p ...




0 Response to "41 is the potential-energy diagram for a 20 g particle that is released from rest at x = 1.0 m."
Post a Comment